* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Resources and Living Things
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
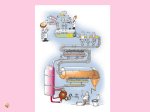
Food, Energy and Healthy Eating Major source of energy and made of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and provides raw materials. Guidelines that show the amounts of nutrients humans need every day. Nutrients that contain nitrogen as well as carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen your body needs for growth and tissue repair. The amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 ̊Celsius. One of 20 kinds of organic compounds that are linked chemically to one another, forming proteins. Nutrients that are not made by living things needed in small amounts to carry out chemical processes. Sugar that is a major source of energy for your body’s cells. Shows how the nutrients in one serving fit into a diet of 2,000 Calories a day. Substances in food that provide the raw materials and energy the body needs to carry out its essential processes. Helper molecules in your body’s chemical reactions. Energy-containing nutrients composed of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen that protect your organs and insulates your body. Food, Energy and Healthy Eating Substance that breaks up fat particles. Triangular organ located between the stomach and the first part of the small intestine that helps break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Last section of the digestive system. Millions of finger-shaped structures folded into the inner surface of the small intestine. Does many jobs in the body such as making bile for the digestive system (largest organ in the body). Where waste material is compressed into solid form. Where bile is stored. A muscular opening at the end of the rectum. Part of the digestive system where most chemical digestion takes place. Fluid released by salivary glands when you eat. A thick, slippery substance produced by the body that lines the esophagus. Flap of tissue that seals off your windpipe and prevents food from entering the lungs as you swallow. J-shaped muscular pouch in the abdomen. Process by which your body breaks down food into small nutrient molecules. Muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. Waves of involuntary muscle contractions that push food toward the stomach. Process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. Protein that speeds up chemical reactions in the body.