* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3,1
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
History of statistics wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of statistics wikipedia , lookup
Infinite monkey theorem wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Inductive probability wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
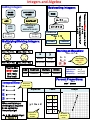
THE quick guide to MATH-7 TEST SUCCESS!! A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I,J,K,L,M,N,O,P,Q,R,S,T,U,V,W,X,Y,Z Fraction Decimal “Take the top #, divide by the bottom #!” Decimal to Percent (D to P): “to the right, to the right” 1 = 8I1 8 .125 = 12.5% Percent to Decimal (P to D): “to the left, to the left” (turn the fraction clockwise) 5% = .05 1) P arenthesis 2) E xponent 3) M ultiply OR D ivide 4) A dd OR S ubtract Perfect Squares: 12 = 1 112 = 121 22 = 4 122 = 144 32 = 9 132 = 169 42 = 16 142 = 196 52 = 25 152 = 225 62 = 36 162 = 256 72 = 49 172 = 289 82 = 64 182 = 324 92 = 81 192 = 361 10²= 100 20² = 400 Scientific Notation: 3.95 x 105 = 395,000 3.12 x 10-4 = .000312 You MATH! Negative exponents do NOT make the answer negative!! Exponents: 10 3 = 10 x 10 x 10 = 1,000 10 -3 = 1 1 1 x x 10 10 10 = 1 1000 = 0.001 Properties (MEMORIZE these!): Commutative (ORDER switches): a + b = b + a Associative (GROUPING): (a + b) + c = a + (b + c) Distributive: a (b + c) = a(b) + a(c) Identity of Addition: a + 0 = a Identity of Multiplication: a x 1 = a Multiplicative Property of Zero: a x 0 = 0 Inverse of Multiplication: (a/b) x (b/a) = 1 Inverse of Addition (zero pair) : -a + a = 0 Square Root Ex.: Absolute Value is ALWAYS positive!! It measures the 𝟐𝟓 = 5 distance from zero on a Both have the 𝟑𝟔 = 6 SAME absolute number line. value! 𝟒𝟗 = 7 I -3 I = 3 I 3 I=3 Integers and Algebra Subtracting Integers: Adding Integers: DIFFERENT SIGNS ADD KCC 4 - 7 = ___ SUBTRACT KEEP SIGN OF LARGER ABSOLUTE VALUE!! KEEP SIGN!! 3+4=7 -3 + -4 = -7 4 + -7 = -3 coefficient -3 + 4 = 1 3 + -4 = -1 3x + 5 Multiplying/Dividing Integers: Neg. x Neg. = Pos. + Pos. x Neg. = Neg. x y Domain Range Independent Dependent - + Neg. x Pos. = Neg. You’re the BEST and will rock the test! Inequalities: > < ≥ ≤ constant Solving an Equation: 2x + 4 = -6 A. 1 If you forget B. -1 steps, PLUG IT IN!! C. -5 Add Subtract Multiply Divide Sum Difference Product Quotient Does the bird get the worm? When multiplying or dividing by a negative #, we switch the inequality sign! -3x > 15 – Switch Sign! Expression– x + 5 Equation– x+5=8 Inequality– x + 5 < 8 Percent Proportions: % 𝒑𝒂𝒓𝒕 = 𝟏𝟎𝟎 Equation > becomes < variable - - + + Pos. x Pos. = Pos. “Seven less than a number is five” x–7=5 “Seven less a number is five” 7–x=5 SAME SIGNS y = 3x + 2 Plug in the “x” values from the table! Table x y -1 -1 0 2 1 5 2 8 𝒘𝒉𝒐𝒍𝒆 Graph All ordered pairs must fit on line! Measurement and Geometry Transformations: Translate – Slide Rotation – Turn Reflection– Flip Dilation– Re-size Coordinate Plane: Volume: Fill Hold Cubic Units3 Plot point-- over left or right (x), then up or down (y). II Rotations: (-3,1) Here is a clockwise rotation about the origin (the x and y switch places with each turn): Original: (-3,1)– Q II 90˚: (1, 3)– Q I 180˚: (3,-1)– Q IV 270˚: (-1,-3)– Q III 360˚: (-3,1)– Q II I Changing an Attribute: If ONE attribute (l, w, h) of a prism is changed (doubled, tripled, halved), then the VOLUME will also change by the same amount! C III IV If we triple the length, the volume will also triple, etc.! Surface Area: RIGHT or LEFT changes X ! UP or DOWN changes Y ! Cover Wrap Square Units2 Quadrilaterals: Parallelogram Trapezoid Opposite sides parallel (2 pairs) One pair of parallel sides Opposite sides congruent Rhombus Rectangle Opposite sides parallel Opposite sides parallel 4 equal sides Must have 4 right angles 4 equal sides 4 right angles SAME shape, DIFFERENT size, CONGRUENT angles, PROPORTIONAL sides! 𝒙 𝟏𝟎.𝟓 = 𝟏𝟏.𝟐𝟓 𝟏𝟕.𝟓 Height on top and shadow on bottom!! Square: ALWAYS UP, SOMETIMES DOWN, NEVER SIDE-TO-SIDE!! Similar Figures: A square is ALWAYS a rectangle, rhombus, & parallelogram! Probability Theoretical Probability: what “should” happen Experimental Probability: what “actually” happens Probability: 𝒇𝒂𝒗𝒐𝒓𝒂𝒃𝒍𝒆 𝒐𝒖𝒕𝒄𝒐𝒎𝒆𝒔 𝒕𝒐𝒕𝒂𝒍 𝒐𝒖𝒕𝒄𝒐𝒎𝒆𝒔 P(roll a 5) = As the # of trials increase, the experimental probability will come closer and closer to the theoretical probability!! 𝟏 𝟔 Tree Diagram: Fundamental Counting Principle: 1) 3 shirts, 2 belts, 3 shorts: 3 x 2 x 3 = 18 possible outfits 2 cone choices x 4 flavors = 8 possible outcomes Independent Events Dependent Events with without replacement replacement Finding the probability of picking a king, putting it back, and picking a king again . . . Finding the probability of picking a king, keeping it, and picking a king again . . . 4 52 x 4 52 4 52 x 2) Roll one die and flip one coin: 6 x 2 = 12 possible outcomes REMEMBER: With replacement– put it back!! Without replacement– keep it !! 3 51 Number/ Letter Codes . . . A code consists of three numbers. The choices for each number range from 0 – 9. How many unique codes? 10 x 10 x 10 = 1,000 Ms. Dyson knows that the odds will be ever in your favor on the SOL test!!