* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants, Fungi and the colonization of Land
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
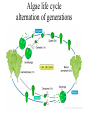
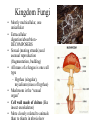
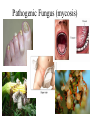
Plants, Fungi and the colonization of Land HBio Ch 17 What is Kingdom Plantae?? • strictly Multicellular – specialized tissues and systems, including growth regions (meristems), true stems and leaves • Chlorophylls a & b, plus accessory pigments • Store food as starch, cellulose in cell walls • Sexual & Asexual reproduction Kingdom Protista vs. Kingdom Plantae Alternation of Generations Sexual Reproduction - • Life cycle alternates between gametophyte generation (haploid) –makes gametes • Sporophyte generation (diploid) • makes spores –embryophytes – multicellular, dependent embryo at gametophyte stage; differs from algae Algae life cycle alternation of generations How did life emerge from the sea? Symbiosis led to invasion of land - Fungal Partners • Lichens – Cyanobacteria or algae + fungi – Pioneer species • Make soil – Ecological indicator Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Fungi • Mostly multicellular, one unicellular • Extracellular digestion/absorbtion DECOMPOSERS • Sexual (mating strands) and asexual reproduction (fragmentation, budding) • All mass of a fungus is one cell type – Hyphae (singular), mycelium (mass of hyphae) • Mushroom is the “sexual organ” • Cell wall made of chiton (like insect exoskeleton) • More closely related to animals Pathogenic Fungus (mycosis) Where did plants come from? -green & red algae (K. Protista) charyophyceans • What is needed to move out of the water environment of algae – What “concerns” do plants have that algae don’t? Earliest plants • Bryophytes – One simple step up from algae – Non-vascular • O&D – Haploid spores produced, not seeds Later - Vascular plants (bigger, better, faster, more) • Tracheophytes – Able to survive dryer conditions – A way to move water and nutrients • Xylem & phloem • Roots, stems, leaves – Symbiosis with fungi • mycorrhizae Protection from dessication • Cuticle • stomata And even later, a way to survive tough times… • Non-seed plants vs. seed plants Sexual Reproduction • Spore – Haploid tissue – can’t survive long without water • Seed – Embyro is diploid tissue – Embryo + endosperm (triploid tissue) + seed coat – Can wait for conditions to be right for survival And more complex ways of making & distributing those seeds… • Gymnosperm vs. Angiosperm (monocot/dicot)