* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Angles and triangles
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
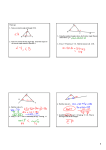
11-B Angles and triangles KEY CONCEPTS Interior angles In the triangle at right, a + b + c = 180°, where a, b and c represent the three interior angles of the triangle. b a c The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180 °. This rule can be used to find unknown values of interior angles of triangles. Calculate the value of the pronumeral in the triangle below. a 65o 33o WRITE 1 The sum of the three interior angles is 180°. Write this as an equation. 2 Simplify by adding 33° and 65°. 3 Solve the equation for a; that is, subtract 98° from 180°. 33° + 65° + a = 180° 98° + a = 180° a = 180° − 98° = 82° Calculate the value of the pronumeral in the triangle below. 70° b WRITE 330 1 The triangle is an isosceles triangle, so the two base angles are equal. The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°. 2 To find the value of b, subtract 140° from 180°. Maths XPRESS 7 180° = b + 70° + 70° = b + 140° b = 180° − 140° = 40° Exterior angles If one edge of a triangle continues past the vertex, the angle formed is called an exterior angle. B The interior angle and the exterior angle next (or adjacent) to it are called supplementary angles because they form a straight line. Supplementary angles sum to 180°. For the triangle at right: A ∠ACB + ∠BCD = 180° ∠ACB = 180° − ∠BCD ∠BCD = 180° − ∠ACB Exterior angle C D B Determine the value of the exterior angle ∠BCD in the diagram at right. 70o 50o A 1 The sum of the supplementary angles, ∠ACB and ∠BCD, is 180°. 2 ∠ACB is 60°. Subtract this value from 180° to determine the value of ∠BCD. 60o C D WRITE ∠ACB + ∠BCD = 180° The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°, and there are 180° in a straight angle. Therefore, we can establish the rule at right: In Example 3, ∠BCD = 50° + 70° = 120°. ∠BCD = 180° − ∠ACB = 180° − 60° = 120° An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles. LEARNING EXPERIENCE Puzzles with shapes Equipment: coloured cardboard, ruler, protractor, scissors 1 Using coloured cardboard, draw and cut out: a one equilateral triangle with edge lengths equal to 4 cm and interior angles equal to 60° b one obtuse-angled, isosceles triangle with a 120° angle and two edges equal to 4 cm c four scalene, right-angled triangles with a hypotenuse of 4 cm and other interior angles of 30° and 60°. 2 Use the cardboard triangles from step 1 to make: a a right-angled triangle using only two pieces b a right-angled triangle using three pieces c a right-angled triangle using four pieces d a single triangle with an exterior angle of 120° using all pieces e a single triangle with an exterior angle of 150° using all pieces. 3 Measure the interior angles of each construction. What do you notice about the sum of the interior angles? Chapter 11 Shapes 331