* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review questions for Chapter 8
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
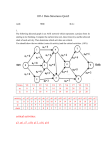
Review questions for Chapter 8 Answer first, then check at the end. True/False 1. The properties of an abstract data type are tightly related to the implementation of that data type. 2. The two general approaches for implementing a container are array-based and linked implementations. 3. The operations on a list differ depending on the implementation strategy used. 4. A stack is managed in a FIFO manner. 5. The operations on a stack occur at one end. 6. . A queue is managed in a FIFO manner. 7. A queue is similar to a waiting line at a bank. 8. Stacks and queues can be implemented only as a linked structure. 9. A tree is a non-linear data structure. 10. In a binary tree, each node has at most two child nodes. 11. A binary tree cannot contain decimal (base-10) data. 12. The root of a tree has no parent node. 13. The root of a tree has no child nodes. 14. A leaf node has no child nodes. 15. In a binary search tree, the value in any node is greater than the value in any node in its left subtree and less than the value in any node in its right subtree. 16. Graphs are useful for representing hierarchies. 17. A directed graph is a graph whose edges go in only one direction. 18. Non-value returning subprograms must always have a RETURN statement 19. Value-returning programs include the RETURN statement followed by a value to be returned. 20. In the parameter passing process, the substitution mechanism can be thought of a message board. Multiple Choice 21. . Which level provides a view of data that focuses on solving a particular problem? A. implementation level B. logical level C. array level D. linked level E. application level 22. Which level provides an abstract view of data and the operations that manipulate them? A. implementation level B. logical level C. array level D. linked level E. application level 23. Which level provides a view that deals with the underlying data structure used to manage the data? A. implementation level B. logical level C. array level D. linked level E. application level 24. Which of the following is managed in a FIFO manner? A.list B. stack C. queue D. binary search tree E. graph 25. Which of the following is managed in a LIFO manner? A. list B. stack C. queue D. binary search tree E. graph 26. Which of the following is organized as a hierarchy? A. list B. stack C. queue D. binary search tree E. graph 27. Which of the following can be directed or undirected? A. list B. stack C. queue D. binary search tree E. graph 28. Which of the following would you use to represent airline flights between cities? A. list B. stack C. queue D. binary search tree E. graph 29. What is the maximum number of nodes in a binary tree with 3 levels? A. 1 B. 3 C. 7 D. 8 E. 16 30. What is the minimum number of nodes in a binary tree with 3 levels? A. 1 B. 3 C. 7 D. 8 E. 16 31. What is the maximum number of nodes on Level 3 of a binary tree (remember that the root of the tree is at Level 0)? A. 1 B. 3 C. 7 D. 8 E. 16 32. What value is at the root of the following tree? A. 16 B. 12 C. 28 D. 30 E. 4 33. . Where would the value 19 be inserted in the following binary search tree? A. as the left child of 16 B. as the right child of 16 C. as the left child of 4 D. as the left child of 21 E. as the right child of 30 34. Where would the value 15 be inserted in the following binary search tree? A. as the left child of 16 B. as the left child of 4 C. as the left child of 21 D. as the right child of 12 E. as the left child of 12 35. How many comparisons would it take to find the value 30 in the following binary search tree? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 E. 6 36. Which of the following scientists developed the basic computer architecture that continues to be used today? A) Wernher von Braun B) George Polya C) Tony Hoare D) John von Neumann E) Richard Feynman Fill in the Blanks 37. A(n) _______________ is a data type whose data and operations are specified independently of any particular implementation. 38. The _______________ view of data is concerned with the specific data structures used to manage the data. 39. A(n) _______________ implementation strategy is based on the concept of a node and pointers between nodes. 40. A(n) _______________ is an abstract data type that operates on a "last in, first out" (LIFO) manner. 41. Adding an item to a stack is called the _______________ operation. 42. Removing an item from a stack is called the _______________ operation. 43. A(n) _______________ is an abstract data type that operates on a "first in, first out" (FIFO) manner. 44. A(n) _______________ is an abstract data type behaves in a manner similar to a waiting line at a bank or supermarket. 45. A(n) _______________ node in a tree has no children. 46. The _______________ node in a tree is the only node that doesn't have a parent. 47. In a(n) _______________ tree, each node has no more than two children. 