* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
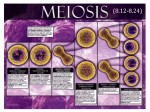
Download A picture of the chromosomes from one cell. Cells with homologous
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
A picture of the chromosomes from one cell. Cells with homologous chromosome pairs 2 N (indicating the cell has two sets of chromosomes; one from each parent) Term describing sperm or egg cells The diploid body cells of an organism Two identical copies of DNA attached at the centromere. (Draw it.) A pair of chromosomes in a diploid cell that carry the same complement of genes but are NOT identical due to different alleles. (Draw it.) Alternative forms of a gene resulting in different versions of a particular trait (Ex: dimples and no dimples) Cells with only one member of each homologous chromosome pair Designated N (one set of chromosomes) The twenty two pairs of homologous chromosomes in males and females that are not involved in gender determination. Specialized form of cell division that produces four haploid cells from a diploid parent cell by separating homologous chromosomes. Homologous chromosomes pair and exchange pieces of DNA mixing maternal and paternal alleles. (Draw it.) Each half of a duplicated chromosome. Identical unless crossing over has occurred. Structure formed when duplicated homologous chromosomes pair up. Phase of Meiosis when homologous chromosomes (tetrads) align in the middle of the cell. Phase of meiosis when sister chromatids split and are pulled to opposite poles. Phase of meiosis when homologous chromosomes (tetrad) split and are pulled to opposite poles. Phase of meiosis when Phase of meiosis when homologous two haploid daughter chromosomes pair up and nuclei form. crossing over occurs. Phase of meiosis when duplicated chromosomes align in the middle of the cell. Phase of meiosis when four haploid daughter nuclei form. Round of meiosis that separates homologous chromosomes creating 2 haploid daughter cells. Round of meiosis that separates sister chromatids into four haploid daughter nuclei. Random alignment of homologues resulting in daughter cells with a mixture of maternal and paternal chromosomes. Form of reproduction in which haploid cells of two parents unite to form the first cell of a new organism. A fertilized egg The male gamete The Female gamete Form of reproduction where cell divides by mitosis to produce a clone of itself. A fertilized egg in its early Diploid cells from which stages of development. sperm cells arise. Capable of mitosis to regenerate population. Process by which sperm cells are formed. Whip-like tail that propels Sac of enzymes at the sperm cells head of the sperm that will eat through the protective layers around the egg for fertilization. The union of sperm and egg Location of spermatogenesis Name of cell produced from meiosis II during spermatogenesis. (Haploid.) Name of cell produced by Name of parent cell that Location of oogenesis meiosis I during undergoes meiosis during spermatogenesis spermatogenesis (diploid) (haploid) Name of cell produced by Name of parent cell that Name of cell produced meiosis I during undergoes meiosis during from meiosis II during oogenesis (haploid) oogenesis (diploid) oogenesis. (Haploid.) Discarded set of chromosomes during oogenesis The 23rd pair of chromosomes that determines gender The diploid cells from which eggs will arise.