* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
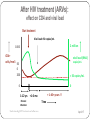
Download 50 copies/mL Viral load <50 copies/mL Time
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
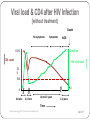
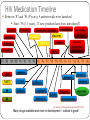
HIV “Myths, controversies and challenges” Dr Emmanuel Nsutebu Consultant Infectious Diseases Physician Tropical and Infectious Diseases Unit Royal Liverpool Hospital “10 questions ....” 1. What is the difference b/w HIV and AIDS 2. What is the origin? 3. How is it transmitted? 4. Does the risk of transmission vary? 5. Can you know when a person got infected? 6. Is lengthy pretest counselling needed before a test is done? 7.How is HIV treated? 8. Can it be cured? 9. What is the life expectancy? 10. What about a vaccine and is there hope? How many people are affected? Globally 34 million PLHAs, 1.7M deaths a year, 2.5M new infections a year 15 million eligible for treatment and 8 million on treatment. 24 million cases in Africa 5% adult prevalence in Cameroon (2011) – 900000 PLHA UK – 70000 PLHA No. Of new cases and deaths Falling due to success of treatment 1. What is the difference b/w HIV and AIDS? Not the same thing but related. AIDS is a stage of HIV infection. NOT ALL HIV INFECTION = AIDS Most people with HIV have no symptoms 2. Origin? Jump from chimpanzees to humans - SIV Figure 1 Source: The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2011; 11:45-56 (DOI:10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70186-9) Terms and Conditions 3. How is HIV transmitted? Unprotected sex – 70% of infections Mother to child transmission – mum must be positive – during pregnancy, at birth or during breastfeeding! Intravenous drug use – sharing needles Blood transfusion and other blood products Medical equipment Mother to child transmission 30% risk of transmission reduced to <2% with ARVS How is HIV not transmitted? Cutlery Mosquitoes Kissing Hugging 4. Does the risk of transmission vary? Varies depending on Positive person Negative person Route of transmission Sex 3/1000 but can happen with first contact Transmission to women easier IV drug user high risk 5. Can you know when a person acquired the infection? No but can guess!!! Viral load & CD4 after HIV Infection [without treatment] Death No symptoms Symptoms AIDS 2 million 1000 CD4 count HIV viral load 50 0 200 0 0 4-8 wks 2-12 mo Up to 12 years 2-3 years Time Understanding HIV Treatment and adherence. April 17 Development of AIDS is like an impending train wreck Viral Load = Speed of the train CD4 count = Distance from cliff HIV infection J. Coffin, XI International Conf. on AIDS, Vancouver, 1996 Infections and cancer! 6. Is lengthy pretest counselling needed? An HIV test is a routine test!!! 7. How is HIV treated and it is effective? HIV Replication Cycle and Sites of Drug Activity NNRTIs Cellular DNA nRTI NRTIs Protease Inhibitors Nucleus New HIV particles HIV Virions Reverse Transcriptase Protease Integrase Capsid proteins and viral RNA CD4 Receptor Fusion Inhibitors Viral RNA Unintegrated double stranded Viral DNA Integrated viral DNA CCR5 or CXCR4 co-receptor 1 3 2 Attachment Uncoating Reverse Transcription Integration Viral mRNA 4 Transcription At least 3 drugs to stop the virus from multiplying gag-pol polyprotein 5 Translation 6 Assembly and Release clinicaloptions.com/hiv HIV Medication Timeline Between ’87 and ’95 (9 years), 4 antiretrovials were launched. Since ’95 (11 years), 25 new products have been introduced!! stavudine lamivudine zalcitabine lamivudine/zidovudine nevirapine didanosine delavirdine zidovudine emtricitabine emtricitabine/ tenofovir efavirenz tenofovir abacavir/ lamivudine/ zidovudine abacavir ’87 ’88 ’89 ’90 ’91 ’92 ’93 ’94 ’95 ’96 ’97 ’98 ’99 ‘00 ’01 ‘02 ‘03 ‘04 ‘05 ‘06 NRTI saquinavir NNRTI ritonavir PI indinavir FI atazanavir tipranavir darunavir nelfinavir saquinavir amprenavir Kaletra didanosine enfuvirtide fosamprenavir Corrections Curriculum Development, NY/NJ AETC Many drugs available and more in development – outlook is good! Treatment & Treatment as prevention Most patients on one or two tablets a day! After HIV treatment (ARVs): effect on CD4 and viral load Start treatment Viral load <50 copies/mL 2 million 1000 CD4+ cells/mm3 viral load (RNA) copies/mL 50 0 200 < 50 copies/mL 0 0 1-12 yrs + 1-40+ years !! +1-6 mo Chronic Infection Understanding HIV Treatment and adherence. Time April 17 8. What is life expectancy like? We don’t know for sure however we have estimates.... HIV survival similar to other chronic diseases! Life expectancy at 25 years diagnosis estimated to be 70 years 9. What about a cure? 10. What about a vaccine? Problem is variability of the virus!!! Stays one step ahead of immune system!!! What are challenges? Early diagnosis Access to treatment in developing countries Thank you [email protected]