48. In a(n) _______________ tree, the values stored in the nodes are organized to allow an item to be found efficiently. 49. A(n) _______________ is made up of a set of nodes called vertices and a set of lines called edges (or arcs). 50. The lines connecting the nodes of a graph are called _______________. 51. In a(n) _______________ graph, the edges point from one node to another. 52. A graphical map with vertices representing the names of cities and with edges linking the vertices representing two-way roads between the cities is an example of a(n)________________graph. 53. In order to answer the question of whether you can travel from Boston to Los Angeles on your favorite airline, you would use a __________________ searching algorithm defined on a graph. 54. In order to determine how you can fly from Boston to Los Angeles in the fewest number of stops, you would use a _____________________ searching algorithm defined on a graph. 55. In order to determine what the shortest flight in miles from Boston to Los Angeles would be, you would use a ___________ searching algorithm defined on a graph. 56. A______________ graph is one in which there are values attached to the edges in the graph. Short Answers 57. Name the three levels at which data can be viewed. 58. Give an example of the application view of data if the problem is to print values in reverse order. 59. Give an example of the logical view of data if the problem is to print values in reverse order. 60. Give an example of the implementation view of data if the problem is to print values in reverse order. . 61. Give an example of the application view of data if the problem is to represent people in a waiting line. 62. Give an example of the logical view of data if the problem is to represent people in a waiting line. 63. Give an example of the implementation view of data if the problem is to represent people in a waiting line. 64. What is the role of a container? 65. Describe the two general approaches to implementing an abstract data type. 66. Are an array and a container the same? Explain. 67. An array is fixed sized, but a container is variable sized. Explain. 68. Distinguish between a sorted container and an unsorted one. 69. Draw the unsorted array-based container containing the following numbers: 23, 17, 19, 33, 5. 70. Draw the sorted array-based container containing the following numbers: 23, 17, 19, 33, 5. 71. Draw the unsorted array-based container containing the following letters: A, B, X, C. 72. Draw the sorted array-based container containing the following letters: A, B, X, C. 73. Draw the unsorted linked-based container containing the following numbers: 23, 17, 19, 33, 5. 74. Draw the sorted linked-based container containing the following numbers: 23, 17, 19, 33, 5. 75. Draw the unsorted linked-based container containing the following letters: A, B, X, C. 76. Draw the sorted linked-based container containing the following letters: A, B, X, C. 77. List five responsibilities of a List ADT. 78. Name three properties that characterize a list. 79. What is the algorithm for Inserting an item into a list? (pseudocode) 80. What is the algorithm for Removing an item from a list? (pseudocode) 81. . What is the algorithm for Printing a list? (pseudocode) 82. What are parameters? 83. What is an argument? 84. What is a value parameter? 85. What is a reference parameter? 86. What is the result of executing subprogram Swap if the parameters are value parameters? 87. What is the result of executing subprogram Swap if the parameters are reference parameters? 88. What is the result of executing subprogram Swap if one of the parameters is a value parameter and one of the parameters is a reference parameter? 89. Explain the acronym LIFO. 90. Explain the acronym FIFO. 91. Why do we use one external pointer in the linked implementation of a stack, but two in the linked implementation of a queue? 92. What are the properties of a binary tree? 93. What are the properties of a binary search tree? 94. What is the content of the root node of the following binary tree? 95. What is the content of all leaves in the following binary tree? 96. What is the content of each node of the following binary tree that has just one child? 97. What is the height of the following binary tree? 98. What does it mean to say that the Delete operation is ambiguous? 99. Give five possible interpretations of the Delete operation in a list. 100. What is the content of all ancestor nodes of the node containing 7 in the following binary tree? 101. Write a recursive algorithm called IsThere that returns a Boolean value indicating if a value is in a binary search tree, where the parameters are a pointer to the root of the tree (or subtree) and the item being searched for. 102. Write a recursive algorithm called NumNodes that returns the number of nodes in a binary tree, where the parameter is a pointer to the root of the tree (or subtree). Answer: integer NumNodes(tree) 103. What is a graph? Essay 104. Name and describe the three levels at which data can be viewed. Give an example for each level. 