* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download O Systems
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
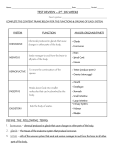
Animal Science Anatomy and Physiology Structure and Function of Organs and Organ Systems 2. Function of the Skeletal System Function Provides protection, support, and structure for all systems and organs. Provides attachment for muscles Provides storage for minerals (ex: Ca) 3. What makes up the skeletal system? Bone Made of minerals that provide housing for living cells Cartilage Firm, flexible tissues that are not as hard as bone Bone Marrow Production site of blood cells and platelets. 5. What else makes up the skeletal system? Joints Where different bones meet Ligaments Connect tissue bones to other bones; tough 6. Function of the Muscle System Function Provides movement for the animal Provides movement for proper function of organs Qui ckT ime™ and a TI FF (Uncompres sed) decompres sor are needed t o s ee thi s pi cture. 7. Three types of muscle tissue Skeletal Muscle Provides movement for the bones Voluntary movement Composed of long, striated bundles that contract and relax Examples: Biceps, Quads 7. Types of muscle cont. Smooth Muscle Controls movements of the internal organs Involuntary movements Composed of spindle shaped cells Examples: Digestive tract, urinary tract 7. Types of muscle cont. 7. Types of muscle cont. Cardiac Muscle Muscle that controls the beating of the heart Involuntary 8. What is the Integumentary System? The Integumentary System includes: Skin Hair Finger and Toe Nails The Integumentary System’s Function: Barrier against infection and injury Regulates body temperature Removes wastes Provides protection from Ultra Violet radiation 9. What is Skin? Layers of Skin Epidermis Outer Layer of the skin Contains both dead and living cells Non-vascular tissue (no blood vessels) Cells in the epidermis make Keratin and Melanin Keratin- tough protein found in hair Melanin- pigment that absorbs UV light 9. What is Skin? Layers of Skin Dermis Inside layer of the skin Contains collagen, hair follicles, nerves, smooth muscle and glands Vascular tissue (has blood vessels) Two types of glands: Sweat glands- secretes water and salts to cool the body down and remove waste from the blood. Sebaceous (oil) glands- secretes Sebum (oil) to keep the epidermis flexible and waterproof and to make hair soft and flexible. 11. Function of the Circulatory System Function Transports: Water Oxygen Wastes Regulates temperature Removes disease 12. What is the heart? Heart Center of the circulatory system Large, powerful muscle Beats continuously to pump blood to the entire body 13. What else makes up Circulatory System? Blood Vessels Arteries Vessels that take blood away from the heart Veins Vessels that return blood to the heart 13. Blood Vessels cont. Capillaries Connects arteries and veins Delivers nutrients and oxygen to the cells Removes wastes from cells 14. What is blood? Red Blood cells White Blood cells Give blood color Carry oxygen Destroy disease Gives white color to pus Platelets Made of plasma proteins Forms blood clots 15. Structure of the heart Four Chambers Right Receives deoxygenated blood into the heart from the body via veins Right Atrium Receives oxygenated blood into the heart from the lungs Left Ventricle Pumps blood out to the lungs Left Atrium Ventricle Pumps blood out into into the body via arteries Superior Vena Cava Aorta Pulmonary Artery Pulmonary Vein Right Atrium Right Ventricle Inferior Vena Cava Left Atrium Left Ventricle 15. Structure of the heart cont. Two Paths of Circulation Systemic Circulation Circulation of blood from the heart, to the body, and then back to the heart Pulmonary Circulation Circulation of blood from the heart, to the lungs, and then back to the heart 16. Function of the Respiratory System Function: Take Oxygen Exchange in oxygen from the air Place oxygen in the bloodstream Remove carbon dioxide from the body 17. Structures of the Respiratory System Structures Nostrils Air intake Nasal Chamber Mouth Air Intake 17. Structures cont. Pharynx Passageway for food, water, and air. 17. Structures cont. Larynx Voice box (Adam’s apple) Trachea (Windpipe) Large tube Made of rigid cartilaginous rings Epiglottis Flap that covers the trachea to prevent food from entering 17. Structures Cont. Bronchi Tubes that branch into the lungs Passage for air Lungs Organ where gas exchange occcurs 17. Structures cont. Alveoli Tiny air sacs that are surrounded by blood vessels Carbon dioxide is removed from the blood Oxygen is absorbed into the blood 17. Structures cont. Diaphragm Large muscle under the lungs When contracted, rib cage expands and air comes in When the diaphragm relaxes, air is forced out 19. Function of the nervous system Function: Central System Nervous Relays messages to and from the rest of the body Processes and analyzes information Includes the brain and spinal cord 19. Function of nervous system cont. Peripheral Nervous System Transmits motor or sensory impulses to the central system Includes all nerves outside of the central system 20. Structures of the nervous system Neurons Cells of the nervous system Sensory Neurons- control impulses from the body to the brain Motor Neurons- control impulses from the brain to the body Nerves Long fiber like structures made up of neurons Impulses travel along nerves to and from the brain The Neuron 20. Nervous System structures cont. Spinal Cord All nerves connect to the spinal cord Runs through the backbone (vertebrae) 20. Nervous System structures cont. Brain Center of the nervous system Divided into 3 sections 20. Nervous System structures cont. Brain 1. 2. 3. Cerebrum Controls voluntary processes and thinking Cerebellum Coordinates actions and movement (talking/running) Brain Stem Controls involuntary activities (heart beat, respiration), homeostasis, and feelings. 21. Function of the digestive system Function: The digestive system breaks down food into a form that the body can use. Breaks food down to a molecular level that the body can absorb into the blood stream This includes vitamins, minerals, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids, and nucleic acids. 