* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide Answers
Alkali metal wikipedia , lookup
Group 12 element wikipedia , lookup
Alkaline earth metal wikipedia , lookup
Boron group wikipedia , lookup
Group 3 element wikipedia , lookup
Dmitri Mendeleev wikipedia , lookup
Period 6 element wikipedia , lookup
Period 3 element wikipedia , lookup
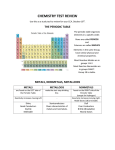
Elements and the Periodic Table Study Guide Answers What is the periodic table? Who created it and when? The periodic table was arranged by Dmitri Mendeleev, it shows all the known elements in the universe and organizes them by their chemical properties What is the benefit of the periodic table? The periodic table arranges the elements to make them easier to study. How is the periodic table arranged? The periodic table is arranged by increasing atomic number. (Remember the Atomic Number is the number of protons in an atom) What are the differences between periods and groups? There are 7 periods on the periodic table and they are the Horizontal rows, There are 18 Families ( or groups), these are the vertical columns; elements in the same group have similar chemical and physical properties, What are families of the periodic table? There are 18 Families ( or groups), these are the vertical columns; elements in the same group have similar chemical and physical properties, What are at least 3 characteristics for: Alkali Metals ● 1st group/ family ● very reactive metals ● soft metal, easy to cut ● reacts violently with water Alkali Earth Metals ● 2nd group/family ● reactive metal that always combines with nonmetal in nature Transition Metals ● group/family 3-12 ● less reactive and harder metal ● used in jewelry and construction ● most common metals are found here Halogens ● Group 17 ● very reactive nonmetal ● always combine with other elements in nature Noble Gases ● Group 18 ● Non reactive non metal ● Gases List the properties of a metal. Where are they located on the Periodic Table? Located on the left side of the periodic table to the left of Boron stair step. ● ● ● ● Good conductors of heat and electricity Shiny Ductile ( can be stretched into wire) Malleable (can be pounded into sheets) List the properties of a non-metal. Where are they located on the Periodic Table? NonMetals are on the right of the boron stair step. ● ● ● ● ● Poor conductors of heat and electricity Dull in color Not ductile Not malleable Many are gases List the properties of a metalloid. Where are they located on the Periodic Table? Metalloids are located on either side of the Boron Stair step have properties of both metals and nonmetals. ● they are solids that can be shiny or dull ● they conduct heat and electricity better than nonmetals, but not as well as real metals ● they are ductile and malleable What is the difference between an element and a compound? An element is composed of a single kind of atom, while a compound is where two or more elements are chemically bonded together. What are the particles that make up an atom, and what are the correct charges that are associated with each particle? Proton Positive Neutron Neutral Electron Negative What two particles make up the nucleus of the atom and how are they held together? The nucleus is made up with protons and neutrons; they are held together by the attraction between the protons and electrons. Which particle spins around the nucleus? Describe the motion around the nucleus and any other characteristics of that particle. The electron travels around the nucleus at a high rate of speed forming the electron cloud, the electrons are very small and light. List the number of Protons, Neutrons, Electrons, Atomic Mass and Atomic Number for the following elements: Sodium, Nickel, Gold, Aluminum, Neon, Silicon Sodium Atomic Number Atomic Mass Protons Neutrons Electrons _____11__ _____23__ _____11____ _____12____ _____11____ Atomic Number = # of protons = # of electrons(Protons and Electrons are always the same amount. Atomic # stands for # of protons) # of Neutrons = Atomic Mass - Atomic Number