* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download pp_Direct-Ophthalmoscopy_en
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
Fundus photography wikipedia , lookup
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment due to intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Photoreceptor cell wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial optic neuropathies wikipedia , lookup
Macular degeneration wikipedia , lookup
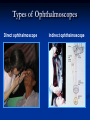
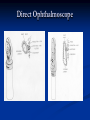
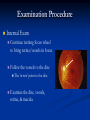
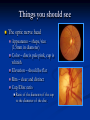
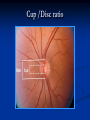
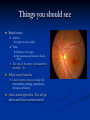
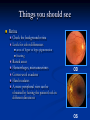
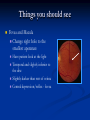
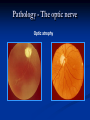
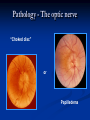
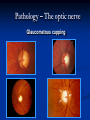
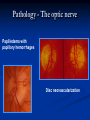
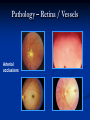
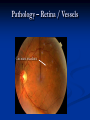
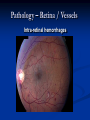
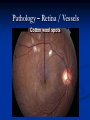
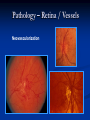
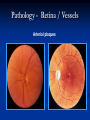
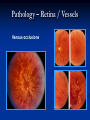
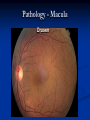
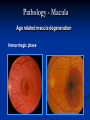
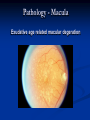
Direct Ophthalmoscopy “THE EYE IS A WINDOW TO SYSTEMIC DISEASE” Sandra Tubito, O.D. July 2007 Discussion Outline Why ophthalmoscopy? Types of ophthomoscopy Direct ophthalmoscope Examination Procedure Setting External Exam Internal Exam What you should see Pathology Questions Why ophthalmoscopy? Only way (and place in the body) that veins and arteries can be seen in their natural state, noninvasively. Part of general optical screening where direct observation of the structures of the fundus may show: Disease of the eye itself (e.g. glaucoma, retinal detachment) Abnormalities indicative of disease elsewhere in the body (e.g. diabetes, hypertension) Evaluation of ocular complaints Types of Ophthalmoscopes Direct ophthalmoscope Indirect ophthalmoscope Types of Ophthalmoscopes Direct X15 magnification 10° field of view Real image Monocular Undilated pupil Maximum resolution of 70µm Indirect X2-3 magnification 30° field of view Inverted and upside down image Binocular Dilated pupil Maximum resolution of 200µm Direct Ophthalmoscope Illuminating system Light bulb Lenses Reflector Aperture stops and filters Different sized stops to change illumination of the retina Green (red free) filter Viewing system Sight hole (3mm in diameter) Focusing lenses Direct Ophthalmoscope Examination Procedure Setting Dark room Seat patient in comfortable chair with head rest Ask patient to look at a slightly elevated target on opposite wall Examination Procedure External Exam Look at R eye with R eye (L with L) Place hand on shoulder or forehead Change viewing angle to 15° to avoid light reflex of cornea Examination Procedure External Exam Red Reflex - hold ophthalmoscope at ~50cm and look through sight hole at the ocular media. Find the red reflex in the pupil. Opacities (eg cataracts) can be seen. Place +8.00D lens in sight hole and move to ~10cm to inspect anterior structures: lids/lashes conjunctiva cornea Examination Procedure Internal Exam Turn focus wheel to bring anterior chamber and iris into focus Gradually reduce power in ophthalmoscope to focus on internal structures: Lens Vitreous Retina Examination Procedure Internal Exam Continue turning focus wheel to bring retina/vessels in focus Follow the vessels to the disc The ‘arrow’ point to the disc Examine the disc, vessels, retina, & macula. Things you should see The optic nerve head Appearance – shape/size (1.5mm in diameter) Color – disc is pale pink, cup is whitish Elevation – should be flat Rim – clear and distinct Cup/Disc ratio Ratio of the diameter of the cup to the diameter of the disc Cup /Disc ratio Things you should see Retinal vessels Arteries Veins Darker in color, larger May spontaneously pulsate at the disc (80%) The ratio of the artery :vein diameter is normally ~ 2:3 Follow vessels from disc Lighter in color, smaller Look at arterio-venous crossings for abnormalities (nicking, compression, elevation, deviation) Check arterial light reflex. This will get whiter and thicker in arteriosclerosis Arteriovenous changes Tapering concealment of the vein appearing as ‘nicking’ Deviation of the vein out of its path Elevation of the vein over the artery Compression of the vein at the arterio-venous crossing, causing stenosis of the distal vein Things you should see Retina Check the background retina Look for color differences areas of hyper or hypo pigmentation Scarring Raised areas Hemorrhages, microaneurisms Cotton wool exudates Hard exudates A more peripheral view can be obtained by having the patient look in different directions OD OS Things you should see Fovea and Macula Change sight hole to the smallest aperature Have patient look at the light Temporal and slightly inferior to the disc Slightly darker than rest of retina Central depression/reflex - fovea Pathology - The optic nerve Optic atrophy Pathology - The optic nerve “Choked disc” or Papilledema Pathology – The optic nerve Glaucomatous cupping Pathology - The optic nerve Papilledema with papillary hemorrhages Disc neovascularization Pathology – Retina / Vessels Arterial occlusions Pathology – Retina / Vessels Circinate exudates Pathology – Retina / Vessels Intra-retinal hemorrhages Pathology – Retina / Vessels Cotton wool spots Pathology – Retina / Vessels Neovascularization Pathology - Retina / Vessels Arterial plaques Pathology – Retina / Vessels Venous occlusions Pathology - Macula Drusen Pathology - Macula Age related macula degeneration Hemorrhagic phase Pathology - Macula Exudative age related macular degeration QUESTIONS?