* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Topic 18 Safety
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
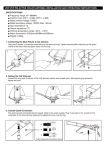
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electrician wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring wikipedia , lookup
General Licensing Class RF & Electrical Safety • Antenna & tower safety • RF safety • AC/DC safety 1 RF & Electrical Safety While working on an antenna system, turn off the transmitter and disconnect the feed line from it so there is absolutely no way that someone could accidentally transmit while you are making the repairs. 2 RF & Electrical Safety To insure that no one starts rotating a beam antenna using the electric powered rotator, double check that the rotator control unit is unplugged and tagged “climber aloft.” 3 RF & Electrical Safety • Preventing falls from a tower is best achieved with a safety harness. Always be sure that the belt is rated for the weight of the climber and is within its service life. You need a hard hat and safety glasses, too. 4 RF & Electrical Safety Performing a routine RF exposure evaluation is a good idea for all amateurs to ensure compliance with RF safety regulations and that you and your neighbors are not being “overexposed” to RF radiation. 5 RF & Electrical Safety It is always a good idea to locate an antenna as far away as possible from living spaces that will be occupied when you are transmitting. This will help ensure that Maximum Permissible Exposure (MPE) limits are not exceeded. 6 RF & Electrical Safety If RF energy from your antenna system is concentrated on the human body, it heats the body tissue just like your microwave oven heats your leftovers. RF burns are a very real thing. They include those experienced from poor grounding of the equipment to those received from touching or standing too close to an antenna while someone is transmitting. 7 RF & Electrical Safety You can determine how your station complies with FCC RF exposure regulation by: • Using the tables to estimated safe distances based on FCC OET Bulletin No. 65, • By your own calculations based on computer modeling, • You can use a field-strength meter and measure the power density level. 8 RF & Electrical Safety Time-averaging is a method of calculating an individual’s total exposure to RF radiation over a given period of time. The premise of timeaveraging is that the human body can tolerate larger amounts of RF radiation if the exposure is received in short “bursts” as compared to a constant exposure at the same high level of RF radiation. 9 RF & Electrical Safety Duty cycle is the percentage of time the transmitter is actually sending out energy. The lower duty cycle permits greater short-term exposure levels to RF radiation. 10 RF & Electrical Safety In Section 97.13, the FCC rules state that if your station’s RF exceeds permissible limits, you “must take action to prevent human exposure to such RF electromagnetic fields.” 11 RF & Electrical Safety Although a simple field-strength meter can show the presence of radio frequency emissions, it takes a precisely calibrated field-strength meter with a calibrated antenna to make accurate measurements of the RF field. 12 RF & Electrical Safety There are all sorts of great 5band trap vertical antennas that work nicely mounted on the ground. When you’re looking for a spot to mount an antenna, keep in mind maximum permissible exposure limits. Install it so that no one can actually walk up to it or stand near it when you are transmitting. This goes for your pets, too. 13 RF & Electrical Safety If your calculations indicate that you may be exposing your neighbors to too much RF, you need to relocate your entire antenna system, or take precautions to ensure it cannot be pointed in their direction when transmitting. 14 RF & Electrical Safety The National Electrical Code covers electrical safety standards as they relate to conductors and wiring inside your ham shack. RF exposure limits to the human body are covered by ANSI, not by the NEC. 15 RF & Electrical Safety Ground fault circuit interrupters are found in newer electrical plug outlets. They instantly open a circuit to halt current flow when they detect current flowing from the hot wire to ground. 16 RF & Electrical Safety Good station grounding ensures that no hazardous or dangerous voltages appear on the metal chassis of your equipment. Without good grounding you could be shocked when you touch a piece of equipment. 17 RF & Electrical Safety Most ham transceivers run on 12 volts DC. Some base stations may have their own 110 VAC power supplies built-in. However, linear amplifiers may require 240 VAC. For single phase 240 VAC, fuse both the black and red hot wires. NEVER fuse the neutral white wire or the neutral ground bare copper wire. Most amplifiers already have the fuse circuits built in. 18 RF & Electrical Safety Based on the American Wire Gauge (AWG) information shown, 14 gauge wire can handle 15 amperes. The easy way to remember this is with the “F” for “Fourteen” (14 gauge) wiring will handle Fifteen (15) amps. 19 RF & Electrical Safety Based on the American Wire Gauge (AWG) information shown, 20 amperes of continuous current requires a wire size of AWG #12. Thick or thin insulation can be misleading about the actual wire size! You need to strip off the insulation from unmarked wire to determine which gauge wire you 20 RF & Electrical Safety Linear amplifiers will have a power supply interlock switch. If the equipment is on and the power supply door is opened, the equipment will instantly power off. This protects you and the equipment from a high voltage shock. 