* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download doc file
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
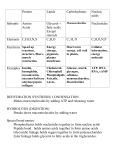
Cedar nut oil description Cedar nut oil is extracted from the shelled cedar nut kernel by means of cold press, which makes it possible to preserve beneficial properties of all its compounds. Unrefined cedar nut oil has a light yellow color with a greenish tone, a delicate scent of nut and highly nutritional properties, and being a food delicacy, it can successfully compete with the best edible oils: olive oil, almond oil, peanut oil. Fatty acid composition of cedar nut oil is rich in mono- and polyunsaturated fatty acids (Table 1). Table 1. Fatty acid content of the following most popular oils (in % from the total mass): Monounsaturated Polyunsaturated FA Saturated Fatty FA Acids Oleic acid Linoleic acid Linolenoic (FA) (class 6) (class 3) (class 9) Oil type Cedar oil nut 10 25 44 21 Linseed oil 8-10 14 25-50 21-45 Soybean oil 7,2-15,1 32,5-35,6 51,7-57 2-3 Olive oil 70-87 4-12 - Sunflower9 seed oil 33,3 39,8 - Corn oil 11,9 (maize) 44,8-45,4 41-48 - Hempseed 4,5 oil 14 65 16 Grape-seed 12 oil 18 70 - Gingili oil 40 43 - 9,1-14,2 14 acid In the previous section told you about the necessity to keep a balance between different classes of fatty acids. The best proportion between omega-6 and omega-3 has not been defined yet. This problem is actively discussed in scientific literature. In a typical diet of a modern human being the proportion of omega-6/omega-3 is within a range of 10:1 25:1. World Health Organization recommends following the proportion from 4:1 to 10:1. Along with this, people should try to increase the part of omega-3 fatty acids, as excess of omega-6 fatty acids has worse effects for health. Investigations of nutrition nature in the Paleolithic epoch and nutrition features of modern hunters and gatherers makes it possible to assume that the proportion of omega-6 and omega-3 has been more balanced in the diet of our ancestors; it has been around 1:1. Development of new technologies in crop science and cattle breeding has led to changing of some types of fats by the other ones. Many cultivated plants have significantly less amount of omega-3 fatty acids in comparison with wild plants. In the same way, meat of domestic animals, fed with fodders from cultivated plants has also less omega-3 fatty acids in comparison with meat of wild animals. The proportion of omega-6/omega-3 fatty acids in cedar nut oil is approximately 2:1. Cedar nut oil is rich in oleic acid, which is necessary for normal metabolism of cholesterol. Having polyunsaturated fatty acids in nutrition requires increasing of the amount of tocopherols, which are natural antioxidants, protecting fatty acids from free radical oxidation. It has been found out that for 1 gram of polyunsaturated fatty acids there should be 0,6 mg of tocopherols, to be more exact, their active forms - alpha and gamma tocopherols. Cedar nut oil has this balance as well: the proportion of alphatocopherol is 55 mg%. The kernel of the cedar nut has a high amount of phospholipids - 6,9% (cedar nut oil has 1,3%). That is more than in all nut and oil plants. The most popular phospholipids are phosphatidylcholines (the old name - lecithins), which contain glycerin, unsaturated fatty acids and a vitamin-like agent choline, fixed with phosphoric acid. Phosphatidylcholine is a replaceable agent. It can be synthesized in the organism, when there are all required elements, including amino acid methionine. Phosphatidylcholine is very important in nutrition; it contributes to digestion, absorption and good fat metabolism, it intensifies biliation, normalizes cholesterol metabolism, reduces fat accumulation in the liver. Cedar nut oil also contains phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylinositol, phosphatodic acid. One should pay attention to the fact that cedar nut oil contains cerebrosides, sulfolipids, glycolipids, which are nonspecific for plants. Unrefined plant oils always contain associated agents, which are extracted together with fats, dissolved in them and influence their physical-chemical, organoleptic and, the most important, pharmacological properties. These agents build so called an unsaponifiable residue of fat. In cedar nut oil associated agents are represented by pigments, phytosterols, triterpene hydrocarbons and fat-soluble vitamins Pigments condition the color of natural fates, they are mainly represented by chlorophylls and carotenes. Chlorophylls, contained in the oil, works like a healing agent. Chlorophyll has a toning effect, intensifies general metabolism, stimulates regeneration of tissues, and has bactericidal properties. Chlorophyll is a green pigment of plants, in chemical sense; it is a relative to hemoglobin of human