* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 5:1 Cell Cycle
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
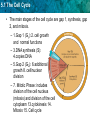
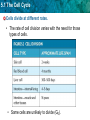
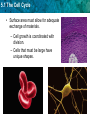
5.1 The Cell Cycle KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. 5.1 The Cell Cycle 5.1 The Cell Cycle More prefixes• Stage-step or part of mere-segment or part • Phase-appearance Soma-body • Divide-to separate Centro-center • Duplicate-an identical copy • Double-to increase twofold Condense-reduce volume • Copy-reproduction from an original • Kine-movement • inter-between • pro-before • meta-middle • Ana-back • telo-end Cells double their DNA in order to divide and create two nearly identical duplicates or copies.” 5.1 The Cell Cycle A. Interphase-cell growth • Gap1 (G1)-rapid protein synthesis, lots of enzyme activity, organelles replicate (copy) • Synthesis (S)-chromosomes become visible, replicate and are now called sister chromatids connected by the centromeres. • Gap 2 (G2)-more metabolic activity, centrioles duplicate and form spindle fibers made of microtubules. 5.1 The Cell Cycle • The main stages of the cell cycle are gap 1, synthesis, gap 2, and mitosis. – 1.Gap 1 (G1):2. cell growth and normal functions – 3.DNA synthesis (S): 4.copies DNA – 5.Gap 2 (G2): 6.additional growth 8. cell/nuclear division – 7. Mitotic Phase: includes division of the cell nucleus (mitosis) and division of the cell cytoplasm 13.cytokinesis 14. Mitosis 15. Cell cycle 5.1 The Cell Cycle Cells divide at different rates • G1-varies the greatest • G0 – this cell is unlikely to divide again 5.1 The Cell Cycle Cells divide at different rates. • The rate of cell division varies with the need for those types of cells. • Some cells are unlikely to divide (G0). 5.1 The Cell Cycle • Cell size is limited • If cell is too small the cell does not contain all the organelles it needs. • If a cell is too large-needed nutrients could not diffuse in and waste could not diffuse out. (starve or poison itself) 5.1 The Cell Cycle Cell size is limited. • Volume increases faster than surface area. 5.1 The Cell Cycle • Surface area must allow for adequate exchange of materials. – Cell growth is coordinated with division. – Cells that must be large have unique shapes.