* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Selection
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
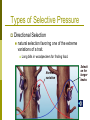
Types of Selection And their results. Types of Selective Pressure Directional Selection natural selection favoring one of the extreme variations of a trait. Long bills in woodpeckers for finding food. Normal variation Selecti on for longer beaks Types of Selective Pressure Stabilizing Selection natural selection that favors average individuals in a population. Small spiders can’t catch big insects Big spiders get eaten by birds Selection for average size spiders Normal variation Types of Selective Pressure Disruptive Selection Individuals with either extreme of a trait’s variation are selected for. Dark limpets on wet, dark colored rocks Light limpets on dry, light colored rocks Selection for light limpets Normal variation Selection for dark limpets Types of Evolution Directional Over time a species adapts to its environment due to directional selective pressures Bird’s bones have become lighter and longer over time to aid in flight and some insects look more and more like plants for disguise. Industrial Melanism Industrial revolution = smoke from coal. Peppered Moth used light colored lichen as camouflage. What happened? Industrial Melanism Directional selection by predation. Types of Evolution Convergent Two species evolve similar adaptations even though they do not share a recent common ancestor. Sharks and dolphins have many similar traits but are NOT closely related. Dolphin ancestors did not have hydrodynamic shapes and shark like pectoral fins, they had legs and bodies built for walking Dolphin ancestors that looked more like sharks were more successful in the ocean Dolphins evolved some shark like features Results of Evolution - Convergence Analogous Structures Convergent evolution causes organisms to develop structures with similar appearances to meet the same need. For example, insect and bird wings probably evolved separately when their different ancestors adapted independently to similar ways of life. Results of Evolution - Convergence Mimicry - A structural adaptation that enables one species to resemble another species. In one form of mimicry, a harmless species has adaptations that result in a physical resemblance to a harmful species. Predators that avoid the harmful looking species also avoid the similar-looking harmless species. Toxic Monarch Butterfly Harmless Viceroy Butterfly Results of Evolution - Divergence Divergent A population of species is separated by a geographical barrier On each side of the barrier different selective pressures cause the species to evolve in different directions. Directional in different directions or different random changes. Results of Evolution - Divergence Adaptive Radiation Species diverge to fill unoccupied niches in a new environment. Disruptive selection or small geographic areas with different directional selection. Honeycreepers of Hawaii Extinct mamo Amakihi Possible Ancestral Lasan finch Crested honeycreeper Kauai Niihau Molokai Oahu Maui Lanai Akialoa Kahoolawe Akepa Akiapolaau Akikiki Liwi Hawaii Apapane Maui parrotbill Palila Ou Grosbeak finch Results of Evolution - Divergence Endemics Each island population undergoes different selective and random evolution. Results of Evolution - Divergence Homologous Structures Divergent evolution causes similar structures to evolve to meet different needs Crocodile forelimb Whale forelimb Bird wing