red cells. Possibly it explains the fact that chlorophyll, received from food, influences the blood system - it facilitates white cells, red cells and hemoglobin increase. Sterols and their ethers are the main part of the unsaponifiable residue of fat. We distinguish sterols of vegetable origin (phytosterols) and animal origin (zoosterols). The most widespread phytosterol is sitosterol, and the most widespread zoosteol is cholesterol. Sitosterols, particularly, the most investigated one beta-sitosterol, has cholesterol lowering action, reducing absorption of cholesterol in the bowels, it also has estrogenic, antitumor, antifungal and bacteriostatic activity (stops growth and reproduction of bacteria). In the recent years is has been found out that phytosterols can participate in lipidic formations of human beings and animals, for example, in red cells' membranes. Cedar nut oil contains squalen, which is an intermediary product of cholesterol biosynthesis. Triperpene hydrocarbons form triperpene saponins and are included in the structure of essence. They have bactericidal, anti-inflammatory and expectorant effect. Cedar nut oil is a rich source of fat-soluble vitamins and some vitamins of group B. (Table 2). Table 2. Content of vitamins in cedar nut oil. Vitamin Content in mg for 100 g of Recommended cedar nut oil allowance Carotenoids (provitamin A) 31 6 mg Е 55 10-12 mg D 0,07 0,0025 mg В1 1,6 1,1-1,2 В2 1,7 1,5 ВЗ (РР) 14 15 daily Vitamin A in vegetable products is contained in the form of provitamins: beta-carotene and other carotenoids. Vitamin A regulates metabolism processes in the organism, participates in processes of tissue respiration, energy metabolism; it affects penetrability of cell membranes, it is necessary for growing, developing and differentiating of tissues, influences functions of endocrine glands (adrenal glands, sex glands), it is in charge for normal condition of skin, mucous membranes of eyes, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory and urinary tracts, strengthen resistance of the organism to respiratory infections, influences eyesight functions specifically (it is a co-factor of rhodopsin - a visual purple, responsible for light perception). When vitamin A is in deficit, skin and mucous membranes diseases progress, eye sight becomes poor. Until recently it has been thought that the main function of carotenoids in the organism is their change into vitamin A. The latest investigations have shown that carotenoids play a very important role in metabolism processes, especially as antioxidants. Beta-carotene is better digested when there are microelements of zinc, selenium, cysteine and glutathione amino acids, bile acids, exogenous antioxidants, such as bioflavonoids, gallocatechines, anthocyanidin. Vitamin E (tocopherol). The mechanism of tocopherol action is related to its participation in keeping stability of cell membranes and cell organs by means of antioxidant properties - the ability to stop peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Vitamin E requirement is directly proportional to receive of polyunsaturated fatty acids by the organism. When there is a deficit of vitamin E, dystrophy of skeletal muscles and a cardiac muscle, capillary fragility is increased, red cells are destroyed, reproductive function gets worse, degenerative changes in nerve cells and liver cells develop. Vitamine E deficit decreases the level of magnesium in tissues, selenium and vitamin E are better digested when they are received together. Vitamin D regulates calcium and phosphor metabolism, ensures digestion of these agents in the intestines and their accumulation in the growing bone, providing strength of bones and teeth. Vitamin D helps magnesium digestion, which is also necessary for bone tissues formation. Vitamin D influences penetrability of cell and sub cell membranes for calcium ions. It is synthesized in the organism when skin receives sunlight. Formation of a biologically active form of the vitamin D takes place in the liver and kidneys. Vitamin D deficit is popular among kids of early age and is important in rachitis developing. Hypovitaminosis of D among adults is rare and exists in the form of osteoporosis. Vitamin D is toxic, hypervitaminosis is possible when people take it unreasonable. So, it's important to receive it in natural way with food. Vitamin B1 (thiamine) participates in metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, ensures normal growth, increases motor and secretory activity of the stomach, normalize cardiac performance. Thiamine turns into coenzyme cocarboxylase in the organism. Thiamine is required for synthesis of the most significant neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Thiamine deficit is in progress when a person abuses alcohol, takes great amount of refined carbohydrates, suffers from a disease of the gastrointestinal tract, problems with this vitamin digestion, antibiotics. The main signs of hypovitaminosis B1 are polyneuritis, problems with cardiac performance and gastrointestinal tract. Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) influences growing and developing of the foetus and the child, plays an important role in metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats, plays an important role in eye sight maintenance, participates in formation of rhodopsin, visual purple, protecting the retina from excessive influence of ultraviolet irradiation., participates in hemoglobin synthesis. Biochemical mechanism of riboflavin action is related to its participation in the processes of biological oxidation and energy metabolism. When there is avitaminosis of B2 oral mucosa and eyes suffer (cornea inflammation, lens-form opacity). Synergism of riboflavin with vitamin B6, zinc and selenium have been discovered. Vitamin PP (niacin, nicotinic acid) participates in reactions of cell respiration and intermediate metabolism, as it is included in the structure of enzymes, performing oxidation-reduction reaction, improves carbohydrate metabolism, works beneficially in light forms of pancreatic diabetes, decreases the cholesterol level in the blood, normalizes secretory and motor functions of the gastrointestinal tract, works beneficially in gastric ulcer, takes vasorelaxant effect. In case of avitaminosis there are pellagra (“rough skin”), which is in the form of dermatitis (skin disorder), dysfunctions of gastrointestinal tract, oral mucosa disorder, mental disturbance. Niacin is generated from amino acid tryptophon in the organism.1 mg of niacin is generated from 60 mg of tryptophon. The kernel of the cedar nut of milky ripeness contains 64 mg/% of vitamin C. The kernel of the cedar nut contains a great amount of minerals, 2,6% out of which is represented by a set of macro- and micro-elements. Table 3. Composition of macro- and micro elements in cedar nut oil: Name Content: mg per 100 g of Recommended cedar nut oil allowance Potassium 650 2-З g Sodium 195 3-6 g Calcium 110 800-1000 mg Phosphor 840 1200-1600 mg Magnesium 552 350-500 mg daily Ferrum 19 10-15 mg Copper 4 2-5 mg Manganese 16 5-10 mg Zinc 20 10-15 mg Iodine 0,6 0,1-0,2 mg Content of phosphor, magnesium, manganese, copper, zinc and iodine is very important for ration. Presence of the above-mentioned macro-and microelements characterizes the cedar nut kernel as a natural source of mineral substances, playing an important role in many biochemical processes of the human organism. Cedar nut oil has nitrogenous compounds, represented mainly by free amino acids. Among them one can find irreplaceable amino acids: valine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, threonine, tryptophan, phenylalanine; replaceable amino acids: arginine, histidine, tyrosine, alanine, glycine, proline, serine, asparagine, glutamin. Significance of amino acids for the organism is defined, first of all, by the fact that they are used for protein synthesis. Besides that, a great amount of substanes of nonpeptidic nature, which perform special functions, is generated from amino acids. Such substances include choline (included in the structure of phospholipids), taurine (participates in metabolism of bile acids), heme (a component of hemoglobin). Amino acid tyrosine is a precursor of thyroid hormones, catecholamines - adrenaline and noradrenaline, it is included in the structure of dark-colored pigments melanins, determining the color of skin, eyes. Biogenic amine - gistamine, playing a role of a local hormone, is generated from gistidine. A small amount of vitamin PP (niacin) is generated from tryptophan in the organism. Also, tryptophan is a precursor of neurotransmitter serotonin, which influences emotional condition of the organism, deficit of serotonin is a feature of depressive mood. Some amino acids have biologic activity. Amino acid lysine increases nonspecific resistance of the organism, influences the tone of cardiac vessels, decreases the cholesterol level in the blood. Methionine prevents from excess fat accumulation in the liver, protects liver cells from influence of toxic substances, and participates in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine. Amino acids alanine and glycine play a role of inhibitory mediators in the brain, but glytamic and asparatic acids - excitatory mediators. Amino acid arginine increases nonspecific resistance of the organism, eliminates cramp of blood vessels, decreases the cholesterol level in the blood, and is an essential amino acid during the period child's growing. Sulfur amino acid cysteine is a natural antioxidant. Information is taken from the book “Cedar oil. Compositions of valuable vegetable oils.” Obukhov L.A., Vyazova E.A.