* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Welcome to our presentation
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
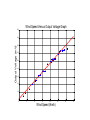
Welcome to our presentation Anemometry We are Group5 Weather station The team Members Saran Jackson Robert Howard Robert Garvey Gene Fitzgerald Introduction • Wind measurements are usually related to the horizontal component. • It is a vector, requiring both a magnitude (speed) and direction (the direction from which the wind is blowing) • Wind velocity is turbulent; it is often reported as a mean and variation about the mean (gustiness) Construction • Ideal (perfect) wind instrument – Respond to slight breezes – Rugged enough to withstand hurricane-force winds – Respond rapidly to turbulence – Have linear output – Exhibit simple dynamic performance characteristics Conditions in Ireland Wind over Ireland The wind at a particular location can be influenced by a number of factors such as obstruction by buildings or trees, the nature of the terrain and deflection by nearby mountains or hills. For example, the rather low frequency of southerly winds at Dublin Airport is due to the sheltering effect of the mountains to the south. The prevailing wind direction is between south and west. Average annual wind speeds range from 11 Km/h in parts of south Leinster to over 29 Km/h in the extreme north. On average there are less than 2 days with gales each year at some inland places like Kilkenny but more than 50 a year at northern coastal locations such as Malin Head. Indeed the north and west coasts of Ireland are two of the windiest areas in Europe and have considerable potential for the generation of wind energy. Notable Storms "The night of the Big Wind" on the 6th-7th January 1839 It was during this storm that a gust of 200 Km/h was recorded at Kilkeel in County Down, making it the highest sea-level wind speed recorded in Ireland. Slope of the line m Calculations y2 y1 0.132 0.010 x2 x1 30.7 2.6 0.00434 V Km / h Offset = 0 Max non linearity (furthest point from line) y = mx+c Y = Vout, m = 0.00434 x = 0.093 [V] c=0 0.93 = (.00434) x (18) Measured value Difference Max non linearity Sensitivity 0.078 0.093 0.015 0.015 0.00434 V Km / h Block Diagram Wind Speed 0 to 30.7 [km/h] DC Generator K1 = 0.0434 V/kmh 0 to 132 [mV] K2 = 38.06 dB AMP 0 to 9.6 [V] PLC (12 BIT) K3 = 197 counts/V Results Our next step was to calibrate our anemometer. We used a mobile hand held weather station that was provided by the college. We set up a hair dryer which was plugged into a variable resistor and turned the resister in increments of 5 volts , we checked the speed using the hand held weather station and the moved the fan across onto the anemometer this gave us an output voltage. We used these results to tabulate V in (V) Speed (Km/h) V out (mV) 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105 110 115 2.6 4 6.5 8.5 10.5 12.5 13.5 15 16.5 18 20.3 21 22 23 25 26 26.4 27.9 29 30.7 10 18.5 28 41 50 63 66 75 75 93 99 105 105 107 120 125 127 127 130 132 Wind Speed Versus Output Voltage Graph 180 Output Voltage (mV) 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 5 10 15 20 Wind Speed (Km/h) 25 30 35 Generating a useful voltage. The DC motor running as a generator has given us the linear output which is needed to give us an accurate picture of wind speed versus output voltage. While the output is linear, the voltage been supplied is to small for the PLC to read so the mill volt output needs a non inverting operational amplifier to increase the Voltage from 0 – 132mV range to a 0 – 9.6 volt range, or as close as can be built. Non inverting Op Amp Calculations The Range = 0 mV and 132 mV 10 0.12 83.3 Is the approximate Gain Gain = Av 1 R2 R1 80 1 R2 R2 79 R1 R1 R1 79 R2 , R1 10 R2 790