* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slides 3
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
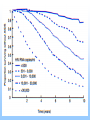
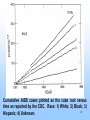
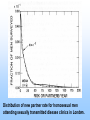
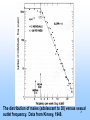
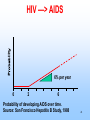
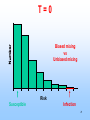
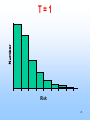
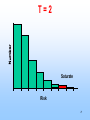
EPIDEMIOLOGY 200B Methods II – Prediction and Validity Scott P. Layne, MD 1 PART 3 Human Immunodeficiency virus Epidemic Between Hosts March 2010 2 TWO EPIDEMICS Between people HIV is a risk-based disease Not all individuals are at equal risk Within people HIV-1 & HIV-2 disable the immune system Predisposes to opportunistic infections & cancer 3 GLOBAL VIEW 2.0 M HIV/AIDS deaths (2007) male-to-female ratio ~ 1 30 - 36 M living with infection (2007) male-to-female ratio ~ 1 2.0 million children < 15 years 2.7 M new infections (2007) male-to-female ratio ~ 1 0.4 million children < 15 years 4 GLOBAL VIEW Becoming #1 infectious disease killer in the world In the US, HIV is #2 cause of death in men 25 - 44 years Millions to billions of viral genotypes Antiviral therapies expensive Antiviral resistance increasing Vaccine trials underway but promise unclear 5 6 CLINICAL FEATURES HIV progressive, chronic disease Infections irreversible, not curable Progression associated with HIV loads Higher viral loads cause faster CD4 cell declines Lower viral loads cause slower CD4 cell declines Viral loads < 102 associated with slower declines Viral loads > 104 associated with faster declines 7 CELLULAR MARKER Normal CD4 counts (range) 900 - 1800 per mm3 Untreated HIV infection Decline is 50 - 80 per year AIDS diagnosis at 180 per mm3 on average (MACS). Immunodeficiency CD4 counts < 200 per mm3 Opportunistic infections CD4 counts < 50 per mm3 8 9 DISEASE PHASES Acute retroviral syndrome 50 – 90% of cases Occurs 2 – 4 weeks post exposure Asymptomatic period 50% develop significant disease within 10 years Symptomatic period 1. Persistent generalized lymphadenopathy (PGL) 10 DISEASE PHASES Symptomatic period (cont.) 2. AIDS related complex (ARC) Fever Fatigue Diarrhea Weight loss Night sweats 3. Full blown AIDS Opportunistic infections Malignancies Progressive wasting Encephalopathy 11 OPPORTUNISTIC INFECTIONS Pneumocystis carinii Toxoplasmosis pneumonia encephalopathy Cryptosporidia Cryptococcus neoformans Candida albicans Histoplasmosis profuse diarrhea meningitis esophagitis disseminated Mycobacterium tuberculosis Mycobacterium avium Herpes simplex pneumonia, disseminated pneumonia mucocutaneous ulcers Cytomegalovirus pneumonia, retinitis, gastroenteritis localized, disseminated12 Varicella-zoster FURTHER MANIFESTATIONS Malignancies Kaposi’s Sarcoma Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma Neurological AIDS dementia Memory Loss Depression Seizures and Coma Wasting Slim disease Severe intractable wasting & diarrhea More common in Africa Associated with mix of opportunistic infections 13 OUTCOMES AIDS Mortality, pre-antiretrovirals 75% mortality within 2 years after AIDS diagnosis Today Drug treatments have slowed progression to AIDS Recent advances have not reduced mortality rates 14 EPIDEMIOLOGY Transmission routes Overall by intimate contact Primarily heterosexual contact worldwide No evidence of airborne, vector transmission Transmission probabilities Sexual (per contact) 0.001 – 0.004 (developed countries) 0.041 – 0.075 (female-to-male in Thailand) Sexual (per partner) 0.1 – 0.2 (homosexual) Perinatal (per birth) 0.25 – 0.40 for HIV-positive mothers Parenteral (per needle-stick) 15 0.002 – 0.004 for health workers EPIDEMIOLOGY Transmission probability increased by Breaks in epithelial surface Presence of ulcerative STDs Lack of circumcision Receptive anal intercourse Multiple partners Fragile mucosa of rectum Various HIV phenotypes / genotypes ? 16 EPIDEMIOLOGY Human ID-50 Undefined Cell-free vs cell-associated virus Relative contributions of each are not determined May depend on the particular route of transmission HIV found in body fluids Plasma Semen Cervical secretions Breast milk Saliva Tears 17 MODEL DEVELOPMENT 18 KEY CONCEPTS Initial growth of the AIDS epidemic in the United States Rate that people become infected with HIV Rate that people progress to AIDS Prior to antiretrovirals Prior to opportunistic infection prophylaxis Why is this easier than today? 19 Cumulative AIDS cases plotted as the cube root versus time as reported by the CDC. Race: 1) White; 2) Black; 3) 20 Hispanic; 4) Unknown. KEY CONCEPTS Risk-based disease Risk is not distributed equally among the population Behavorial mixing People with similar risk tend to interact among themselves Biased mixing People interact equally with others Unbiased mixing Which one is it? 21 Distribution of new partner rate for homosexual men 22 attending sexually transmitted disease clinics in London. The distribution of males (adolescent to 30) versus sexual 23 outlet frequency. Data from Kinsey, 1948. HIV —> AIDS 6% per year 0 2 6 Probability of developing AIDS over time. Source: San Francisco Hepatitis B Study, 1988 24 T=0 Biased mixing vs Unbiased mixing Risk Susceptible Infection 25 T=1 Risk 26 T=2 Saturate Risk 27 T=3 Saturate Risk 28 T=4 Infection Wave Risk 29 T=5 Risk 30 Calculation of fraction infected versus risk behavior when mixing is biased at various times (t = 5, 10, 15, ... 40 units) 31 Homogenous Mixing The fastest growth of infection of infection occurs in average risk group Early growth is nearly exponential and larger than biased mixing case Calculation is not consistent with CDC observations 32 Calculation of fraction infected when mixing is 33 homogeneous at various times (t = 5, 10, 15, ... 40 units) Biased Mixing Infection grows to saturation in the highest risk group and moves progressively to lower risk groups Calculation is consistent with CDC observations 34 IMPLICATIONS & INSIGHTS Vaccines Define efficacy as probability of preventing infection Vaccine shifts or rescales peoples' position in risk-space Even with highly effective vaccines, high-risk people will maintain transmission STDs and core groups 35 Vaccine given at T = 5 Risk 36 T=6 Infection Wave Risk 37 PREVENTION HIV transmission is risk-based Identify the risks that are associated with transmission Intervene and modify the risks that facilitate transmission 38 PREVENTION Modify sexual behavior Number of partners Type of practices Safe sex practices and failure rates (condoms) Reduce co-factors Sexually transmitted diseases Programs to identify and treat STDs Intravenous drugs Reduce abuse Reduce sharing of injection equipment Promote disinfection of injection equipment Provide clean injection equipment 39 PREVENTION Disruption of family and tribal units Education to modify behaviors Technology Reduce cost of HIV testing Make HIV testing more widely available Rapid testing Vaccines Phase III trials underway / promise? Variability of the viral genome is a problem Selecting viral strain for vaccine is a problem Not clear which immune responses are protective False sense of protection that increases infection 40 READING Stirling A. Colgate, et al. 1989. Risk behavior-based model of the cubic growth of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 4793 – 4797. 41