* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - singhscience
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
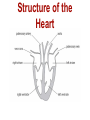
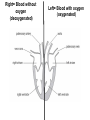
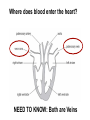
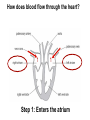
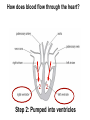
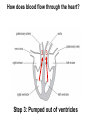
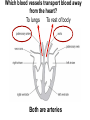
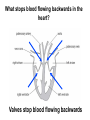
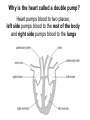
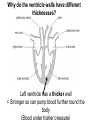
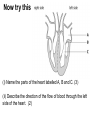
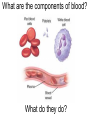
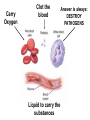
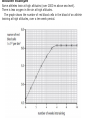
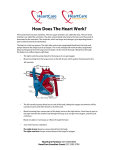
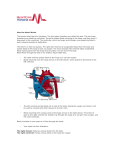
B2 Topic 3 -The structure of the Heart -Blood -The Circulatory System - Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration In past foundation papers from 2011 to 2015, 24 questions have been about this topic = Really important that you know it!!!! Starter: Stick in the heart diagram Structure of the Heart Questions in the past have asked: -Label the structure in the heart -Describe how blood travels through the heart - Where the blood flows into and out of the heart Structure of the Heart Right= Blood without oxygen (deoxygenated) Left= Blood with oxygen (oxygenated) Where does blood enter the heart? NEED TO KNOW: Both are Veins How does blood flow through the heart? 1 1 Step 1: Enters the atrium How does blood flow through the heart? 2 2 Step 2: Pumped into ventricles How does blood flow through the heart? 3 3 Step 3: Pumped out of ventricles Which blood vessels transport blood away from the heart? To lungs To rest of body Both are arteries What stops blood flowing backwards in the heart? Valves stop blood flowing backwards Why is the heart called a double pump? Heart pumps blood to two places; left side pumps blood to the rest of the body and right side pumps blood to the lungs Why do the ventricle walls have different thicknesses? Left ventricle has a thicker wall = Stronger so can pump blood further round the body Now try this (i) Name the parts of the heart labelled A, B and C. (3) (ii) Describe the direction of the flow of blood through the left side of the heart. (2) 6 mark question- Model answer Explain how the structures of the heart are related to their function. (6) Valves - prevent backflow of blood. Right side- pumps blood to the lungs Left side- pumps to the rest of the body Two sides- stops blood mixing Thicker left ventricle wall- pump blood around the body. 1-2 marks= One structure of heart linked to its function. 3-4 marks= Two structure linked to their function. 5-6 marks= Three structures linked to their function. Why do we have a heart? To transport gases, glucose, nutrients and water around the body. These are carried by the blood. Key words: Components- What something is made up of, i.e. the components of blood What are the components of blood? What do they do? Carry Oxygen Clot the blood Liquid to carry the substances Answer is always: DESTROY PATHOGENS Red blood cells carry oxygen in the blood. Explain how one feature of a red blood cell helps it to carry oxygen around the body. (3) An explanation including three the following points • small cells (1) • to squeeze through capillaries (1) • to reach all cells (1) OR • no nucleus (1) • so more haemoglobin (1) • to carry more oxygen (1) OR • biconcave shape (1) • so large surface area (1) • for faster movement of oxygen into / out of cell (1) Why does the blood transport substances around the body? • Respiration • Blood transports oxygen and glucose to cells so they can make energy in respiration. • Blood transports carbon dioxide and waste away from cells. At the cells Aerobic Respiration = Lots of oxygen available Come from blood Anaerobic Respiration = No oxygen Exam questions on this topic often involve graphs. What does it mean? More exercise More oxygen needed by the cells for respiration Heart rate and breathing rate will increase Now try these Explain why the breathing rate of a person changes during exercise. (2) Now you try Explain why the breathing rate of a person changes during exercise. (2) Another example Some athletes train at high altitudes (over 2000 m above sea level). There is less oxygen in the air at high altitudes. The graph shows the number of red blood cells in the blood of an athlete training at high altitudes, over a ten-week period. graph (i) Describe the change in the number of red blood cells during this ten-week training period. (2) (ii) Suggest the minimum training period this athlete needs to produce the highest number of red blood cells. (1) (iii) State the function of red blood cells. (1) (b) When athletes train, the size of their hearts can increase. Suggest how an increase in the size of the heart is an advantage to an athlete. (2)