* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Embryo
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Drosophila melanogaster wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Regional differentiation wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
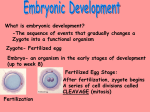
What is this? Homunculus -A sperm cell with a tiny human in it -1678 – Leeuwenhoeck – each sperm contained a tiny preformed animal - only needed nourishment of the female’s womb to grow Fertilization http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6CBBzw6 xUJE http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y Yqnqr8X-Nw&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=09kLIsNfaO8&NR=1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_5OvgQW6FG4 •Fertilization membrane •nuclei •egg cytoplasm •A Fertilized Egg •Fertilization • – the union of sperm and egg nuclei Zygote (fertilized egg) Cleavage http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=w_ydqBz Ve9g Sand dollar cleavage http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GO5YN_t1fqw Xenopus cleavage - awesome embryo 2 cells Embryo 4 cells Cleavage In a fertilized egg, the series of cell divisions that occur without growth Continues until the cells of the embryo are reduced to the size of the cells of the adult organism Twins Fraternal 2 different eggs fertilized by 2 different sperm Identical 1 egg fertilized by one sperm; embryo splits into two embryos Siamese Twins http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BcC_qaqRTBA& feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K57IcN9DWXo Siamese twins Cleavage to Implantation http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=raDDvuSf bhY 16 cell embryo morula Solid ball of cells Morula blastula Hollow center filled with fluid trophoblast Inner cell mass Blastocyst When does pregnancy begin? pregnancy begins with implantation implantation - the fastening of the embryo to the endometrium (wall of the uterus) trophoblast (outer layer of cells of blastula) develops into the chorion secretes HCG human chorionic gonadotropin •Sperm gets to egg sperm egg 2 cells Sperm penetrates egg 4 cells Fertilization Fertilization membrane 8 cells zygote 16 cells solid ball of cells (morula) solid ball of cells (morula) hollow ball of cells (blastula) http://www.luc.edu/depts/biology/dev/urchgast.htm Gastrulation http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8v6cXkzl EQA&feature=related D solid ball of cells (morula) gastrula Hollow (blastula) gastrulation tadpole gastrula ectoderm endoderm mesoderm gastrulation gastrula ectoderm endoderm mesoderm Gastrula Stage of embryonic development in which the germ layers are formed Germ layers give rise to all the tissues and organs of animals Differentiation the series of changes that transforms unspecialized embryonic cells into specialized cells, tissues, and organs that make up the adult organism What is differentiation? The process in which unspecialized cells become specialized cells If every cell in the body has the entire genome in its nucleus (in other words each cell has all the same genes), then what makes cells become specialized? Differential gene expression Some Genes are expressed only in certain cells. ex. gene for pepsin is only active in certain stomach cells What is gene expression? When a gene is activated and is making the polypeptide it codes for. Germ Layers Endoderm lining of digestive tract and respiratory system, liver, pancreas, urinary bladder Mesoderm dermis musculoskeletal system circulatory system reproductive organs, excretory system Ectoderm epidermis nervous system 1. The process in which sperm and egg nuclei fuse ___________________. fertilization 2. The structure which prevents more than one sperm from Fertilization membrane entering the egg_________________________. 3. The cell divisions (without growth) which the fertilized cleavage egg goes through ___________________. 4. The kind of cell division (nuclear division) occurring throughout the development of the embryo is ______________. mitosis 5. The ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm are called ___________________. Germ layers 6. The ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm give rise to all the structures in the fully developed animal. The specialization of cells during this process of development is differentiation called____________________. 7. During cleavage, the number of cells increases _______________________. 