* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Circulatory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
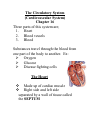
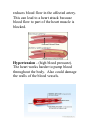
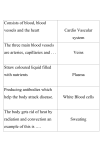
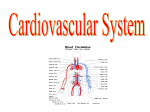
The Circulatory System (Cardiovascular System) Chapter 16 Three parts of this system are; 1. Heart 2. Blood vessels 3. Blood Substances travel through the blood from one part of the body to another. Ex: Oxygen Glucose Disease fighting cells The Heart Made up of cardiac muscle Right side and left side separated by a wall of tissue called the SEPTUM Each side has an upper and lower chamber Upper chamber is the ATRIUM which receives blood from the heart In the right atrium is a pacemaker (group of heart cells) Lower chamber has a right/left ventricle which pumps blood out of the heart Atria and ventricles are separated by valves. Valves are also between ventricles and large blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Valves are flaps of tissue that prevent blood from flowing backward Two Phases of the Heart P 1- The heart muscle relaxes and fills up with blood. P2 – The heart muscle contracts and pumps blood forward. When the heart beats it sounds like lub-dub during the pumping phase. After blood leaves the heart the blood travels through the body there are three types of blood vessels; 1. Arteries – carry blood AWAY from the heart 2. Capillaries – tiny narrow vessels that exchange substances between the blood and body cells 3. Veins – carry blood BACK to the heart Pattern of Blood Flow Blood flows through the body like a figure eight (8). o Loop 1 – blood travels from the heart to the lungs and then back to the heart. o Loop2 – blood is pumped from the heart throughout the body and then returns again to the heart. *Blood travels in one direction. Loop1 Blood from the body flows into the right atrium, it contains little oxygen but a lot of carbon dioxide. Blood is DARK red. Goes from the right atrium to the right ventricle. Ventricle pumps the oxygen-poor blood into the artery that leads to the lungs. Blood flows through lungs into smaller vessels into tiny capillaries. Loop 2 Left atrium fills with oxygen-rich blood coming from the lungs and the blood moves into the left ventricle Left ventricle pumps blood into the aorta. After passing through branching arteries the blood will flow through capillaries in different parts of your body. Oxygen moves out of the blood into body cells. At the same time the carbon dioxide passes from the body cells into the blood. This blood is LOW in oxygen then flows back to the right atrium through VEINS completing the second loop. **The PULSE is caused by the alternating expansion and relaxation of the artery wall. Blood Pressure – blood exerts a force against the walls of blood vessels. This is caused by the force with which the ventricles contract. Section 2 Blood Blood is made of 4 components; 1. plasma 2. red blood cells 3. white blood cells 4. platelets Plasma – liquid part of the blood (water makes up 90%. The other 10% is dissolved materials). Plasma carries nutrients, glucose, fats, vitamins, and minerals. It also sends chemical messengers to direct body activities. Protein molecules give plasma its yellow color. The three groups of proteins; 1) Regulate the amount of water in the blood 2) Helps fight disease (white blood cells.) 3) Interacts with platelets to form blood clots. There are 4 blood types; A B AB O (Each type is either negative or positive). The marker molecule on your red blood cell determines your blood type. *Type O is the universal donor. *Type AB is the universal recipient. Rh factor – is a protein on the red blood cell that determines if your blood type is positive or negative. Lymphatic System Blood and fluid that leaks out of the capillaries into surrounding tissues has materials that tissue cells need. After this fluid is used by the cells it goes through a drainage system called the LYMPHATIC SYSTEM. This system is a network of veinlike vessels that returns the fluid to the bloodstream. LYMPH – once the fluid is inside this system it is called the lymph. The lymph consists of water and dissolved materials. LYMPH NODES – are small knobs of tissue. They filter lymph, trapping bacteria and other disease-causing microorganisms in the fluid. When the body is fighting infection the lymph nodes enlarge. They are located near your arm pits. Section 3 Cardiovascular Diseases Atherosclerosis – artery wall thickens from a build up of fatty materials. It reduces blood flow in the affected artery. This can lead to a heart attack because blood flow to part of the heart muscle is blocked. Hypertension - (high blood pressure). The heart works harder to pump blood throughout the body. Also could damage the walls of the blood vessels.