* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
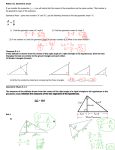
TEKS: G5B, G5D, G11A, G11B, G11C The student will use numeric patterns to make generalizations about geometric properties including properties of polygons and ratios in similar figures. The student will identify and apply patterns from right triangles. The student will use and extend similarity properties and transformations to explore and justify conjectures about geometric figures. The student will use ratios to solve problems involving similar figures. The student will develop, apply, and justify right triangle ratios. Remember In a right triangle, an altitude drawn from the vertex of the right angle to the hypotenuse forms two right triangles. Example: 1 Write a similarity statement comparing the three triangles. Sketch the three right triangles with the angles of the triangles in corresponding positions. W Z By Theorem 8-1-1, ∆UVW ~ ∆UWZ ~ ∆WVZ. Example: 2 Write a similarity statement comparing the three triangles. Sketch the three right triangles with the angles of the triangles in corresponding positions. By Theorem 8-1-1, ∆LJK ~ ∆JMK ~ ∆LMJ. extremes means Consider the proportion means extremes In this case, the means of the proportion are the same number, and that number is the geometric mean of the extremes. The geometric mean of two positive numbers is the positive square root of their product. So the geometric mean of a and b is the positive number x such that ,or x2 = ab. Example: 3 Find the geometric mean of each pair of numbers. If necessary, give the answer rounded to the nearest tenth. 4 and 25 Let x be the geometric mean. x2 = (4)(25) = 100 x = 10 Def. of geometric mean Find the positive square root. Example: 4 Find the geometric mean of each pair of numbers. If necessary, give the answer rounded to the nearest tenth. 5 and 30 Let x be the geometric mean. x2 = (5)(30) = 150 Def. of geometric mean x = 150 Find the positive square root. x≈12.2 Helpful Hint Once you’ve found the unknown side lengths, you can use the Pythagorean Theorem to check your answers. Set Up # 1 B altitude A segment1D C segment2 segment1 altitude altitude segment2 Set Up # 2 B leg A C adj. D hypotenuse adjacent segment leg leg hypotenuse Set Up # 3 B leg A D adj. C hypotenuse adjacent segment leg leg hypotenuse Example: 5 B Find BD 2 BD BD 8 (BD)2 16 BD 4 A 2 D 8 C Example: 6 B Find BD 3 BD BD 8 (BD)2 24 BD 24 BD 4 6 BD 2 6 BD 4.9 A 3 D 8 C Example: 7 B Find DC and AC 10 5 10 10 DC 5(DC )2 100 DC 20 AC 20 5 25 A 5 D C Example: 8 Find AD and AC AD 3 2 12 3 2 12( AD) 9 4 12 12 AD 1.5 AC 12 1.5 13.5 B 3 2 A D 12 C Example: 9 B Find BC 5 BC BC 9 (BC )2 45 BC 9 5 3 5 C 5 D4 A Example: 10 B Find CD 9 12 12 9 DA 81 9DA 144 DA 7 12 C D9 A Example: 11 B Find BC 3 7 7 3 7 3 7 CD D 7 A C 9 49 7(CD) 63 7(CD) CD 9 9 BC BC 16 (BC )2 144 BC 12 Example: 12 B Find AD 12 3 2 a2 b2 c 2 2 2 2 (3 2) AD 12 C 18 AD2 144 AD2 126 AD 126 9 14 3 14 AD 11.22 D A Example: 13 To estimate the height of a Douglas fir, Jan positions herself so that her lines of sight to the top and bottom of the tree form a 90º angle. Her eyes are about 1.6 m above the ground, and she is standing 7.8 m from the tree. What is the height of the tree to the nearest meter? 1.6 7.8 7.8 x x 38.025 The tree is about 38025+1.6 = 39.625, or 40m tall Example: 14 A surveyor positions himself so that his line of sight to the top of a cliff and his line of sight to the bottom form a right angle as shown. What is the height of the cliff to the nearest foot? 5.5 28 28 x x 142.5 The cliff is about 142.5 + 5.5, or 148ft high Example: 15 Pre AP Find CA and CD B 12 3 2 12 12 CA 3 2(CA) 144 3 3 CA 48 2 48 2 CA 2 C D3 2 2 CA 24 2 CD 24 2 3 2 21 2 2 A