* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plate Tectonics Unit Trivia
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
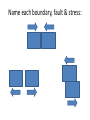
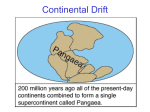
Plate Tectonics Unit Trivia How well do you know your stuff? What is the dark colored rock that makes up much of the ocean floor? Basalt What is the cycle that slowly moves the soft rock in the mantle, transferring heat, and moving the plates around on Earth? Convection Currents A force that acts on rock to change its volume or its shape What is this a definition of? Stress What do you call the record of events and life forms that have lived on Earth throughout history? Geologic Time Scale Multiple Choice: As a tsunami gets closer to shallow water, its wave height gets____. a. b. c. Smaller Bigger Crushed Define extinct Extinct means that an organism no longer exists on Earth. All are dead. True or False? Volcanoes may form along divergent and convergent boundaries. Geologists or Seismologists draw circles on a map to determine the _______________ of an earthquake. Epicenter A belt of major volcanic activity around the Pacific Ocean is called _______. The Ring of Fire The large, flat area of the ocean floor is called the ______________. Abyssal Plain Scientists who study fossils are called ______________. Paleontologists What do scientists study to learn about how animals change over time? The Fossil Record The layer of Earth that is described as a dense, metal ball is the _____________. Inner Core _________ is a stress that pushes rock in 2 different directions. Shearing A wide, gently sloping mountain describes a ___________ volcano. Shield Which layer of Earth is made of liquid nickel & iron and moves to create Earth’s magnetic field? The Outer Core Two examples of geothermal activity are ______ & ______ Hot Springs & Geysers Molten material inside Earth is called _______. Magma When molten material reaches the surface of Earth, it is called __________. Lava What is the technique used to measure the depth of the ocean? Sonar Cinder Cone Volcanoes form when _____, ______, and ________ build up in a steep pile. Ash Cinders & ? Mt. Saint Helens is an example of a ________ volcano. Composite Wegener’s hypothesis of _________________ states that the continents were one joined together. Continental Drift What is the type of heat transfer where a metal spoon heats up if its left in a hot pot of soup? Conduction Multiple Choice: An energy source that comes from water heated by magma is a. radiation transfer b. conduction c. geothermal energy True or False? Hot spots can form in the ocean floor, under continents, in the middle of a plate and near plate boundaries. The single landmass that broke apart millions of years ago is called ___________. Pangaea The ________ is the point underground where rock breaks & where seismic waves radiate from in an earthquake. Focus True or False? Volcanoes never form along mid-ocean ridges at divergent plate boundaries. What is the stress that pulls on the crust where two plates are moving apart? Tension Multiple Choice: Fossils of tropical plants found in Antarctic tell us that Antarctica was once much _______. A. smaller B. colder C. warmer Fountains of steam and water that erupt from the ground are called _________. Geysers Ocean floor sinking under a deep ocean trench & back into the mantle is called _________. Subduction _______ can be used to help scientists understand Earth’s interior. Seismic Waves What is an underwater mountain called? A Seamount At transform boundaries a _________ fault will result from the stress of shearing. Strike-Slip Multiple Choice: The ______ heats the mantle and makes the convection currents move. A. sun B. inner core C. geothermal activity A huge hole left by the collapse of a volcanic mountain is a __________. Caldera What are the 3 types of volcanoes we talked about in class? Shield Composite Cinder Cone Multiple Choice: The rigid upper mantle and the crust make up the ____. A. asthenosphere B. atmosphere C. lithosphere What kind of stress pulls on the plates at divergent boundaries? Tension What kind of fault results from converging plates? Reverse Mid-Ocean Ridges are similar to ____ and form at ____ boundaries. Mountain Ranges at Divergent Boundaries st 1 What is the topographical feature of the sea floor you would see if you could step off of a continent and walk across the ocean? The Continental Shelf What are 3 geologic events/formation that happen on Earth due to plate tectonics? Earthquakes, Volcanoes, Mountain Building True or False? If convection currents stopped moving it would mean that the inner core is no longer heating the mantle. TRUE! The heat from the inner core heats the mantle. The movement in the mantle make the plates of the lithosphere move slowly. Name each boundary, fault & stress: