* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name Date Class LESSON 2 Landforms at Plate Boundaries
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
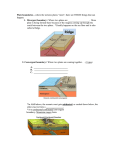
Name Date Class Content Vocabulary LESSON 2 Landforms at Plate Boundaries Directions: Each of the sentences below is false. Make the sentence true by replacing the underlined words with a term from the list below. Write your changes on the lines provided. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. fault zone ocean trench transform fault volcanic arc 1. Volcanic arcs form perpendicular to mid-ocean ridges as tectonic plates slide horizontally past each other. 2. The San Andreas Fault system in California is a(n) transform fault that includes an extensive series of visible and underground faults. 3. A curved line of islands, or fault zone, may form where two plates converge. 4. The deepest places in the ocean are found at transform faults. 30 Earth Dynamics Name Date Class Content Practice B LESSON 2 Landforms at Plate Boundaries Directions: Use the map to find the locations listed on the chart. Then complete the chart with the correct type of boundary in the space provided. convergent A convergent boundary occurs where two plates are pushing toward each other. divergent A divergent boundary marks two plates that are moving apart from each other. transform A transform boundary occurs where two plates slide past each other. Location Type of Boundary 1. the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between the North American and Eurasian Plates in the North Atlantic; between the South American and African Plates in the South Atlantic 2. the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate in California 3. the boundary between the Pacific and Antarctic Plates 4. the boundary between the Nazca Plate and the South American Plate along the west coast of South America 5. the boundary between the Eurasian Plate and the Indian Plate at the Himalayas 6. the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the Australian Plate crossing New Zealand Earth Dynamics 3 Name Date Key Concept Builder Class LESSON 2 Landforms at Plate Boundaries Key Concept What features form where two plates converge? Directions: In each part of the circle, write the number of the statement that best describes each landform. Some numbers may be used more than once. 1. Islands formed where plates converge and one plate subducts under another. 2. A deep, underwater trough is formed when one plate is forced under another. 3. The plates move horizontally, but the crust also can move vertically. 4. These emerge as islands about 100 km away from the plate boundary. 5. These form slowly and in stages over millions of years. 6. These are the deepest places in Earth’s oceans. 7. One of these contains most of the active volcanoes in the United States. 8. These can be produced by a collision between two continental plates. Ocean Trenches Mountain Ranges Earth Dynamics Volcanic Arcs 37 Name Date Class Key Concept Builder LESSON 2 Landforms at Plate Boundaries Key Concept What features form where two plates diverge? Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly completes each sentence. Each term is used only once. boundaries mantle continent seafloor divergent tension downward valleys Mid-Ocean Ridges 1. Mid-ocean ridges are created by stresses as plates diverge. 2. At divergent plate from each other. the plates move away 3. As tension stresses cause oceanic crust to spread apart, hot rock from the rises. 4. Rising hot rock is less dense than cold rock, so the hot rock pushes the upward. Continental Rifts 5. Continental rift continents at divergent boundaries. 6. are created within boundaries occurring within a continent split Earth’s crust. 7. Faults in the cold upper crust cause large blocks of crust to move . 8. An active continental rift may eventually split a into two parts. Name Date Challenge LESSON 2 Mountains at the Edges Many of Earth’s largest mountains have formed at the boundaries of colliding plates. Map Mountain Ranges 1. Research the locations, highest points, and type of formation (folded, fault-block, uplifted, or volcanic) of the mountain ranges formed at the plate boundaries listed below: Location Alps Andes Applachian Atlas Himalayas Urals Zagros Class Highest Type of formation Point