* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Age
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
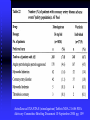
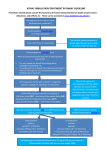
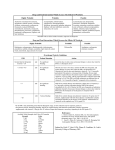
ANTICOAGULATION ISSUES In Geriatric Population Ann McBride, M.D. UW Anticoagulation Service • No financial disclosures • Underuse of Anticoagulation for Atrial Fibrillation – Balance of Stroke vs. Bleeding Risks – Alternatives • Warfarin Initiation and Maintenance • Bridging Therapy Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy: Evidence Based Guidelines • CHEST Supplement, September 2004 • Overall CVA Risk for AF 4.5% per year • Risk increases with Age – 1.5% per year 50-59 yo – 10% per year 80-89 yo – 20% per year 90 yo C H A D S2 Gage et al, Circulation 2004 Congestive Heart Failure Hypertension -Treated; untreated >140/90 mmHg Age -Older than 75 Diabetes Stroke - 2 CHADS2 CVA risk/yr on ASA Low = 0 0.8 Med = 1-2 2.7 High = 3 or more 5.3 • Adjusted dose warfarin—Target INR 2.5— reduces CVA risk 60% • ASA reduces CVA risk 20% Warfarin Also Decreases Severity • INR 2.0-3.0 • Associated with reduced severity of stroke • Greater likelihood of survival INR Intensity & CVA Severity • 596 strokes/13,559 pts w/ NVAF – 32% warfarin – 27% ASA – 42% neither Hylek, et al, N Engl J Med 2003 1. Risk for CVA sharply increased INR < 2 2. CVA severity & fatality with INR 1.5 – 1.9 ~ INR < 1.5 3. With INR 2-3, CVA more likely to be “minor” Bleeding Risk • Warfarin increases risk of major hemorrhage 1.7 x risk associated with ASA Bleeding Risk • • • • 65 yo and older Hx of noncardioembolic CVA Hx of GI Bleed > 1 Comorbid Conditions – Recent MI – Hct less than 30 – Creatinine > 1.5 – Diabetes Beyth et al. Am J Med 1998 250 Patients with AF or VTE SCORE Low = 0 MAJOR BLEED Less than 3% Moderate = 1-2 12% High = 3 48% (First 12 mos) • Overall incidence of major bleed 6.5% • Greatest risk for bleed first 30 days • Most were avoidable maintaining therapeutic INR range and avoiding NSAIDs Other Risk Factors Excess Warfarin Anticoagulation • • • • • • • APAP intake 9100 mg/wk or more New medication known to increase warfarin effect (Note: antibiotic, PPI, amiodarone, SSRI) Bleed vs. CVA risk Recent diarrheal illness Decreased oral intake Incorrectly taking higher dose of warfarin than prescribed Hylek et al. JAMA 1998 STROKE RISK -CHF vs. Bleeding Risk Hx GI Bleed -Hypertension -75 yo & Older 65 yo & Older -DM -Stroke Hx CVA Comorbid > 1 Recent MI Hct 30 or less Cr > 1.5 DM • 145 pts w/ ICH on warfarin • 870 pts on warfarin w/o ICH • Increasing Age (especially > 85) • Increasing INR (especially > 3.5) Fang et al. Annals of Internal Medicine 2004 • Risk of ICH was NOT lower in elderly pts w/ AF when INR < 2.0 compared to INR 2.0-3.0 • EVEN FOR PTS OLDER THAN 75 ACCP Recommendations No Risk Factors 0-1 risk factor More than 1 risk factor ASA 325 mg/day Warfarin (INR=2.5) or ASA 325 mg/day Warfarin (INR = 2.5) Atrial Flutter & Paroxysmal AF recommendations same as for sustained NVAF Bottom Line • Stroke Risk • Bleeding Risk • Patient Functional & Cognitive Status • incl. falls risk Patient Compliance • Patient Preference Suggest: 1. INR 2.5 (2.0 - 3.0) 2. Attention to risk factors for bleeding If bleed occurs, target INR 2.2 (1.8 - 2.5) 3. More frequent monitoring 4. Attention to Rx med or OTC med change • Role of Anticoagulation Clinic Patient Sample #1 Initiating Warfarin Elderly Frail Malnourished CHF Liver Disease Concurrent Medications (cytochrome P450 isoenzymes mutation) Lower Dose In Elderly • “…starting dose of less than 5 mg might be appropriate in the elderly…” • Nomograms available, but few geriatric patients represented Daily Warfarin Dose (in AF) Age Male Female 50-59 5.4 mg 5.0 mg 60-69 4.6 mg 4.0 mg 70-79 4.3 mg 3.5 mg 80-89 3.9 mg 3.0 mg > 90 3.6 mg 3.0 mg Garcia et al, CHEST June 2005 • In each age group, median daily dose for afib pts less than for VTE pts • Older women require lowest doses • When warfarin initiated, 5 mg/day will lead to overanticoagulation for many geriatric patients • Lower initiation and maintenance doses for elderly patients Warfarin Initiation (hospitalized*) • 4 mg daily x 3 days @ dinnertime • INR – Morning 4th Day • INR 1.0 to < 1.3 5 mg 1.3 to < 1.5 4 mg 1.5 to < 1.7 3 mg 1.7 to < 1.9 2 mg 1.9 to < 2.5 1 mg > 2.5 daily INR hold until INR < 2.5 resume @ 1 mg/day • Otherwise, INR repeated every 2-3 days Siguret et al. Am J Med 2005;118:137-142 Other Options ??? • For NVAF pts – ACTIV Study – Warfarin vs. ASA/Clopidigrel • Ximelagatran Ximelegatran • Oral Direct Thrombin Inhibitor • Fixed Dose • Fast onset and offset activity • Very few food/drug interactions • No laboratory monitoring Ximelegatran, cont. • Adverse Effects 1. Liver enzyme elevation 2. Risk for CAD AstraZeneca EXANTA® (ximelagatran) Tablets NDA 21-686 FDA Advisory Committee Briefing Document 10 September 2004 pg. 109 Bridging Therapy Anticoagulation Perioperative Interruption of Warfarin VTE Risk vs. Hemorrhage Risk Chest 2001, September Supplement Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine, 2005;72(Suppl 1) Chest 2004;126(3):September 2004 Supplement, pg. 215S