21 RF & Electrical Safety Any time you are working on radio equipment innards, wash your hands when you finish to remove any lead that might be contained in that roll of old solder before you grab a sandwich. 22 RF & Electrical Safety Good engineering practice for a lightning ground indicates that all grounds be bonded together with all other grounds. 23 RF & Electrical Safety Carefully inspect tower grounding circuits and you will find that all the ground connections have been swaged rather than soldered. Solder might melt on a direct lightning strike destroying the route to ground. 24 RF & Electrical Safety In an emergency you might power your house with your generator. Any time you connect a generator into your home, you MUST ABSOLUTELY trip all of the breakers to disconnect the incoming utility power feed. This ensures you are not sending voltage back into the grid through your electrical panel, which could prove dangerous for anyone working on the lines. Disconnecting the utility power feed at the panel will also prevent damage to the generator when 25 the power is restored. RF & Electrical Safety Any time you use a generator for power, make sure the generator is located in a well-ventilated area; not where someone could inhale the toxic exhaust. The generator should be properly grounded, and always store the generator’s fuel in a safe place away from any inhabited area. 26 G0A12 What precaution should you take whenever you make adjustments or repairs to an antenna? A. Ensure that you and the antenna structure are grounded. B. Turn off the transmitter and disconnect the feed line. C. Wear a radiation badge. D. All of these choices are correct. 27 G0B08 supports What should be done by any person preparing to climb a tower that electrically powered devices? A. Notify the electric company that a person will be working on the tower. B. Make sure all circuits that supply power to the tower are locked out and tagged. C. Unground the base of the tower. D. All of these choices are correct. 28 G0B07 Which of these choices should be observed when climbing a tower using a safety belt or harness? A. Never lean back and rely on the belt alone to support your weight. B. Confirm that the belt is rated for the weight of the climber and that it is within its allowable service life. C. Ensure that all heavy tools are securely fastened to the belt D-ring. D. All these choices are correct. 29 G0A08 Which of the following steps must an amateur operator take to ensure compliance with RF safety regulations when transmitter power exceeds levels specified in part 97.13? A. B. C. D. Post a copy of FCC Part 97.13 in the station. Post a copy of OET Bulletin 65 in the station. Perform a routine RF exposure evaluation. All of these choices are correct. 30 G0A11 What precaution should you take if you install an indoor transmitting antenna? A. Locate the antenna close to your operating position to minimize feed line radiation. B. Position the antenna along the edge of a wall to reduce parasitic radiation. C. Make sure that MPE limits are not exceeded in occupied areas. D. Make sure the antenna is properly shielded. 31 G0A01 What is one way that RF energy can affect human body tissue? A. It heats body tissue. B. It causes radiation poisoning. C. It causes the blood count to reach a dangerously low level. D. It cools body tissue. 32 G0A03 How can you determine that your station complies with FCC RF exposure regulations? A. By calculation based on FCC OET Bulletin 65. B. By calculation based on computer modeling. C. By measurement of field strength using calibrated equipment. D. All of these choices are correct. 33 G0A04 What does “time averaging” mean in reference to RF radiation exposure? A. The average amount of power developed by the transmitter over a specific 24 hour period. B. The average time it takes RF radiation to have any long-term effect on the body. C. The total time of the exposure. D. The total RF exposure averaged over a certain time. 34 G0A07 What effect does transmitter duty cycle have when evaluating RF exposure? A. A lower transmitter duty cycle permits greater short-term exposure levels. B. A higher transmitter duty cycle permits greater short-term exposure levels. C. Low duty cycle transmitters are exempt from RF exposure evaluation requirements. D. High duty cycle transmitters are exempt from RF exposure requirements. 35 G0A02 Which of the following properties is important in estimating whether an RF signal exceeds the maximum permissible exposure (MPE)? A. B. C. D. Its duty cycle. Its frequency. Its power density. All of these choices are correct. 