* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Constants and Equations
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Crab Nebula wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
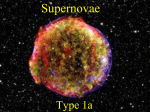
Astronomy This test has 40 questions, with a total of 89 points. Please refer to the constants, equations, and image sets for some questions. Constants and Equations 1AU 1.51011 m Absolute Magnitude of Sun 4.83 Mass Luminosity Relation: R☉ 7.0108 m T☉ 5.8103 K M☉ 2.01030 kg G (Gravitational Constant) 6.6710-11m3kg-1s-2 (Stephan-Boltzmann Constant) 5.6710-8 Wm-2K-4 c (Speed of Light in Vacuum) 3108 ms-1 h (Planck Constant) 6.62610-34 Js Ionization Energy of Hydrogen Atom 2.1810-18 J 1) Which of the images is Henize 2-428? (1 pt.) 2) Based on observations and predictions of general relativity, the orbital period of the binary system HM Cancri is: (1 pt.) a) Increasing b) Decreasing c) Staying constant d) Sometimes increasing, sometimes decreasing 3) Briefly explain the reason for your answer in 2). (3 pt.) 4) Image 2 shows an artist’s illustration of the binary white dwarf system J075141. What type of celestial object is this? a) Type Ia Supernova b) Mira Variable Stars c) AM CVn System (1 pt.) d) Dwarf Novae 5) Under what category will J075141 fall on the H-R diagram (Image 1)? (1 pt.) 6) Image 3 is NGC 2392. What type of celestial object is this? (1 pt.) a) Dark Nebula b) Reflection Nebula c) Planetary Nebula d) Supernova remnant e) Globular Cluster f) Open Cluster g) Quasar h) Protostar i) Galaxy 7) In Images 4-18, find those that fall into the same category of NGC 2392 in 6). (5 pt.) (0.3 pt. penalty for every wrong answer) 8) Which of the image is SNR 0509-67.5? (1 pt.) 9) Which of the image is SNR G1.9+0.3? (1 pt.) 10) Which of the image is Tycho’s SNR? (1 pt.) 11) Which image represents the light curve of SN 2011fe? (1 pt.) 12) What reaction is the main source of energy for a type O star on the main sequence? (1 pt.) 13) Order the spectral types B, A, G, K, M in order of weakest to strongest Hα spectral lines. (2 pt.) 14) TiO lines occur in stars of which spectral types? (1 pt.) a) O, B b) A, F, G c) K, M 15) What is the heaviest element that can be produced by nuclear fusion in a star? a) Mg b) Si c) Fe d) Au e) U (1 pt.) 16) Which of the following statements about AM CVn stars is not true? (1 pt.) a) AM CVn stars are binary systems with an orbital period of less than 65 minutes. b) AM CVn stars may produce a type II supernova after the white dwarf reaches a critical mass. c) AM CVn stars are sources of gravitational waves. d) AM CVn stars are binary systems where a white dwarf accretes mass from a donor star. e) AM CVn stars may have evolved through a common envelope event, in which one star is inside the atmosphere of the other. 17) If the mass of a white dwarf exceeds a certain limit, it will form a Type Ia supernova. What is this mass limit known as? (1 pt.) a) Roche limit b) Tolman–Oppenheimer–Volkoff limit c) Chandrasekhar limit d) Critical Density 18) How many solar mass (M☉) does the white dwarf have to exceed in order to trigger a Type Ia supernova? 19) Briefly explain why is the limit equals to that you answered in 18)? (1 pt.) (3 pt.) Problem 20) to 25) is a problem set. Show your calculations for full credit. 20) Given the power released by a Type Ia supernova during its peak brightness is 8.01035 W, please calculate the absolute magnitude of a Type Ia Supernova during its peak brightness. (5 pt.) 21) Assume a Type Ia Supernova is 163 Mly away from Earth, please calculate the brightest apparent magnitude of this supernova. 22) Please calculate the wavelength of Hα spectral line in nm. (5 pt.) (5 pt.) 23) As you observe the stars near the supernova, you find that their Hα spectral lines are all shifted to 665 nm. Please calculate the relative radial speed of the supernova to Earth in kms-1. (5 pt.) 24) You find a distant quasar with the radial velocity of 1.7105 kms-1. Assuming the expansion of our universe is linear, and using information from 21) and 23), please calculate the quasar’s distance from Earth in Mly. (5 pt.) 25) In spite of our assumption in 19), based on our many observations of Type Ia Supernovae, we find out that our universe’s expansion rate is: (1 pt.) a) Constant b) Accelerating c) Deceleration 26) Which image represents the light curve of Omicron Ceti? (1 pt.) 27) What kind of variable is Omicron Ceti? (1 pt.) a) Cepheid Variable b) Dwarf Nova c) Pulsating White Dwarf d) Beta Cephei Variable e) Mira Variable 28) What caused the variability of Omicron Ceti? (1 pt.) a) -mechanism b) Helium Flash c) Type Ia Supernova explosion d) Change of luminosity of the accretion disk 29) Briefly explain the phenomenon you answered in 28). (3 pt.) 30) Which image represents the light curve of SS Cygni? (1 pt.) 31) What kind of variable is SS Cygni? (1 pt.) a) Cepheid Variable b) Dwarf Nova c) Pulsating White Dwarf d) Beta Cephei Variable e) Mira Variable 32) What caused the variability of SS Cygni? a) -mechanism (1 pt.) b) Helium Flash c) Type Ia Supernova explosion d) Change of luminosity of the accretion disk Problem 33) to 37) is a problem set. Show your calculations for full credit. 33) Which star is Sirius in Image 24? (1 pt.) 34) Observed from Earth, Sirius has a parallax of 0.38 arcsec. Please find out the distance between Earth and the Sirius system in parsec. (5 pt.) 35) Observed from Earth, Sirius A has an apparent magnitude of -1.47. Please find out the absolute magnitude of Sirius A. 36) Please use the mass-luminosity relation to estimate the mass of Sirius A in M☉. (5 pt.) (5 pt.) 37) Suppose that the mass of Sirius B is 0.98 M☉, and the semi-major axis between Sirius A is 7.5 arcsec observed from Earth, and that we are viewing the system face-on, please calculate the period for the Sirius system to complete one orbit in years. (5 pt.) 38) Which image is M15? (1 pt.) 39) We plot four clusters onto a H-R diagram in Image 22, which one is the oldest? (1 pt.) 40) Briefly explain why the cluster you answered in 34) is the oldest. (3 pt.)