* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide: Circulatory System
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
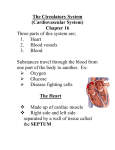
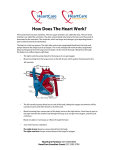
Name_______________________________________ Period________ Study Guide: Circulatory System Directions: Read pages 400-411 in Prentice Hall Science Explorer. Answer the following questions. 1. What is the function of the circulatory or cardiovascular system? It carries needed substances to cells and carries waste products away from cells. Also, blood contains cells that fight disease. 2. Describe the structure of the heart. It consists of four chambers: the right and left atriums and the right and left ventricles. 3. What is the function of the heart? The heart produces muscular contractions that push blood throughout your body. 4. What is the difference between a ventricle and an atrium? Atriums form the upper chambers and ventricles form the lower chambers; the left ventricle has the thickest walls because it pumps blood out to the body. 5. What is the function of the valves in the heart? The valves open to allow blood to flow in one direction through the heart. This prevents the blood from flowing backwards. 6. The heart is a two-phase pump. Describe the action of the heart. The right side receives blood from the body and pumps it to the lungs. The left side of the heart receives blood from the lungs and pumps it to the rest of the body. 7. What causes the “lub-dup” sound in the heart? The closing of valves in the heart as the ventricles contract and relax; these are the two phases of the heart. 8. What is the “pacemaker” in the heart? What is its function? The pacemaker is a group of cells located in the right atrium that sends out signals that make the heart muscle contract and that regulates heart rate. It receives internal stimuli about the body’s oxygen needs and responds to that need. 9. What are the three types of blood vessels? Give the function of each type. a. Arteries: carry blood away from the heart to other parts of the body. b. Capillaries: nutrients, oxygen, and waste move across the thin walls and into the body cells. c. Veins: carry blood back to the heart. Name_______________________________________ Period________ 10. The blood travels through the body in two loops. In the first loop, or pulmonary system, the blood travels from the heart to the lungs and back. What happens to the blood in the lungs? The blood releases CO2 and picks up oxygen. 11. In the second loop, or systemic system, the blood travels from the heart throughout the body and returns to the heart. What happens to the blood in the capillaries in the body? The capillaries are in close contact with body cells. Oxygen is removed from the blood and into the body cells. Carbon dioxide is removed from the body cells and into the blood. 12. Briefly describe the structure of the following: a. Arteries- Thick walls that consist of three layers of muscle and tissue that enable it to withstand the pressure of the blood pumping throughout the body. b. Capillaries- Very small and thin structures that allow materials (wastes and nutrients) to pass through between the blood and the body cells. c. Veins-Blood vessels with thin walls that consist of three layers of muscle and tissue 13. What causes a “pulse” in your artery? A pulse is caused when an artery expands then relaxes as blood surges through the artery. 14. Define blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force at which blood moves through your arteries. Directions: Using page 403 in your book. Label and describe the parts of the heart. Major vein from the upper body to the heart Pacemaker: Regulates the beating of the heart. Right Atrium: Receives blood from the body that’s low in oxygen and high CO2 Right Ventricle: When it contracts, it pumps oxygen poor blood to the lungs. Major vein from the lower body to the heart Aorta: the largest blood vessel in the body that carries blood from the left ventricle to the body Artery from the heart to lungs Left Atrium: Oxygen rich blood moves from the lungs into left atrium Left Ventricle: Pumps oxygen rich blood to all parts of the body Septum: Thick muscular layer that separates left side of heart from right side. Prevents mixing of oxygen-rich blood and oxygen-poor blood.