* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
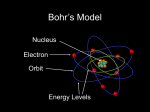
Page 74 #’s 1-5 1. Define each of the following: a. atom b. electron c. nucleus d. proton e. neutron a. the smallest piece of an element that is still that element b. a negative part of the atom which give the atom its volume c. the positively charged, extremely dense center part of an atom that contains nearly all the atom's mass but takes up a extremely small part of its volume d. the subatomic particle that has a positive charge equal (in size) to the negative charge of an electron; found in the nucleus e. the electrically neutral subatomic particle found in atomic nuclei 2. Describe one conclusion made by each of the following scientists that led to the development of the current atomic theory: a. Thomson b. Millikan c. Rutherford a. concluded that all atoms have charged parts some positive, some negative b. confirmed the negative charge of the electron and suggested the mass of an electron is ~ 1/2000 of the mass of a hydrogen atom c. determined that most of the mass of an atom is found in the nucleus and that the nucleus occupies very little space within an atom 3. Compare and contrast the three types of subatomic particles in terms of location in the atom, mass, and relative charge. Electrons surround the nucleus and have a negative charge and small mass relative to protons and neutrons Most of an atom's mass Is In its nucleus, which is near the center and is composed of protons and neutrons Protons have a positive charge; neutrons have no charge. 4. Why is the cathode-ray tube in Figure 3-4 connected to a vacuum pump? Because charges (Electrons) will flow through gases only at very low pressures 5. Label the charge on the following in a cathode-ray tube. State the reasons for your answers. a. anode: positive, connected to the positive terminal of the voltage source b. cathode: negative, connected to the negative terminal of the voltage source Page 87 #’s 3-6 3. a. What is an atom? b. What two regions make up all atoms? a. the smallest piece of an element that keeps the chemical properties of that element b. the nucleus and the electron clouds 4. Describe at least four properties of electrons that were determined based on the experiments of Thomson and Millikan. An electron is negatively charged (Thomson), it has a mass approximately 1/2000 that of a hydrogen atom (Millikan), it has a fixed charge-to-mass ratio (Millikan), and it is present in atoms of all elements (Thomson). 5. Summarize Rutherford’s model of an atom, and explain how he developed this model based on the results of his famous gold-foil experiment. His model had mostly all of the mass in the nucleus; He bombarded gold atoms with positively charged particles (beta particles). Most beta particles went through the atom, but some bounced back (the atom is mostly empty space with the very small, very dense nucleus at the center – giving the atom its mass; and the electrons spinning around the nucleus – giving the atom its volume. 6. What one number identifies an element? The atomic number