105. Compare and contrast a stack and a queue from a logical view. 106. Compare and contrast a stack and a queue from an implementation view. 107. Compare and contrast a binary tree and a binary search tree. 108. What is the difference between a directed graph and an undirected graph? 109. How did the Internet influence the 2008 presidential election campaign? 110. Compare and contrast the functions of lists, stacks, queues, and trees with the function of graphs. Answers and solutions True/False 1. The properties of an abstract data type are tightly related to the implementation of that data type. Answer: False 2. The two general approaches for implementing a container are array-based and linked implementations. Answer: True 3. The operations on a list differ depending on the implementation strategy used. Answer: False 4. . A stack is managed in a FIFO manner. Answer: False 5. The operations on a stack occur at one end. Answer: True 6. .A queue is managed in a FIFO manner. Answer: True 7. A queue is similar to a waiting line at a bank. Answer: True 8. Stacks and queues can be implemented only as a linked structure. Answer: False. They can be implemented as arrays, too (but it’s harder – take CS 241 if interested) 9. A tree is a non-linear data structure. Answer: True 10. In a binary tree, each node has at most two child nodes. Answer: True 11. A binary tree cannot contain decimal (base-10) data. Answer: False 12. The root of a tree has no parent node. Answer: True 13. The root of a tree has no child nodes. Answer: False 14. A leaf node has no child nodes. Answer: True 15. In a binary search tree, the value in any node is greater than the value in any node in its left subtree and less than the value in any node in its right subtree. Answer: True 16. Graphs are useful for representing hierarchies. Answer: False 17. A directed graph is a graph whose edges go in only one direction. Answer: True 18. Non-value returning subprograms must always have a RETURN statement Answer: False 19. Value-returning programs include the RETURN statement followed by a value to be returned. Answer: True 20. In the parameter passing process, the substitution mechanism can be thought of a message board. Answer: True Multiple Choice 21. . Which level provides a view of data that focuses on solving a particular problem? A. implementation level B. logical level C. array level D. linked level E. application level Answer: E 22. Which level provides an abstract view of data and the operations that manipulate them? A. implementation level B. logical level C. array level D. linked level E. application level Answer: B 23. Which level provides a view that deals with the underlying data structure used to manage the data? A. implementation level B. logical level C. array level D. linked level E. application level Answer: A 24. Which of the following is managed in a FIFO manner? A.list B. stack C. queue D. binary search tree E. graph Answer: C 25. Which of the following is managed in a LIFO manner? A. list B. stack C. queue D. binary search tree E. graph Answer: B 26. Which of the following is organized as a hierarchy? A. list B. stack C. queue D. binary search tree E. graph Answer: D 27. Which of the following can be directed or undirected? A. list B. stack C. queue D. binary search tree E. graph Answer: E 28. Which of the following would you use to represent airline flights between cities? A. list B. stack C. queue D. binary search tree E. graph Answer: E 29. What is the maximum number of nodes in a binary tree with 3 levels? A. 1 B. 3 C. 7 D. 8 E. 16 Answer: C 30. What is the minimum number of nodes in a binary tree with 3 levels? A. 1 B. 3 C. 7 D. 8 E. 16 Answer: B 31. What is the maximum number of nodes on Level 3 of a binary tree (remember that the root of the tree is at Level 0)? A. 1 B. 3 C. 7 D. 8 E. 16 Answer: D 32. What value is at the root of the following tree? A. 16 B. 12 C. 28 D. 30 E. 4 Answer: A 33. . Where would the value 19 be inserted in the following binary search tree? A. as the left child of 16 B. as the right child of 16 C. as the left child of 4 D. as the left child of 21 E. as the right child of 30 Answer: D 34. Where would the value 15 be inserted in the following binary search tree? A. as the left child of 16 B. as the left child of 4 C. as the left child of 21 D. as the right child of 12 E. as the left child of 12 Answer: D 35. How many comparisons would it take to find the value 30 in the following binary search tree? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 E. 6 Answer: C 36. Which of the following scientists developed the basic computer architecture that continues to be used today? A) Wernher von Braun B) George Polya C) Tony Hoare D) John von Neumann E) Richard Feynman Answer: D Fill in the Blank 37. A(n) _______________ is a data type whose data and operations are specified independently of any particular implementation. Answer: abstract data type (ADT) 38. The _______________ view of data is concerned with the specific data structures used to manage the data. Answer: implementation 39. A(n) _______________ implementation strategy is based on the concept of a node and pointers between nodes. Answer: linked 40. A(n) _______________ is an abstract data type that operates on a "last in, first out" (LIFO) manner. Answer: stack 41. Adding an item to a stack is called the _______________ operation. Answer: push 42. Removing an item from a stack is called the _______________ operation. Answer: pop 43. A(n) _______________ is an abstract data type that operates on a "first in, first out" (FIFO) manner. Answer: queue 44. A(n) _______________ is an abstract data type behaves in a manner similar to a waiting line at a bank or supermarket. Answer: queue 45. A(n) _______________ node in a tree has no children. Answer: leaf 46. The _______________ node in a tree is the only node that doesn't have a parent. Answer: root 47. In a(n) _______________ tree, each node has no more than two children. Answer: binary 48. In a(n) _______________ tree, the values stored in the nodes are organized to allow an item to be found efficiently. Answer: binary search 49. A(n) _______________ is made up of a set of nodes called vertices and a set of lines called edges (or arcs). Answer: graph 50. The lines connecting the nodes of a graph are called _______________. Answer: edges (or arcs) 51. In a(n) _______________ graph, the edges point from one node to another. Answer: directed 52. A graphical map with vertices representing the names of cities and with edges linking the vertices representing two-way roads between the cities is an example of a(n)________________graph. Answer: undirected 53. In order to answer the question of whether you can travel from Boston to Los Angeles on your favorite airline, you would use a __________________ searching algorithm defined on a graph. Answer: depth-first 54. In order to determine how you can fly from Boston to Los Angeles in the fewest number of stops, you would use a _____________________ searching algorithm defined on a graph. Answer: breadth-first 55. In order to determine what the shortest flight in miles from Boston to Los Angeles would be, you would use a ___________ searching algorithm defined on a graph. Answer: single-source shortest-path 56. A______________ graph is one in which there are values attached to the edges in the graph. Answer: weighted Short Answer 57. Name the three levels at which data can be viewed. Answer: Application (user) level, logical level, and implementation level. 58. Give an example of the application view of data if the problem is to print values in reverse order. Answer: The application view focuses on the container used, such as a stack, to reverse the order of the values. 59. Give an example of the logical view of data if the problem is to print values in reverse order. Answer: The logical view focuses on the Push and Pop operations that will add and remove values from the stack to reverse them. 60. Give an example of the implementation view of data if the problem is to print values in reverse order. Answer: The implementation view focuses on the manner in which the container (the stack) is implemented, such as using an array or linked strategy, with attention to efficient Push and Pop operations. 61. Give an example of the application view of data if the problem is to represent people in a waiting line. Answer: The application view focuses on the container used, such as a queue, to represent the waiting line. 62. Give an example of the logical view of data if the problem is to represent people in a waiting line. Answer: The logical view focuses on the Enqueue and Dequeue operations that will add and remove people from the queue to simulate the waiting line. 63. Give an example of the implementation view of data if the problem is to represent people in a waiting line. Answer: The implementation view focuses on the manner in which the container (the queue) is implemented, such as using an array or linked strategy, with attention to efficient Enqueue and Dequeue operations. 64. What is the role of a container? Answer: A container is an object whose role is to hold other objects. 65. Describe the two general approaches to implementing an abstract data type. Answer: An array-based approach stores items in the array, whereas a linked approach dynamically connects nodes containing the items into a linked structure. 66. Are an array and a container the same? Explain. Answer: No. An array holds the items in the container. That is, an array is the data structure used to implement a container. 67. An array is fixed sized, but a container is variable sized. Explain. Answer: An array has a set number of slots, established when it is declared. A container can contain none, one, or as many items as the structure containing the items can hold. 68. Distinguish between a sorted container and an unsorted one. Answer: In a sorted container, the items are kept in order by some data within the items. In an unsorted container, the items are stored without regard for the semantics of the items. 