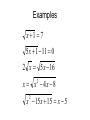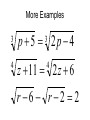* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 9.5 and 9.6
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Cubic function wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
Matrix calculus wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic equation wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
System of linear equations wikipedia , lookup
Section 8.5 and 8.6 Multiplying and Dividing Radicals/Solving Radical Equations Multiplying Radicals Multiplying radicals utilizes the previouslydiscussed concepts: • The distributive property • The FOIL method • Simplifying radicals • Combining like radical terms The Rules a b ab a b c d ac bd a a a a 2 a a b a b Be Careful!!! • Do not confuse the rules for multiplication with the rules for addition. Examples 2 32 9 7 14 7 14 13 7 3 11 6 2 4 p 7 p 9 6 y 4 6 y 4 2 Dividing Radicals • Dividing radicals is actually not division. • Rationalizing the denominator is the process of removing radicals from the denominator. • There are two cases for rationalizing the denominator. Case 1: One term in the denominator • Multiply numerator and denominator by the term in the denominator. 12 6 5 24 52 y 242t 9 u 11 Case 2: Two terms in the denominator • Multiply numerator and denominator by the conjugate of the denominator. 4 5 6 5 6 3 2 a b a b Solving Radical Equations 1. Isolate the radical expression, if possible. 2. Raise each side of the equation to a power equal to the index. 3. Solve the resulting equation: a. If linear, isolate the variable b. If quadratic, solve by factoring 4. If you have more than one solution, sometimes one of them won’t work. You might want to check them. Examples x 1 7 5 x 1 11 0 2 x 5 x 16 x x 4x 8 2 x 15 x 15 x 5 2 More Examples 3 p 5 2p 4 4 z 11 2 z 6 3 4 r 6 r 2 2