* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide for Nervous System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
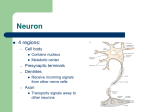
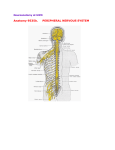
Nervous System Study Guide Ch 11 up to synapse- The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous system II. Organizational levels and functions of each(chart page 389) a. CNS- Brain and Spinal Cord i. Brain: voluntary movement, interpretation, sensory integration, consciousness, cognition ii. Spinal cord: conduction of afferent and efferent nerves, reflex center b. PNS- 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 32 pairs of spinal nerves, ganglia provides communication lines between CNS and body’s muscles, glands and sensory receptors i. Sensory ii. Motor 1. Somatic 2. Autonomic a. Sympathetic and parasympathetic III. Histology a. Neuroglia and glia cells- 6 types- know functions and PNS vs CNS i. Astrocytes, microglia, ependymal, oligodendrocites, Schwann cells, and satellite cells b. Neurons i. Cell body, dendrite and axon- function and structure of each ii. Cell body- ganglia and nuclei 1. nissl body iii. Dendrits and axons- tracts and nerves iv. Axon 1. axon collaterals 2. axon hillock 3. terminal branches (telodendria) and synaptic knobs v. general characteristics- extreme longevity, amitotic, high metabolic rate, irritability, conductivity c. myelination i. nodes of Ranvier ii. gray matter vs white matter d. Classification of neurons- structural and functions IV. Neurophysiology a. Voltage and potential energy b. Current and resistance c. Role of Ion Channels i. Leaky, voltage gated, chemical (ligand) gated d. Resting potential characteristics (voltage and permeability to Na+, K+ and Cl-) e. Depolarization V. i. Na+ rushes in to dendrite or cell body local depolarization, if threshold stimulus is applied, starts a positive feedback loop (change of charge causes voltage gated Na+ channels nearby to open) f. Repolarization i. Happening to section of neuron behind the depolarization, slower K+ gates remain open as Na+ close, ends the positive feedback loop, brings back towards resting potential 1. Absolute refractory period g. Hyperpolarization i. K+ gates remain open, cell overshoots the resting potential 1. Refractory period ii. ATP pumps must be used to return to original resting potential h. Graded potentials i. Action potentials i. Subthreshold vs Threshold ii. Axon hillock iii. All or none iv. propagation j. absolute refractory period vs refractory period k. stimulus intensity l. conduction velocity i. continuous vs salutatory conduction ii. diameter of axon m. MS Synapse- know what it is and how it is crossed (basics, covered during muscle phys) a. Pre and post synaptic neurons b. Synaptic knob i. Electricity causes Ca2+ gates to open, Ca2+ enters causing vacuoles containing neurotransmitters to exocytose c. Neurotransmitters i. Excitatory or inhibitory Helpful websites: Resting Potential Action Potential Action Potential 2 Action Potential 3 Channel gating during an action potential Action Potential arriving at the synapthic knob Animated Neurotransmission Guided notes for Ch 12 Helpful websites: Human Brain Anatomy & Functions Online Brain dissection Ch 13 guided notes **coming soon! Helpful websites: Cranial Nerves Tutorial Cranial nerve testing