8. During cleavage, the size of cells decreases _______________________. A tiny fish, the embryo is formed The three-layered stage develops to form organs Stages having 2 and then 3 layers of cells develop A hollow ball, made of a single layer of cells, develop The 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, and 128 cell stages develop The fertilized egg divides into 2 cells Place these events in the right order • • • • • • • • Implantation Differentiation Fertilization Formation of organs Ovulation Gastrulation Cleavage Formation of placenta • • • • • • • • Ovulation Fertilization Cleavage Implantation Formation of placenta Gastrulation Differentiation Formation of organs Sperm + egg More cleavage Fertilization Blastula (blastocyst) Zygote Cleavage 2 celled 4 celled etc. More cleavage Morula Hatches Implantation Gastrulation and cleavage Gastrula (germ layers) http://www.luc.edu/depts/biology/dev/urchgast.htm ectoderm mesoderm endoderm Gastrula Embryo to fetus http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HBBNu_d AGhs&feature=related Each cell in a human embryo has the same genetic material (DNA), yet some cells become heart cells, other cells become brain cells, and others will develop into kidney cells (etc…) How do the many different kinds of cells in the body develop if they have the same DNA? Review: Trace the path of sperm from where it is produced to where it fertilizes the egg. List all the structures it travels through to get to the egg. Testes Epididymis Vas Deferens Urethra (penis) Vagina Cervix Uterus Oviduct Fetal membranes (extraembryonic membranes) amnion yolk sac allantois chorion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LKvez9duEHQ http://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=tof5b1Qs_OE&feature=r elated amniotic fluid chorion allantois Chicken embryo airspace shell albumin yolk sac yolk amnion thin, tough, membranous sac that encloses the embryo or fetus of a mammal, bird, or reptile. It is filled with amniotic fluid in which the embryo is suspended Yolk sac birds – stores yolk (food) humans - blood cell formation has no yolk Allantois - forms primitive urinary bladder; becomes blood vessels on embryonic side of placenta; allantoic stalk becomes part of umbilical cord (yolk sac and allantois become the umbilical cord) chorion – membrane surrounding embryo and other extra-embryonic membranes; chorionic villi - projections of chorion containing blood vessels; project into maternal pools of blood chorionic villi and uterine lining become the placenta chorion Who has a larger egg cell, an elephant or a chicken? Animal Internal Fertilization Amphibians External Fertilization Internal Development External Development Reptiles Birds Mammals nonplacentals placentals 3 11 6 9 5 1 2 8 4 7 10 How could a man become pregnant? •placenta http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gHnFoWEVs7o http://health.howstuffworks.com/ada m-200109.htm placenta Placenta Fetus Uterus Umbilical Cord Amniotic Sac (Amnion) Amniotic Fluid Umbilical Vein Umbilical Artery Placenta Fetal Capillary Chorionic Villus placenta -A temporary organ (gland) forming from the chorion and the endometrium from mother What are the functions of the placenta? Functions of the Placenta 1. 2. 3. 4. source of nourishment for embryo respiratory surface for embryo excretory organ of embryo attaches embryo/fetus to wall of uterus 5. secretes chorionic gonadotropin, progesterone, estrogen regulation of pregnancy The blood of the embryo/fetus and the mother do not mix! (embryonic and maternal circulatory systems are not connected ) How do substances get for the mom’s blood to the fetus and vice versa? Substances diffusing through the placenta From mom to embryo/fetus Oxygen Nutrients Antibodies From embryo/fetus to mom Wastes Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Dangerous substances can pass through the placenta Viruses (e.g. measles, AIDS) Drugs (e.g. nicotine, prescription drugs) Alcohol development http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UgT5rUQ 9EmQ&feature=related 3 weeks 4 weeks 5 weeks 6 weeks http://health.howstuffworks.com/ adam-200127.htm Amniotic fluid 6 weeks 3 months Development – series of events that give rise to a fully grown organism Mass – the amount of matter in an object Premature – a baby born before it is fully developed Fetus – the developing baby after the second month of pregnancy; has all the organs and organ systems formed Embryo - A multicellular organism in an early stage of development Place these in the correct order: Ovulation Stage Menstruation Corpus Luteum Stage Follicle Stage Stages of the Menstrual Cycle Follicle Stage Ovulation Corpus Luteum Stage Menstruation What is happening to the 2 chromosomes in the middle? Crossing Over cleavage of embryo implantation uterus Sperm deposited in vagina oviduct fertilization egg moves down oviduct ovulation https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L3z_aJnWOM&NR=1&feature=fvwp Week 7 •http://www.youtube.com/user/cellmedicine?v=gCVlvq7e uek&feature=pyv&ad=7945556449&kw=ms%20cure Stem cell therapy for MS