* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Functions Protection for organs of the inferior abdominopelvic
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
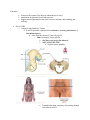
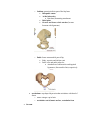
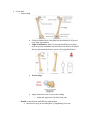
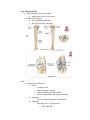
Functions Protection for organs of the inferior abdominopelvic cavity Attachment for powerful lower limb muscles Support and weight-transfer from axial to lower skeleton while standing and walking Pelvic Girdle o Complete ring formed by 3 bones R and L hip bones (right and left coxal bones, os coxae, pelvic bones, or innominate bones) Arise from the fusion of 3 bones by age 25 o Ilum: fan shaped, largest portion Ala, iliac crest, body, iliac tubercle ASIS, AIIS, PSIS, PIIS Superior spines palpable Trantubercular plan: imaginary line passing through iliac tubercle and L5 o Ischium: posteriorinferior part of the hip bone Ishiopubic ramus ischial tuberosity Butt bone, hamstring attachment Ishial spine Greater and lesser sciatic notches (become foreman with ligaments) o Pubis: forms anteromedial part of hip Body, superior and inferior rami Pubic crest and pubic tubercles Attachment of abd muscles and inguinal ligaments (Abercrombie line) respectively acetabulum: cup shaped depression that articulates with head of femur o means vinager cup in latin o acetabular notch, lunate surface, acetabular fossa Sacrum Lower limb o Femur: thigh Greater trochanter allows hip abductors and rotators to be placed away from leg extensors Angle of inclination: allows for increased mobility by keeping neck away from acetabulum and also allows for tibias to be placed directly underneath the body to assist with weight distribution Torsion angle Angle dictates direction of foot when walking o Abnormal: pigeon toe (in), duck foot (out) o Patella: sesamoid bone embedded in quads tendon Increases leverage in extending knee by lengthening lever arm o Leg: Fibula and tibia Tibia: medially placed is dominant Application of force (like radius) Fibula: posterolateral No weightbearing function Does not articulate with femur o Foot Anatomical classification: Tarsus o Calcaneus: heel o Talus: articulates with leg o Cuboid (lateral) navicular (medial) o Lateral, intermediate, and medial cuneiform Metatarsus o Great toe (halex) metatarsus considered 1 Phalanges o Each digit has 3 except great toe DIP, MIP, PIP