* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8-5 The brain and spinal cord are surrounded by three layers of
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
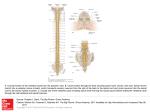
8-5 The brain and spinal cord are surrounded by three layers of membranes called the meninges The Central Nervous System • The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the: » Brain » Spinal Cord • The organs in the CNS… » Require abundant nutrients and consistent supply of oxygen » Must be protected from blood-borne compounds » Must be protected from contacting surrounding bone (in the cranium) The Central Nervous System • The CNS receives physical stability and shock absorption from the meninges » Consist of three layers of specialized tissue surrounding brain and spinal cord • Blood vessels within meninges deliver oxygen and nutrients • Three layers: » Dura mater » Arachnoid » Pia mater The Three Meningeal Layers • The Dura Mater Brain • Tough and fibrous outermost layer of the CNS • Consists of two layers in the brain – Cranially: » Fuses with periosteum of occipital bone – Caudally: » Tapers to dense cord of collagen fibers The Three Meningeal Layers • The Dura Mater Brain • At several locations, the inner layer of the dura mater extend deep into the cranial cavity » Called dural folds » Hold the brain in position The Three Meningeal Layers The Three Meningeal Layers • The Dura Mater Spinal Cord • Outer layer is not fused to bone • Space found between spinal cord and vertebral canal is called the epidural space: » Contains loose connective and adipose tissue » Anesthetic injection site to affect spinal nerves in immediate area of injecetion (aka: epidural) The Three Meningeal Layers • The Arachnoid • Middle meningeal layer • Space contains small amount of lymphatic fluid » Reduces friction between opposing surfaces • Subarachnoid space: » Simple squamous epithelia » Contain collagen and elastic fibers » Filled with cerebrospinal fluid that acts as a shock absorber and transfers nutrients and waste The Three Meningeal Layers The Three Meningeal Layers • The Pia Mater • Is the innermost meningeal layer • Is a mesh of collagen and elastic fibers • Is bound to underlying neural tissue • Highly vascular region » Provide blood and nutrients to the superficial areas of the neural cortex The Three Meningeal Layers 8-6 The spinal cord contains gray matter surrounded by white matter and connects to 31 pairs of spinal nerves Gross Anatomy • The Spinal Cord • Serves as the information “highway” for the passage of sensory and motor impulses • Integrates information on its own • Controls spinal reflexes » Automatic motor responses Gross Anatomy • The Spinal Cord • About 18 inches (45 cm) long • 1/2 inch (14 mm) wide • Ends between vertebrae L1 and L2 • Bilateral symmetry » Grooves divide the spinal cord into left and right » Posterior median sulcus: on posterior side » Anterior median fissure: deeper groove on anterior side Gross Anatomy • Enlargements of the Spinal Cord • Caused by: » Amount of gray matter in segment » Involvement with sensory and motor nerves of limbs • Cervical enlargement: » Nerves of shoulders and upper limbs • Lumbar enlargement: » Nerves of pelvis and lower limbs Gross Anatomy Gross Anatomy • Spinal Cord • Central canal » Narrow internal passageway filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) • Posterior surface » Shallow groove called the posterior median sulcus • Anterior surface » Deeper groove called the anterior median fissure Gross Anatomy Gross Anatomy Gross Anatomy • 31 Spinal Cord Segments • Based on vertebrae where spinal nerves originate (letter and number) • Positions of spinal segment and vertebrae change with age: » Cervical nerves are named for inferior vertebra » All other nerves are named for superior vertebra Gross Anatomy • Every spinal segment is associated with a pair of dorsal root ganglia (singular: ganglion) » Contain cell bodies of sensory neurons • Ventral roots: (anterior) » Contains axons of motor neurons » Send information to PNS • Dorsal roots: (posterior) » Contains axons of sensory neurons » Bring information to CNS Gross Anatomy Gross Anatomy • Distal to each dorsal root ganglion, the sensory (dorsal) and motor (ventral) roots are bound together into a single spinal nerve • All spinal nerves are considered mixed nerves: » Carry both afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) fibers Sectional Anatomy • Left and right sides of spinal cord are created by the… » Anterior median sulcus » Posterior median fissure Sectional Anatomy • Gray matter » Surrounds central canal of spinal cord » Contains neuron cell bodies, neuroglia, unmyelinated axons » Has projections (gray horns) that extend into the white matter Sectional Anatomy • Organization of Gray Matter • Gray matter contains cell bodies of motor and sensory neurons • Horns have specific functions » Posterior gray horn sensory nuclei » Anterior gray horn motor control of skeletal muscles » Lateral gray horn visceral motor neurons » Gray commissures connect horns on both sides Sectional Anatomy Sectional Anatomy • White matter » Is superficial; surrounds the gray matter » Contains myelinated and unmyelinated axons Sectional Anatomy • Organization of White Matter • White matter is divided into 3 columns (or regions) » Posterior white columns » Anterior white columns » Lateral white columns • Each column contain tracts whose axons carry sensory or motor information » Ascending Tract sensory info to the brain » Descending Tract convey motor commands into spinal cord Sectional Anatomy