69. Draw the unsorted array-based container containing the following numbers: 23, 17, 19, 33, 5. Answer: 70. Draw the sorted array-based container containing the following numbers: 23, 17, 19, 33, 5. Answer: 71. Draw the unsorted array-based container containing the following letters: A, B, X, C. Answer: 72. Draw the sorted array-based container containing the following letters: A, B, X, C. Answer: 73. Draw the unsorted linked-based container containing the following numbers: 23, 17, 19, 33, 5. Answer: 74. Draw the sorted linked-based container containing the following numbers: 23, 17, 19, 33, 5. Answer: 75. Draw the unsorted linked-based container containing the following letters: A, B, X, C. Answer: 76. Draw the sorted linked-based container containing the following letters: A, B, X, C. Answer: 77. List five responsibilities of a List ADT. Answer: Create itself. Insert an item. Delete an item. Print itself. Know the number of items it contains. 78. Name three properties that characterize a list. Answer: The items are homogeneous, the items are maintained in a linear fashion, and the list has a varying length. 79. What is the algorithm for Inserting an item into a list? Answer: 80. What is the algorithm for Removing an item from a list? Answer: 81. . What is the algorithm for Printing a list? Answer: 82. What are parameters? Answer: Identifiers listed in parentheses in a subprogram declaration that accept values passed in when the subprogram is called. 83. What is an argument? Answer: A value passed into a subprogram when it is invoked. 84. What is a value parameter? Answer: A parameter that accepts a copy of the data passed in as an argument. 85. What is a reference parameter? Answer: A parameter that accepts the address of the data passed in as an argument. 86. What is the result of executing subprogram Swap if the parameters are value parameters? Answer: Nothing changes; there is no effect. 87. What is the result of executing subprogram Swap if the parameters are reference parameters? Answer: The contents of the arguments are exchanged. 88. What is the result of executing subprogram Swap if one of the parameters is a value parameter and one of the parameters is a reference parameter? Answer: Both arguments will have the same value, that of the value parameter. 89. Explain the acronym LIFO. Answer: It stands for last in, first out, which means that the last item added to the container is the first one to be removed. 90. Explain the acronym FIFO. Answer: It stands for first in, first out, which means that the first item added to the container is the first one to be removed. 91. Why do we use one external pointer in the linked implementation of a stack, but two in the linked implementation of a queue? Answer: All stack operations take place at the same end, so only one pointer to the node at that end is needed. Queue operations take place at both ends, so there must be access to the nodes at both ends. 92. What are the properties of a binary tree? Answer: A binary tree is a tree in which each node can have zero, one, or two child nodes. 93. What are the properties of a binary search tree? Answer: A binary search tree is a tree with the binary shape property and the semantic property that value in any node is greater than the value in any node in its left subtree and less than the value in any node in its right subtree. 94. What is the content of the root node of the following binary tree? Answer: 1 95. What is the content of all leaves in the following binary tree? Answer: 7, 5, 8 96. What is the content of each node of the following binary tree that has just one child? Answer: 3, 4, 6 97. What is the height of the following binary tree? Answer: 3 98. What does it mean to say that the Delete operation is ambiguous? Answer: Delete is ambiguous because there is more than one logical meaning. For example, given an item to delete, the operation could mean to delete the first copy found or delete all copies of the item. 99. Give five possible interpretations of the Delete operation in a list. Answer: Delete all items that match a specified item. Delete a matching item (if it exists). Delete a matching item (it must be present). Delete the matching item that has been in the list the longest time. Delete the matching item that has been in the list the shortest time. 100. What is the content of all ancestor nodes of the node containing 7 in the following binary tree? Answer: 4, 2, 1 101. Write a recursive algorithm called IsThere that returns a Boolean value indicating if a value is in a binary search tree, where the parameters are a pointer to the root of the tree (or subtree) and the item being searched for. Answer: Boolean IsThere(tree, item) IF (tree is null) RETURN false ELSE Set result to item.compareTo(info(tree)) IF (result = 0) RETURN true ELSE IF (result < 0) IsThere(left(tree), item) ELSE IsThere(right(tree), item) 102. Write a recursive algorithm called NumNodes that returns the number of nodes in a binary tree, where the parameter is a pointer to the root of the tree (or subtree). Answer: integer NumNodes(tree) IF (tree is null) RETURN 0 ELSE RETURN NumNodes(right(tree)) + NumNodes(left(tree)) 103. What is a graph? Answer: A graph is a data structure that consists of a set of nodes and a set of edges that relate the nodes to each other. Essay 104. .Name and describe the three levels at which data can be viewed. Give an example for each level. Answer: The application level views data in the context of the problem being solved (ex: managing the cars using queues during the simulation of a traffic intersection). The logical level takes an abstract view of the data values and the set of operations used to manage them (adding and removing cars from the queues during the simulation). The implementation level deals with the underlying data structure used to implement the logical view (ex: using a linked structure to implement a queue). 