* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Geometry Student Project Material Outline
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
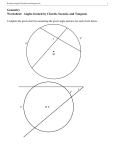
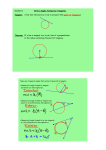
Geometry Student Project Material Outline- Ch. 10 Pelosi Circles Sec 1 -In a circle define, draw and label: the name of a circle, center, radius, chord and diameter. -Explain congruent circles and concentric circles. -Explain how to find the circumference of circles. -Explain inscribed and circumscribed polygons on a circle. Sec 2 -Explain central angles, minor arcs, major arcs and semicircles. -Explain congruent arcs and adjacent arcs. -Explain how to solve for arc lengths. Sec 3 -Explain that when a diameter or a radius are perpendicular to a chord it bisects the chord and the arc. Explain the converse of this. -Explain that 2 chords are congruent if they are equidistant from the center. Sec 4 -Explain inscribed angles and intercepted arcs. -Explain how to solve for inscribed angles. -Explain that inscribed angles intercepting the same arc are equal. -Explain that an inscribed angle intercepting the diameter is a right angle. -Explain an inscribed quadrilateral has supplementary opposite angles. Sec 5 -Define and explain a tangent, point of tangency, common internal and common external tangents. -Explain how a tangent to a radius is perpendicular and its converse. -Explain if 2 segments from one point are tangent to the same circle they are equal. Sec 6 -Define and explain a secant. -Explain that if a tangent and a secant intersect at a point of tangency that the angle formed is half of the intercepted arc. -Explain that the angle formed by 2 secants outside a circle is half of the difference of the intercepted arcs. -Explain that the angle formed by 2 secants inside a circle is half of the sum of the intercepted arcs. -Explain that the angle formed by 2 tangents from the same point is half of the difference of the intercepted arcs. Sec 7 -Explain that intersect chords segments are equal when multiplied together. -Explain that the product of a secant and its external secant segment equals the other if two secants intersect at the same point. -Explain that the same is true for a tangent and a secant.