* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The muscular system
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
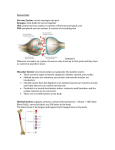
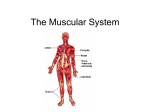
The muscular system: The muscular system is an organ system consisting of skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscles. It permits movement of the body, maintains posture, and circulates blood throughout the body. The muscular system in a vertebrates is controlled through the nervous system, although some muscles (such as the cardiac muscle) can be completely autonomous. Types of muscles: Muscle is a contractile tissue in animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move each other and change the size of the cell. Muscle tissue has four main properties: Excitability (ability to respond to stimuli), Contractibility (ability to contract), Extensibility (ability to be stretched without tearing) and Elasticity (ability to return to its normal shape). Based on certain structural and functional characteristics, muscle tissue is classified into three types: •Cardiac muscles are involuntary and found only in the heart. They are controlled by the lower section of the brain called the medulla oblungata, which controls involuntary action throughout body. Cardiac muscle cells are located in the walls of the heart, appear striated. •Smooth muscles: like cardiovascular muscles, are involuntary. They make up internal organs, such as stomach, small intestine-hyper link, and all the others, except heart. Unlike cardiac muscles are generally spherical, as most other human cells, and each contains one nucleus. •Skeletal muscles are the only voluntary muscles of body, and make up what we call the muscular system. They are all the muscles that move bones and show external movement. Unlike either of the other two classes, skeletal muscles contain multiple nuclei because of its large size, being in strips up to a couple of feet long. Myoglobin & Mitochondria: Myoglobin is a protein and has oxygen bound to it, thus providing an extra reserve of oxygen so that the muscle can maintain a high level of activity for a longer period of time. Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell. They act like a digestive system that takes in nutrients, breaks them down, and creates energy for the cell. •Type I Fibres These fibres, also called slow twitch or slow oxidative fibres, contain large amounts of myoglobin, many mitochondria and many blood capillaries. Such fibres are found in large numbers in the postural muscles of the neck. •Type II Fibres These fibres contain very large amounts of myoglobin, very many mitochondria and very many blood capillaries. Such fibres are infrequently found in humans. • Type II Fibres These fibres; contain a low content of myoglobin, relatively few mitochondria, relatively few blood capillaries. Such fibres are found in large numbers in the muscles of the arms.