* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Candy Dish Selection: Author
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation–evolution controversy wikipedia , lookup
Mormon views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
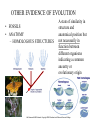
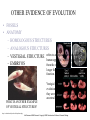
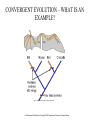
Summer 2006 Workshop in Biology and Multimedia for High School Teachers THEORY OF EVOLUTION Beth Mick - LESSON PLAN • DISCUSSION ON WHAT DOES THE WORD EVOLUTION MEAN? • LECTURE - PPT • SPECIATION ANIMATION - 2006 LS-HHMI • Breeding Bunnies Activity www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/educators/lessons/lesson4/act1notes.html • Candy Dish Selection: Author: Carol Tang http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/education/lessons/candy_dish.html Investigating Natural Selection Activity - • http://bob.nap.edu/html/evolution98/evol6-c.htm • CLASS DISCUSSION ON VIRUS EVOLUTION TO INCLUDE HIV Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. REFERENCES • Biology: The Dynamics of Life; Glencoe 2004 • • • • • • http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php http://www.hhmi.org/biointeractive/evolution/index.html http://www.accessexcellence.org/AE/AEPC/WWC/1995/ http://www.darwinday.org/englishL/life/beagle.html http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/evolution/index.html DR. LUE, LIFE SCIENCE-HHMI OUTREACH PPT. Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. CHAP 15 – THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION • • • • • CHARLES DARWIN EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION MECHANISMS FOR EVOLUTION NATURAL SELECTION SPECIATION http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. CHAP 15 – THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION • • • • • CHARLES DARWIN EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION MECHANISMS FOR EVOLUTION NATURAL SELECTION SPECIATION Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php CHARLES DARWIN – 1809-1882 • ENGLISH • TRAVELED AROUND THE WORLD ON THE BEAGLE – FAMOUS IN THE GALAPAGOS ISLANDS • OBSERVED MANY SPECIES AND FOSSILS • WHY DID SOME SPECIES SURVIVE WHILE OTHERS BECAME EXTINCT? • NATURAL SELECTION Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php www.darwinday.org/englishL/life/beagle.html www.darwinday.org/englishL/life/beagle.ht Used by permission of Darwin Day Celebration (at DarwinDay.org), 2006 I have called this principle, by which each slight variation, if useful, is preserved, by the term Natural Selection. —Charles Darwin from "The Origin of Species" http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. CHAP 15 – THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION • • • • • CHARLES DARWIN EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION MECHANISMS FOR EVOLUTION NATURAL SELECTION SPECIATION http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION • STRUCTURAL ADAPTATIONS resemblance of one organism to – MIMICRY another or to natural objects – CAMOUFLAGE among which it lives that secures it a selective advantage (as protection from predation) Protective coloring or another feature that conceals an animal and enables it to blend into its surroundings. http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php http://science.howstuffworks.com/animal-camouflage2.htm Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION • STRUCTURAL ADAPTATIONS – MIMICRY – CAMOUFLAGE – MILLIONS OF YEARS • PHYSIOLOGICAL ADAPTATIONS – CHANGE IN A METABOLIC PROCESS – WHAT DO YOU HEAR ABOUT IN THE NEWS ABOUT SOME BACTERIA? Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php WHAT OTHER INDUSTRIES WOULD BE WORRIED ABOUT RESISTANCE? Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. OTHER EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION • FOSSILS • ANATOMY – HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES A state of similarity in structure and anatomical position but not necessarily in function between different organisms indicating a common ancestry or evolutionary origin http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. OTHER EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION • FOSSILS • ANATOMY – HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES – ANALOGOUS STRUCTURES -it performs the same function http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. OTHER EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION • FOSSILS • ANATOMY – HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES – ANALOGOUS STRUCTURES – VESTIGIAL STRUCTURE refers to an organ or part (for example, the human appendix) which is greatly reduced – EMBRYOS from the original ancestral form and is no longer functional or is of reduced or altered function. WHAT IS ANOTHER EXAMPLE OF VESTIGIAL STRUCTURES? http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Vestigial structures provide a clue to the evolutionary history of a species because they are remnants of structures found in the ancestral species. Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. OTHER EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTION • FOSSILS • ANATOMY – HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES – ANALOGOUS STRUCTURES – VESTIGIAL STRUCTURE – EMBRYOS • BIOCHEMISTRY – WHAT 2 THINGS? http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. CHAP 15 – THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION • • • • • CHARLES DARWIN EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION MECHANISMS FOR EVOLUTION NATURAL SELECTION SPECIATION http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. MECHANISMS FOR EVOLUTION • DO POPULATIONS OR INDIVIDUALS EVOLVE? • WHAT IS A GENE POOL the total number of genes of every individual in an interbreeding population. • HOW CAN THE GENE POOL CHANGE? – MUTATION – GENETIC DRIFT – GENE FLOW • WOULD THESE THINGS EFFECT A LARGE POPULATION OR A SMALL POPULATION MORE? Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. ALL IMAGES: http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. Gene Pool •Large •high genetic diversity •increased chances of biological fitness, and survival. •Small •low genetic diversity •reduced chances of acquiring biological fitness, and increased possibility of extinction •Increases when mutation occurs and survives •Decreases when the population size is significantly reduced •e.g. famine, genetic disease, etc. •Consequences when gene pool is small •low fertility •increased probability of acquiring genetic diseases and deformities •Gives an idea of the number of genes, the variety of genes and the type of genes existing in a population. It can be used to help determine gene frequencies or the ratio between different types of genes in a population. CHAP 15 – THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION • • • • • CHARLES DARWIN EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION MECHANISMS FOR EVOLUTION NATURAL SELECTION SPECIATION http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. WHAT IS NATURAL SELECTION? There is variation in traits. For example, some beetles are green and some are brown. There is differential reproduction. Since the environment can't support unlimited population growth, not all individuals get to reproduce to their full potential. In this example, green beetles tend to get eaten by birds and survive to reproduce less often than brown beetles do. There is heredity. The surviving brown beetles have brown baby beetles because this trait has a genetic basis. End result: The more advantageous trait, brown coloration, which allows the beetle to have more offspring, becomes more common in the population. If this process continues, eventually, all individuals in the population will be brown. http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. CHAP 15 – THE THEORY OF EVOLUTION • • • • • CHARLES DARWIN EVIDENCE FOR EVOLUTION MECHANISMS FOR EVOLUTION NATURAL SELECTION SPECIATION http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. WHAT IS SPECIATION? • GEOGRAPHIC ISOLATION • REPRODUCTIVE ISOLATION http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. WHAT IS SPECIATION? • • • • GEOGRAPHIC ISOLATION REPRODUCTIVE ISOLATION GRADUALISM PUNCTUATED EQUILIBRIUM The view that speciation proceeds by imperceptibly small, cumulative steps over long periods of time rather than by abrupt, major changes. The theory that speciation occurs in spurts of major genetic alterations that punctuate long periods of little change. Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. WHAT IS SPECIATION? • • • • • GEOGRAPHIC ISOLATION REPRODUCTIVE ISOLATION GRADUALISM PUNCTUATED EQUILIBRIUM DIVERGENT EVOLUTION – ADAPTIVE RADIATION • CONVERGENT EVOLUTION Organisms NOT closely related, independently evolve similar traits as a result of having to adapt to similar environments or ecological niches. Evolution of a number of divergent species from a common ancestor, each species becoming adapted to occupy a different environment. Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. ADAPTIVE RADIATION – AN EXAMPLE OF DIVERGENT EVOLUTION http://www.vanderbilt.edu/AnS/english/Clayton/Galapago_finches.gif http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College. CONVERGENT EVOLUTION – WHAT IS AN EXAMPLE? http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/home.php Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2006 President and Fellows of Harvard College.