* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
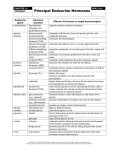
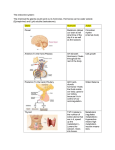
HORMONES AND THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Chapter 45 The glands of the endocrine system secrete hormones that send a stimulus to another cell. The response that is elicited by the target cell helps bring the organism back to homeostasis I. Overview of endocrine control Primarily occurs by negative feedback control General mechanism of action: Stimulus (out of homeostasis) acts on Endocrine gland Negative Feedback to A response is elicited Secretes hormone Acts on target tissue Purpose: to maintain homeostasis ENDOCRINE GLANDS AND THEIR HORMONES ENDOCRINE HORMONE TARGET TISSUE GLAND POSTERIOR Antidiuretic kidney PITUITARY hormone (ADH) oxytocin Uterus and mammaries ANTERIOR PITUITARY Growth hormone (GH) Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) Leutinizing hormone (LH) Many organs Stimulates water reabsorption Stimulates contraction and milk release Growth thyroid Stimulates release of thyroxine Ovaries and testes Stimulates ovulation and testosterone secretion Stimulates egg maturation and production od sperm Stimulates milk production Increases metabolism Lowers blood calcium by decreasing calcium loss by bone Raises blood calcium levels by stimulating bone breakdown and calcium reabsorption Lowers blood sugar by stimulating conversion of glucose to glycogen Raises blood sugar Follicle stimulating Ovaries and testes hormone (FSH) prolactin mammaries thyroxine Many cells calcitonin bone PARATHYROID Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Bone, kidneys, digestive tract PANCREAS insulin Liver fat cells, skeletal muscle glucagon Liver, fat cells THYROID RESPONSE TESTES testosterone Testes and other male parts and other body parts OVARIES estradiol Many body parts progesterone uterus by stimulating breakdown of glycogen to glucose Stimulates secondary sex characteristics and spermatogenesis Stimulates secondary sex characteristics Prepares for pregnancy http://health.howstuffworks.com/human-body/systems/endocrine/adam200091.htm II. Endocrine control mechanisms A. Blood calcium levels Low Blood Calcium →stimulates parathyroid →to secrete PTH (parathyroid hormone) → which stimulates calcium release from bones, increases calcium uptake by intestines, increases calcium reabsorption by kidneys → which increases blood calcium → which negatively feeds back on parathyroid High Blood calcium →stimulates thyroid →to secrete calcitonin →which increases calcium deposition in bone, decreases calcium uptake by kidneys and intestines → which lowers blood calcium → which negatively feeds back on thyroid http://www.mhhe.com/cgibin/netquiz_get.pl?qfooter=/usr/web/home/mhhe/biosci/genbio/animation_quizz es/animate_79fq.htm&afooter=/usr/web/home/mhhe/biosci/genbio/animation_q uizzes/animate_79fa.htm&test=/usr/web/home/mhhe/biosci/genbio/animation_q uizzes/animate_79q.txt&answers=/usr/web/home/mhhe/biosci/genbio/animation _quizzes/animate_79a.txt C. Blood sugar Before a Meal: Low blood glucose →stimulates pancreas → to secrete glucagon → which increases breakdown of glycogen to glucose → which increases blood glucose → which negatively feeds back on pancreas After a Meal: High blood glucose → stimulates pancreas → to secrete insulin → which stimulates conversion of glucose to glycogen → which lowers blood sugar → which negatively feeds back on pancreas http://health.howstuffworks.com/human-body/systems/endocrine/adam200092.htm