* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ancient Greece
Regions of ancient Greece wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek literature wikipedia , lookup
Acropolis of Athens wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek religion wikipedia , lookup
Athenian democracy wikipedia , lookup
Spartan army wikipedia , lookup
Economic history of Greece and the Greek world wikipedia , lookup
Corinthian War wikipedia , lookup
Battle of the Eurymedon wikipedia , lookup
List of oracular statements from Delphi wikipedia , lookup
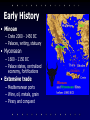
Ancient Greece Land and History Overview • Geography & Environment • Archaic Period & The Rise of The Polis • Colonies & Tyrants • Athens & Sparta • The Persian Wars • The Peloponnesian Wars • Alexander the Great Oracle at Delphi Rise of the Greeks • Greeks were resource poor – Poor soil – Mountain chains – No large river systems ancient Greek shipping • Consequences – Oriented to the ocean – Stimulated geography, history – Rivalry with Persian Empire Persian King Darius III The Middle Sea – Uniform ecozone: climate, plants, animals – Hot summers, stormy winters – Easy to travel • sea as connector, not barrier Mediterranean Geography • Aegean Sea coastlines • Empire included – Mainland Greece – Many islands – Ionia: western Asia Minor • Exploiting the sea – Fishing – Trading – Mercenary soldiers Environment • Unstable geology – Volcanic zone • European and African tectonic plate contact • Frequent earthquakes Oracle of Apollo at Delphi – Consequences • Religion of oracles • Deforestation – Probably during Iron Age (800 BC) – Consequences • Used stone for building Ephesus Valley Resources By Land • Arable land – Thin topsoil, limited rainfall, no large river systems • Limited carrying capacity – Dry farming • Barley, olives, grapes • Sheep, goats • Building stone – Marble • Clay for pottery • No timber, metals Marble quarry - Naxos Resources By Sea • Coastline with natural harbours – Difficult travel overland • Ports of Call – Northern Aegean • timber – Anatolia • gold, iron – Cyprus • copper – Western Mediterranean • tin – Black Sea, Egypt, Sicily • grain Early History • Minoan – Crete 2000 - 1450 BC – Palaces, writing, statuary • Mycenaean – 1600 - 1150 BC – Palace states, centralized economy, fortifications • Extensive trade – Mediterranean ports – Wine, oil, metals, grain – Piracy and conquest Minoan and Mycenaean Lion Gate - Mycenae Palace of Minos - Knossos Atlantis and Santorini • Plato’s legend • Atlantis lost civilization that sank beneath the sea • Minoan period Santorini – volcanic eruption 1600 BC – destroyed island of Thera – caused climate change, decline of Minoan civilization Archaic Period • Dark Ages – 1150 - 800 BC – collapse of empires eastern Mediterranean – loss of trade & knowledge, isolation • Phoenician traders – arrived 800 BC – brought trade, writing system – population explosion • Intensive farming • Available imports Phoenician traders The Rise of the Polis • Polis = City-State – Urban centre and rural territory – Rising population - villages merge into cities – Specialized labour - crafts, commerce, religion • Independent Cities – Fiercely jealous – Created rivalry, political and economic conflict Hoplite Warfare • New warfare – hoplite: heavily armed citizen foot soldier – phalanx: tight, square formation of hoplites • Relation to agriculture – Clash of hoplite lines = quick decision – Survivors returned to fields Colonization • Population pressure – People left or forced out – founded colonies in • • • • Aegean Black Sea Libya Southern Italy, Sicily • Impact: new – – – – Markets Urban planning Forms of government Ideas Colony at Samos An Age of Tyrants • Feudal kings of Dark Ages replaced with aristocratic councils • Society included – Merchants & craftsmen – Peasant farmers – Debt slaves • City-State Tyrant – 7th - 6th cent BC – Held power contrary to established community traditions – Backed by middle class, hoplite forces • Rejection of Tyrant Families – transition from oligarchy - power by wealthy families – to democracy - power by free adult males Sparta • conquest, not colonies – 7th cent BC shortage of land – Attacked Messenia in west Peloponnese – Reduced population to status of helots (landless farmers) • fear of uprising – Sparta as military camp – Soldiers owned land, helots worked it – Best army in Greece through training The Peloponnese • Huge personal price • Peloponnesian League – Defensive alliances – Isolationist, thus no cultural development Spartan hoplite • Solon Athens – Appointed lawgiver 594 BC: crisis over population, oligarchy – Created 4 social classes • Based on farm income • Top three: held office • Bottom: vote only – Abolished debt slavery • The Tyrant Pisistratus – Seized power 546 BC – Created public buildings, festivals • Temple of Athena • City Dionysia – drama festival • Panathenaea - religion, athletics, poetry – Overthrown by 500 BC Solon Athenian Democracy • Pericles transferred power to – Assembly - legislature – Council of 500 - executive – People’s Courts • Public Office: all men eligible – Elected office • Public finance • Defence – Some offices filled by lot – Paid public servants • Assembly of All Citizens – Public debate of issues – Decisions openly made Pericles of Athens The Persian Wars • Cyrus conquered Anatolia 546 BC – Put down Ionian revolt 499 BC • Invasion of Greece – Athens defeated Persians at Marathon 490 BC – Invasion by Xerxes 480 BC Battle of Thermopylae • Battle of Thermopylae - 300 Spartans under Leonidas held off army of thousands • Sack of Athens • Battle of Salamis - Themistocles & victory at sea – Persian defeat at Plataea 479 BC • Provisioning large army in the field • Tactical errors at Salamis • Superiority of hoplite arms & training Battle of Salamis Height of Athenian Power • Delian League – Defensive alliance under Athens • Freed Ionia from Persia • Later dominated by Athens • Athenian Navy – Reinforced democracy • Rowers were from lower classes – Controlled large occupied territory • Tribute paid for works like Parthenon (Athena), development of arts & sciences – Promoted commercial interests Parthenon The Peloponnesian Wars • Rise of Athens – Control over Delian League – Reaction to sacking • Fortification of city – Double wall linked city with port of Piraeus, supplies by sea • New strategy: delay, refusal to join battle • Sparta – Earthquake & helot revolt 462 BC – Withdrew from conflict • Peace of Nicias 421 BC Spartan hoplite Alexander the Great • Battle of Chaeronea 336 BC – Philip II of Macedonia defeated Thebes, Athens – Corinthian League & loss of democracy • Alexander, son of Philip II – – – – 334 BC invasion of Persia Conquest of Persia, India, Egypt Established local rule, Greek-style cities Died 323 BC • Division of Empire – Seleucids in Persia – Ptolemies in Egypt – Antigonids in Macedon & Hellas • Spread of Hellenistic culture The Hellenistic Age • Greek domination of Middle East – Long lasting impact • Diffusion of Greek culture – Privileged class of soldiers, scholars, administrators – Integration with local culture • Greek Cities – Alexandria The Lighthouse - Alexandria • Library, Museum, Lighthouse – Greek Gymnasia • Taught alphabet, writing Alexander Gate - Jerusalem Next Lecture • Ancient Greece Cities