21. What does the Digestive System look like? 22. Where does digestion start? The Mouth Teeth- tear and crush food to small pieces Salivary Glands- secrete saliva which moistens food so it can be swallowed Saliva also contains enzymes that break down starches into sugars and destroys bacteria in food Tongue forms a ball of food called the bolus With help from the throat muscles pushes food to the esophagus. 23. Where does the food go next? The Esophagus The “food tube” Smooth muscles line this tube. Contractions of these muscles, called peristalsis, push the bolus down to the stomach. 24. What is the stomach? The Stomach The stomach is a large, muscular sac. Most mechanical digestion occurs in the stomach. Glands in the stomach secrete mucus to protect the stomach, hydrochloric acid (HCL) to activate enzymes, and pepsin. The mixture in the stomach is now called chyme 25. What is the Small Intestine? The small intestine has three parts, the duodenum, the ileum, and the jejunum. Most chemical digestion (break down of chyme by enzymes) occurs in the small intestine. 26. What are the accessory organs in the digestive system? Pancreas The pancreas is a gland that lies near the stomach The pancreas has three functions: Produces insulin to regulate blood sugar levels Produces enzymes that are secreted into the small intestine to break down carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Produces sodium bicarbonate to neutralize the acidity of the stomach. 26. Accessory organs cont. Liver Largest internal organ in the body Produces Bile Bile helps dissolve fat The Liver is also responsible for detoxifying the blood 27. The rest of the system Large Intestine (or Colon) Primary Function is to remove water from the remainder of undigested material Also stores this material until excreted Rectum Muscular the body tube that passes waste out of 28. Digestive System disorders Peptic Ulcers Caused by bacteria in the stomach Creates a hole in the lining of the stomach Acid Reflux Caused by acid contents in the stomach being regurgitated into the esophagus. Damages the lining of the esophagus. Often referred to as heartburn. 29. What is the excretory system? Functions of the excretory system: Every cell in the body produces metabolic wastes. The excretory system removes wastes from the bloodstream and the digestive tract, then removes these wastes from the body. Excretion plays an important role in homeostasis. 30. What is the function of the kidneys? Kidney Function The kidneys remove wastes from the blood (urea), maintain blood pH, and regulate the volume of the blood. Kidneys reabsorb 99% of the water that enters them. Kidneys filter the blood of the body every 45 min. Kidneys are made up of nephrons. 31. Structure of the Kidney 32. Other excretory structures Ureter Tube that carries urine from the kidney to the bladder Bladder Sac-like organ that stores urine until excreted Urethra Tube that carries urine from the the bladder to the outside of the body 32. Other excretory structures Skin The Skin excretes excess water and salts (sweat). Lungs The lungs excrete carbon dioxide when animals exhale. Liver The liver removes toxins from our bloodstream. 33. What is the Endocrine System? Function: Composed of glands that secrete hormones. Hormones: Chemicals that affect specific parts in the body. Hormones control vital function of the body. Growth Reproduction Hormones play a primary role in homeostasis of the body 34. What are glands? Exocrine glands Release secretions through ducts directly to the organs that use them Examples- sweat glands, digestive glands Endocrine glands Release secretions directly into the bloodstream 35. Glands of the endocrine system Pituitary Gland Secretes nine different hormones that regulate other endocrine glands Hypothalamus Regulates hormone production of the Pituitary 35. Endocrine glands cont. Adrenal Gland Releases Adrenaline and other hormones that help our body deal with stress This includes the fight or flight response Thyroid Gland Controls rate of digestion and metabolism 35. Endocrine glands cont. Pancreas Has both exocrine and endocrine function Exocrine Secretes digestive enzymes into the small intestine Endocrine Secretes insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar levels 35. Endocrine glands cont. Ovaries Produce and secrete estrogen and progesterone Estrogen is responsible for development of eggs and physical “female characteristics” (e.g. widening of hips, breast formation) Testes Produce and secrete testosterone Testosterone is responsible for sperm production and physical “male characteristics” (e.g. deep voice, facial hair) 37. The Male Reproductive System Function Produce and deliver sperm Sperm development is triggered by testosterone and FSH secreted by the pituitary Sperm production is called spermatogenesis 37. The Male Reproductive System Structures Testes- site of sperm production The testes reside outside the body where the temperature is 1-3 degrees lower. This creates the ideal temperature for spermatogenesis Seminiferous tubules Tight coils within the testes. These coils are where sperm is produced 37. The Male Reproductive System Epididymis Site where sperm mature and are stored Vas Deferens Some sperm move into this tube to be ejaculated Urethra The Vas Deferens joins the urethra where semen is ejaculated though the penis to the outside of the body 37. The Male Reproductive System Male Reproductive Glands Seminal Vesicle, Prostrate gland, and bulbourethral glands add fluids to the sperm to create semen Semen- acts as a carrier to get the sperm inside the vaginal canal during conception 38. The Female Reproductive System Function Production of Ova (eggs), and development of the embryo after fertilization Females are born with thousands of immature eggs. Ova maturation is triggered by estrogen and FSH Production of mature ova is called oogenesis. 38. The Female Reproductive System Structures Ovaries- Site of ova storage and maturation Ovulation- process where the mature follicle releases its egg. This happens once every 28 days Fallopian The Tube (oviduct) fallopian tube is usually the site of fertilization Once fertilized, the egg is called a zygote 38. The Female Reproductive System Structures Uterus If a zygote exists, it will implant to the wall of the uterus and mature Cervix Opening between the uterus and vagina Vagina Muscular passage. Site where semen enters the female and also site where fetus is delivered