* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digestive System (Human): Key Words
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
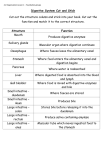
Digestive System (Human): Key Words Large intestine Liver Stomach Alimentary canal (or Gastrointestinal tract or Gut) The digestive tract: a tube starting at the mouth and ending at the anus. Anus The lower end of the rectum, forming the outlet of the alimentary canal. It is normally closed by a sphincter. Appendix (or Vermiform appendix) A short, wormlike tube opening into the cecum but closed at the other end. It contains lymphoid tissue, which is involved in immunity. Bile ducts Tiny tubes that carry bile (a liver secretion) from the liver to the duodenum. Bowel See Large intestine. Buccinator A cheek muscle used in chewing. Cecum The first part of the large intestine, forming a blind pouch. Colon The part of the large intestine between the cecum and rectum. It consists of four sections: the ascending, transverse, and descending colons, and the rectum. Digestion The chemical and mechanical breakdown of foods into simple substances that can be absorbed by the body. Duodenum The upper part of the small intestine, where most chemical digestion takes place. Enzymes Biological catalysts: proteins that speed up chemical reactions without themselves undergoing change. Epiglottis A cartilage flap behind the tongue that is closed during swallowing to stop food entering the larynx. Esophagus (or Gullet) The muscular tube through which food travels between the pharynx and the stomach. Gallbladder A pear-shaped bag where bile is stored, below the liver. Gastric Relating to the stomach. Gastrointestinal tract See Alimentary canal. Gullet See Esophagus. Gut See Alimentary canal. Haustrum One of the pouches on the outer surface of the colon (plural: haustra). Hepatic Relating to the liver. Ileum The last part of the small intestine. Jejunum The middle part of the small intestine. Large intestine (or Bowel) The lower part of the alimentary canal, comprising the cecum, colon, and rectum. It absorbs water and eliminates body wastes as feces. Liver The largest organ in the body, © Diagram Visual Information Ltd. divided into four lobes. Its many functions include the manufacture of bile, a digestive juice. Masseter A cheek muscle used to chew. Mesentery Peritoneum (abdominal membrane) attaching digestive and other organs to the rear abdominal wall. Mucous membranes The mucussecreting linings of the digestive, respiratory, reproductive, and urinary tracts. Pancreas A tongue-shaped gland located in the abdomen that produces glucagon, insulin, and pancreatic juice. Omentum Peritoneum (abdominal membrane) linking the stomach to other abdominal organs. Palate The roof of the mouth. Pancreatic islets (or Islets of Langerhans) Scattered areas of the pancreas that produce glucagon and insulin. Parotid glands See Salivary glands. Peristalsis Waves of muscular contractions that force substances, such as food, through internal passageways. Pharynx The throat. Pylorus The narrow exit from the stomach into the duodenum, closed by a sphincter. Rectum The last part of the colon, where feces collect before leaving the body. Salivary glands The lingual, parotid, sublingual, and submandibular glands that produce saliva. Sigmoid colon The S-shaped final part of the colon. Small intestine The alimentary canal between the stomach and large intestine, comprising the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Most digestion occurs here. Sphincter A ring-shaped muscle that contracts to close an orifice, such as the pyloric sphincter and the anal sphincters. Stomach A muscular baglike part of the alimentary canal between the esophagus and small intestine. It stores, churns, and partially digests food. Taste buds Tiny sensory organs (circumvallate papillae, filiform papillae, fungiform papillae) on tongue and palate. Teeth Bonelike structures in the jaws. Different types (incisors, canines, premolars, molars) are specialized to pierce, tear, crush, and/or grind food. Tongue A mobile, muscular organ in the mouth, involved in tasting, chewing, swallowing, and speech. Vermiform appendix See Appendix. Villus A minute fingerlike projection. Huge numbers line the small intestine, increasing its surface area (plural: villi).