105. Compare and contrast a stack and a queue from a logical view. Answer: Both are linear containers that manage their data without regard to the semantics of that data. And both add and remove items only from the end points of the list. The Push and Pop stack operations add and remove data from the same end of the list, whereas the Enqueue and Dequeue operations of a queue operate at different ends. 106. Compare and contrast a stack and a queue from an implementation view. Answer: A stack and a queue can both be implemented using an array-based or a linked strategy. Since stack operations occur at only one end, its implementation is less complicated using either strategy. The implementation of a queue, whose operations occur at both ends, must facilitate that processing by shifting items in an array-based approach or using a second external pointer in a linked approach. 107. Compare and contrast a binary tree and a binary search tree. Answer: Both trees have the structural property that every node has at most two children. A binary search tree has the added characteristic that the elements contained in the nodes have a particular semantic relationship, namely that the value in a node is greater than the value in any node in its left subtree and less than the value in any node in its right subtree. 108. What is the difference between a directed graph and an undirected graph? Answer: In a directed graph, edges go in a particular direction between nodes, affecting whether one node is accessible from another. In an undirected graph, an edge between two nodes is bidirectional. If you can get to one, you can get to the other, and vice versa. 109. How did the Internet influence the 2008 presidential election campaign? The Internet permitted Democratic and Republican presidential primary and general election candidates to raise millions of dollars of campaign contributions through several million donors contributing relatively small amounts of dollars in a relatively short period of time. For example, almost half of the $639 million raised by Barack Obama came from 3 million donors who gave $300 or less. In addition, the Internet provided Obama and the Republican presidential candidate, John McCain, with the technological instrument to create a broad and diverse social media platform that advanced information and ideas to millions of Americans who were online. For example, both presidential candidates used Internet tools such as campaign websites, Facebook, MySpace, Twitter, and YouTube, along with thousands of personal forums and blogs, to communicate and respond to the concerns of campaign supporters and would-be supporters in an efficient manner. The blog “buzz,” consisting of heavily promoted issues on certain liberal and conservative political blogs, was frequently picked up by the mainstream media for use in their articles and broadcasts and soon became matters of general discussion among the electorate. Furthermore, the Internet permitted the managers of campaigns to respond quickly to negative feedback about online campaign advertisements and promotional efforts by editing online text and video. Finally, the democratic instruments of the Internet arguably revived and extended the participatory nature of the nation’s democratic electoral process. 110. Compare and contrast the functions of lists, stacks, queues, and trees with the function of graphs. Lists, stacks, queues, and trees are all merely holding containers. The user chooses which of these abstract data types would be most useful to solve a given problem. There are no inherent semantic other than those built into retrieval process. For example, a stack returns the item that has been in the stack the least amount of time; a queue returns an item that has been in the queue the longest amount of time. Lists and trees return only the specific information that is requested. On the other hand, a graph has algorithms defined upon it that solve particular problems. Graphs contain searching algorithms, for example, depth-first search, breadth-first search, and singlesource shortest-path search algorithms that respectively answer questions to particular problems posed by the computer user. Consequently, graphs do not merely represent or hold data as lists, stacks, queues and trees do, but have distinctive meanings defined by the particular searching algorithms used for a particular graph.