* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rheumatic heart disease
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Pericardial heart valves wikipedia , lookup
Infective endocarditis wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
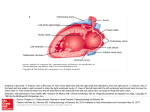
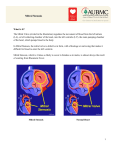
Rheumatic heart disease Mitral stenosis Valvular heart disease • Rheumatic • Age related • congenital Mitral valve • Stenosis • Regurgitation • Prolapse Mitral stenosis • • • • 2/3 females Usually rheumatic Rarely congenital 40% of all RHD Structural defects • Diffusely thickened –fibrous tissue /calcified deposits • Mitral commisures fuse • Corde tendinae fuse /shorten • Narrowing of the apex of funnel shaped valves • Calcification of slender valves immobilises the leaflet and narrows the orifice –thrombus formation –arterial thrombus from calcified Valves Pathophysiology • Normal mv –dia -4-6 cm2 • <2 cm 2-atrial to ventricular flow is maintained by increased av pressure gradient –the hallmark of ms • <1 cm2 –LAP should be atleast 25mm hg is required to maintain normal output . • Increased Lap --------increased pulm pressure -----increased capillary pressure -----decreased pulm compliance -------exertional dyspnoea. • Increased heart rate –decreased transvalvular gradient ----increased LAP • Lv diastolic pressure in normal in ms • Co is normal at rest ---at exercise –decreased co. $ • • • • • Clinical /hemodynamic Features –influenced by Passive backward transmission of LAP Pulmonary arteriolar constriction Intertitial edema Organic obliterative changes in the pul vascular bed • Phtn----Tr------rt sided failures---bornheimeffect symptoms • Carditis---ms-----2 decades, • Dyspnoea on exertion ----4 th decade— progressive worsening to death---2-5 yrs • Doe ,orthopnoea ,pnd,arrthmia-premature atraial complex,paroxysysmal tachycardia,flutter,fibrilation • Haemoptysis –increased pulm venous pressure • • • • • Recurrant pulm embolism Pulm infection Endocarditis Chest pain -10% Thrombus formation in the left atrium-af— appendages of LA • Pedunculated thrombus –ball valve thrombi • -syncope-angina –changing ascultatory signs On examination • Malar flush-pinched blue facies • JVP-a wave prominence –af –a wave absent • Palpation-tapping apical impulse ,s1 loud,palpable ,s2 p2 loud • Diastolic thrill • Auscultation-s1 accentuated /snapping – delayed –mv doesn’t close till LVP>LAP • Qs prolongation ,p2 loud • • • • • • A2-p2-os -0.05-0.12 P2-os –severity of ms Intensity of s1/os –pliability of leAFLET MDM after os Duration correlates with ms severity S1-closure of mitral /tricuspid valve • • • • • Intensity of s1 Pos of mv at onset of vent systole Rate of increase in LAP Degree of structural damage of the valve Amt of tissue bet heart and sthetoscope • S1 loud –diastole is shortened by tachycardia • S1 split -10-30 msec • S1 –m1t1-----prolonged in rbbb • t1m1 –severe ms ,left atrial myoma lbbb Mitrl regurgitation etiology • Chronic rhd –severe mr- 1/3 • Seen in males mostly • Rheumatic processrigidity,deformity,retraction of the valve cuspscommisural fusion • Congenital-endocardial cushion defects • Fibrosis of papillary muscles in MI • Ischeamia –paplillary dysfn • • • • Lv dilated in DCM HOCM-ant displace ment of the ant leaflet Mitral prolapse –MR Acute MR-inf endocarditis pathophysiology • Clinical pic depends on p-v relation ship of LA AND PUL -VENOUS BED • Increased LAP-Increased pulm edema • Effective forward pressure of lv decreases • Inc-LA volume –due to atrial compliance • Low cardiac out put • Atrial fibrillation SYMPTOMS • • • • • • • FATIGUE Doe Orthopnea Pnd Haemoptysis Sys embolism Rh f-jvp inc,tr,phtn,hep congestion Physical examination • • • • • Sys thrill-left apex Hyperdynmic apical impulse Laterally displaced Palpable p2 Parasternal heave auscultation • S1-absent/softor buried in systolic murmur • Decreased co-aorta closes early-a2 early-wide spliting of s2 • Os –indicates ms • Gallop rhythm • Pansystolic murmur lab • Ecg –sinus rhythm ,prominent p waves ,af lvh • Echo • Cxr-kerley b lines management • • • • • • • Medical Dec exertion Dec NA intake Diuretics Digitalis/vasodilators-inc co Ace inhibitors /hydralazine Surgical-valve replacement