* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 31-1: Sum of the Measures of the Interior Angles of Polygons
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
History of Grandi's series wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and architecture wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Pentagram map wikipedia , lookup
Elementary arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
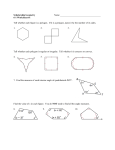
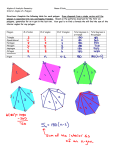
Lesson 31-1: Sum of the Measures of the Interior Angles of Polygons We will develop a formula for the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon and I will determine the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon. March 31, 2017 The sum of the angle measures of a triangle is 180º. We can use that to figure out the sum of the measures of a convex polygon. Sum of the s of a Quad. = Sum of the s of two ∆s = 2(180º) = 360º Pentagon - 3 s 3(180º) = 540º Angle Sum Worksheet Polygon Triangle Number of Sides Number of Triangles Sum of the measures of the interior angles 3 1 (1)180º = 180º Quadrilateral 4 2 (2)180º = 360º Pentagon 5 3 (3)180º = 540º Hexagon 6 4 (4)180º = 720º Heptagon 7 5 (5)180º = 900º Octagon 8 6 (6)180º = 1080º Nonagon 9 7 (7)180º = 1260º N-gon n n-2 (n – 2)180 Polygon Interior Angles Theorem The sum of the interior angles of an n-gon is (n - 2)(180) Examples Find the measure of angle x. 116º 72º 155º x 148º What do we need to know first? Sum of the interior angles: (n-2)(180) = (5 - 2)(180) = 3(180) = 540 155 + 116 + 72 + 148 + x = 540 491 + x = 540 x = 49 Example: The measures of the interior angles of a polygon are related as shown. Find the measure of each angle. x + 20 x + 40 x x + 80 x + 60 x x 20 x 40 x 60 x 80 540 5x 200 540 5x 340 x 68 68º, 88º, 108º, 128º, 148º Observe that as the number of sides increases by one, the sum of the angle measures also increases by a constant amount. What type of function models this behavior? linear Sum of Int. For the first six polygons in the previous chart, plot the ordered pair (number of sides, sum of angle measures) on the axes below. Carefully choose and label your scale on each axis. 1260 1170 1080 990 900 810 720 630 540 450 360 270 180 90 The data points you graphed above should appear collinear. Write an equation for the line determined by these points. (3, 180); (4, 360) 360 180 m 4 3 m 180 y y1 m(x x1 ) y 180 180(x 3) y 180 180x 540 y 180x 360 y 180(x 2) How does this compare to what we found previously? 10. State the numerical value of the slope of the line in Item 11 and describe what the slope value tells about the relationship between the number of sides and the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a polygon. Use units in your description. The numerical value of the slope of the line is 180. This slope tells us that each time a side is added to a polygon, the sum of the measures of the interior angles of the polygon increases by 180°. Whole numbers ≥ 3 The function forms a straight line. Domain is restricted because 1. a polygon cannot be formed with fewer than 3 sides 2. it cannot have a fractional number of sides.