36 G0A05 your What must you do if an evaluation of your station shows RF energy radiated from station exceeds permissible limits? A. Take action to prevent human exposure to the excessive RF fields. B. File an Environmental Impact Statement (EIS97) with the FCC. C. Secure written permission from your neighbors to operate above the controlled MPE limits. D. All of these choices are correct. 37 G0A09 What type of instrument can be used to accurately measure an RF field? A. A receiver with an S meter. B. A calibrated field strength meter with a calibrated antenna. C. An SWR meter with a peak-reading function. D. An oscilloscope with a high-stability crystal marker generator. 38 G0A06 What precaution should be taken when installing a ground-mounted antenna? A. It should not be installed higher than you can reach. B. It should not be installed in a wet area. C. It should limited to 10 feet in height. D. It should be installed such that it is protected against unauthorized access. 39 G0A10 directional What is one thing that can be done if evaluation shows that a neighbor might receive more than the allowable limit of RF exposure from the main lobe of a antenna? A. Change to a non- polarized antenna with higher gain. B. Post a warning sign that is clearly visible to the neighbor. C. Use an antenna with a higher front-to-back ratio. D. Take precautions to ensure that the antenna cannot be pointed in their direction. 40 G0B14 A. B. C. D. Which of the following is covered by the National Electrical Code? Acceptable bandwidth limits. Acceptable modulation limits. Electrical safety inside the ham shack. RF exposure limits of the human body. 41 G0B05 disconnect device? Which of the following conditions will cause a Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter (GFCI) to the 120 or 240 Volt AC line power to a A. Current flowing from one or more of the voltage-carrying wires to the neutral wire. B. Current flowing from one or more of the voltage-carrying wires directly to ground. C. Over-voltage on the voltage-carrying wire. D. All of these choices are correct. 42 G0B06 Why must the metal enclosure of every item of station equipment be grounded? A. It prevents blowing of fuses in case of an internal short circuit. B. It prevents signal overload. C. It ensures that the neutral wire is grounded. D. It ensures that hazardous voltages cannot appear on the chassis. 43 G0B01 Which wire or wires in a four-conductor connection should be attached to fuses or circuit breakers in a device operated from a 240-VAC single phase source? A. B. C. D. Only the two wires carrying voltage. Only the neutral wire. Only the ground wire. All wires. 44 G0B03 that uses A. B. C. D. Which size of fuse or circuit breaker would be appropriate to use with a circuit AWG number 14 wiring? 100 amperes. 60 amperes. 30 amperes. 15 amperes. 45 G0B02 to 20 A. B. C. D. What is the minimum wire size that may be safely used for a circuit that draws up amperes of continuous current? AWG number 20. AWG number 16. AWG number 12. AWG number 8. 46 G0B12 What is the purpose of a transmitter power supply interlock? A. To prevent unauthorized changes to the circuit that would void the manufacturer’s warranty. B. To shut down the unit if it becomes too hot. C. To ensure that dangerous voltages are removed if the cabinet is opened. D. To shut off the power supply if too much voltage is produced. 47 G0B10 Which of the following is a danger from lead-tin solder? A. Lead can contaminate food if hands are not washed carefully after handling the solder. B. High voltages can cause lead-tin solder to disintegrate suddenly. C. Tin in the solder can “cold flow” causing shorts in the circuit. D. RF energy can convert the lead into a poisonous gas. 48 G0B11 Which of the following is good practice for lightning protection grounds? A. They must be bonded to all buried water and gas lines. B. Bends in ground wires must be made as close as possible to a right angle. C. Lightning grounds must be connected to all ungrounded wiring. D. They must be bonded together with all other grounds. 49 G0B09 of a Why should soldered joints not be used with the wires that connect the base tower to a system of ground rods? A. The resistance of solder is too high. B. Solder flux will prevent a low conductivity connection. C. Solder has too high a dielectric constant to provide adequate lightning protection. D. A soldered joint will likely be destroyed by the heat of a lightning strike. 50 reason for not placing a gasolinegenerator inside an occupied fueled area? A. B. C. D. Danger of carbon monoxide poisoning. Danger of engine over torque. Lack of oxygen for adequate combustion. Lack of nitrogen for adequate combustion. 51 G0B13 What must you do when powering your house from an emergency generator? A. Disconnect the incoming utility power feed. B. Insure that the generator is not grounded. C. Insure that all lightning grounds are disconnected. D. All of these choices are correct. 52 G0B15 Which of the following is true of an emergency generator installation? A. The generator should be located in a wellventilated area. B. The generator should be insulated from ground. C. Fuel should be stored near the generator for rapid refueling in case of an emergency. D. All of these choices are correct. 53