* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacteria v Virus
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Horizontal gene transfer wikipedia , lookup
Trimeric autotransporter adhesin wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Plant virus wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Virus quantification wikipedia , lookup
Disinfectant wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to viruses wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Human microbiota wikipedia , lookup
History of virology wikipedia , lookup
Marine microorganism wikipedia , lookup
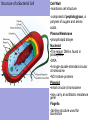
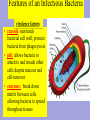
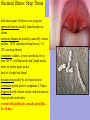
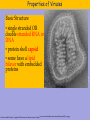
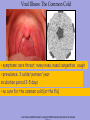
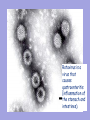
Bacteria v Virus Structure of a Bacterial Cell http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Average_prokaryote_cell-_en.svg Cell Wall -maintains cell structure -composed of peptidoglycan, a polymer of sugars and amino acids Plasma Membrane •phospholipid bilayer Nucleoid •The region DNA is found in prokaryotes •DNA •A single double-stranded circular chromosome •NO histone proteins Plasmid •small circular chromosome •may carry an antibiotic resistance gene Flagella -tail-like structure used for locomotion Features of an Infectious Bacteria • capsule: surrounds bacterial cell wall; protects bacteria from phagocytosis • pili: allows bacteria to attach to and invade other cells despite mucous and cell-turnover • enzymes: break down matrix between cells allowing bacteria to spread throughout tissues Bacteria create Toxins exotoxins: cause lysis (breakage) of specific host cells enterotoxins: cause secretion of fluid into the small intestine leading to vomiting and diarrhea http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Average_prokaryote_cell-_en.svg endotoxins: cell-bound lipopolysaccharides; causes fever and inflammation Fast Reproduction • Bacterial Transcription and Translation is quicker then eukaryotes • Reproduction occurs independent of host cell Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2008 President and Fellows of Harvard Bacterial Illness: Strep Throat Infectious agent: Streptococcus pyogenes spherical bacteria usually found in pairs or chains most sore throats are actually caused by viruses and are NOT considered strep throat (~1535% are strep throat) symptoms: sudden, severe sore throat, fever over 101°F, swollen tonsils and lymph nodes, white or yellow spots on the back of a bright red throat transmission usually by air-born bacteria incubation period prior to symptoms 2-5 days diagnosed with a throat culture and detection of strep-specific molecules treated with antibiotics, usually penicillin for 10 days Antibiotic Treatment of Bacterial Infections • antibiotics kill bacteria or prevent bacteria from dividing • antibiotics are produced naturally by bacteria and fungi • antibiotics are mass produced by growing huge cultures of the source microbe Why might microbes produce antibiotics in nature? Staphyloccocus aureus antibiotic http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Staphylococcus_aureus_%28AB_Test%29.jpg Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2008 President and Fellows of Harvard College. Antibiotics: Mechanisms of Action Inhibition of Bacterial Protein Synthesis - some antibiotics bind to the large or small subunit of the bacterial ribosome Examples: neomycin, streptomycin, azithromycin, erythromycin, tetracycline http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Average_prokaryote_cell-_en.svg ife Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2008 President and Fellows of Harvard College. Antibiotics: Mechanisms of Action Inhibition of Cell Wall Synthesis -some antibiotics prevent peptidoglycan formation Examples: vancomycin, amoxicillin, ampicillin, penicillin e Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2008 President and Fellows of Harvard College. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Average_prokaryote_cell-_en.svg Animation of Antimicrobial Resistance Properties of Viruses Basic Structure • single stranded OR double stranded RNA or DNA • protein shell capsid • some have a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2008 President and Fellows of Harvard College. Host Cell Influenza http://microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Image:8430_lores.jpg Properties of Viruses Virus Life Cycle and reproduction virus attaches to host cell • virus enters cell via endocytosis • capsid degraded • host transcribes viral DNA • host ribosomes translate viral RNA • new viruses assemble Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2008 President and Fellows of Harvard Host Cell Viral Illness: The Common Cold http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image:Rhinovirus.PNG • symptoms: sore throat, runny nose, nasal congestion, cough • prevalance: 3 colds/ person/ year incubation period 2-5 days • no cure for the common cold (or the flu) Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2008 President and Fellows of Harvard Rotavirus is a virus that causes gastroenteritis (inflammation of the stomach and intestines). Bacterial vs. Viral Infections Watch Video Why don’t antibiotics work for viral infections? MicrobeLibrary.org; © Jean-Yves Sgro, University of Wisconsin Streptococcus http://www.microbelibrary.org/microbelibrary/files/ccImages/Articleimages/simonson/Images/Streptococcus%20sobrinus%20fig1.jpg Polio Virus Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2008 President and Fellows of Harvard College. Bacterial Infections Viral Infections • strep throat • the flu • gastroenteritis • colds • cholera • AIDS • tuberculosis • hepatitis • food poisoning • chicken pox • botulism • gastroenteritis • gangrene • measles • necrotizing fasciitis • mumps • boils, abscesses • E. Bola • pneumonia • pneumonia • acne • West Nile • meningitis • cervical cancer • ulcers Life Sciences-HHMI Outreach. Copyright 2008 President and Fellows of Harvard College.