* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 15- Lateral mesoderm and endoderm
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Regional differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
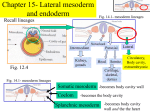
Chapter 15- Lateral mesoderm and endoderm Recall lineages Fig. 14.1- mesoderm lineages Notochord Intermediate Kidney, gonads Fig. 12.4 3 regions: Fig. 14.1- mesoderm lineages Paraxial Lateral Circulatory, Head Somite Body cavity, extraembryonic Cartilage, skeletal, dermis a. _________________-becomes body cavity wall b. _______ -becomes the body cavity c. ___________________ -becomes body cavity wall and the the heart Lateral mesoderm c. Splanchnic mesoderm How does the heart develop?? 25hr 26hr Fig. 15.3 ___________ 1. Splanchnic mesoderm halves begin to ______ 2. These cells differentiate into ___________ (heart lining and valve precursors and ______________ (heart muscles) 28hr 27hr Myocardium 3. Endocardium tubes _______ 4. Mycocardium ________ 5. Heart begins beating even while ________ is occurring 72hr Blood vessel formation Lateral mesoderm 2 steps- 1._____________ and 2. ____________ Note: Blood vessels form independently of the heart, then link up Some background Info Constraints on blood vessel construction 1. ____________ an organism must: • • • Obtain ___________before the intestine develops Use __________ before there are lungs Excrete _________ before there are kidneys Fig. 15.13- “extra” archs in mammal development 2. ________________• Six pairs of __________ loop out- these enable primitive fish gills to oxygenate blood, but these serve no obvious purpose in mammals and birds. 3. ____________- Blood flows easier through large vessels, yet efficient ____________requires small vessels and ________________ blood Solution- Large vessels branch into very small ones with overall more cumulative volume capacity Blood vessel formation 1. Vasculogenesis Blood vessels and blood cells are intimately connected Lateral mesoderm Fig. 15.14 BMP Endothelial cells line __________ Angiogenic cell cluster (_________ ________) __________ Fig. 15.16 Primitive blood cells __________cells 1. Vasculogenesis Transcription factors in vasculogenesis 1. _______ is required for _____________formation 2. ________ is required for blood island and blood vessel formation VEGF is a target for ______________ “Tumors gotta eat” 3. ______ is required proper blood vessel formation (involved in communication between endothelial cell and _____________) Lateral mesoderm Lateral mesoderm 2. Angiogenesis Definition- _________ and _______ of capillary beds, arteries and veins Note- Capillary networks of each organ arise within the organ itself, not from larger _______! VEGF plays key role ________ stabilizes capillary network ______ recruits pericyte cells to ensure __________ of capillaries Lateral mesoderm 2. Angiogenesis Arteries vs. veins?? •Arteries have _____________in cell membranes •Veins have _________________ (called EphB4) in cell membranes Arterial Venous (__________) (______) Fig. 15.17 Functions of the EphrinB2/EphB4 system 1. Ensure that arteries only link up with _____, not other arteries 2. Ensure capillary fusion only occurs with like cells (e.g. only arteries with arteries) Lateral mesoderm 2. Angiogenesis Many organs make their own angiogenesis factors •Example- placenta Developing placenta secretes ___________ to promote angiogenesis, then later secretes ___________________ to inhibit angiogenesis Angiogenesis plays key role in tumor development •A tumor must induce _________________ in order to ______ •Hence, if use a drug that inhibits this ______________, can possibly slow cure some ___________ Lateral mesoderm Development of Blood Cells Fig. 15.20 ____________ – embryonic cells capable of producing many cell types, including other ______________ Largest population of stem cells is in the _______________ “Committed” Stem Cell (CFU-M,L) B-cell lineage T-cell lineage “Differentiating” “Differentiated” Lateral mesoderm Development of Blood Cells The stem cell (CFU-M,L) also gives rise to another cell lineage: “Committed” Stem Cell (CFU-M,L) B-cell lineage “Differentiating” “Differentiated” ____________ Platelets _________ Myeloid T-cell lineage precursor cell Fig. 15.21 Eosinophils ___________ ____________ ___________ factors that direct blood cell formation are termed “_________” Note that this is the point of ___ _______- cells are __________ to a becoming only one cell type Lateral mesoderm Development of Blood Cells Blood development (hematopoiesis) occurs in two phases: 1. _____________ Angiogenic cell cluster • Occurs in blood islands in mesoderm (blood islands) near the yolk (recall fig. 15.16) • Supplies developing embryo with oxygen • ___________ inhibit blood and blood vessel formation Fig. 15.16 • __________- disappear later in development 2. ___________ •Formed in nodes of mesoderm surrounding aorta (in a region called the _________________________ (AGM) region) •Lasts the _______ of the individual Example- In mouse, stem cells originate in yolk sac, then later in AGM region Fig. 15.24 Endoderm Recall Fig. 12.4 Embryonic endoderm gives rise two ____ Endoderm Buds into __________ tube Primitive gut endoderm (Esophagus,stomach,small intestine,colon) __________ tube _____, _________, pancreas _________ 1. _______ endoderm – tissues are derived from _________________ Auditory cavities Tonsil walls _______(T-cell development) Fig. 13.1 Pharyngeal arches ______________ _____(sprout form base of forth arch) 2. ____________ endoderm The _________________ buds out form the foregut, then branches to form ________, _________ and ___________ The ____________ is actually formed by the fusion of two distinct buds (one ventral and one dorsal) Liver bud Stomach Gall Bladder Pancreas Pancreas (ventral) (dorsal) Fig. 15.29 What directs formation of liver from the endoderm?? The notochord (and mesenchyme) produces factors that ________ liver induction The __________________ secretes ____ that ________ the factors that inhibit liver induction Thus, _____signals the __________ region of the endoderm to become liver Fig. 15.30 The respiratory tube • ______ are one of the last _________ to differentiate • Alveolar cells of the lung produce _________ at 34 weeks gestation • Thus, a premature infant cannot breathe properly foregut Pharynx trachea Lung buds esophagus Week 4 (humans) Fig. 15.31 Four problems of a land-dwelling egg Problem Solution Day 2 chick embryo 1. ____________ Amnion secretes amnionic fluid into ________ 2. ____________ ______ exchanges gases 3. ____________ _________ supplies nutrients from blood vessels in yolk 4. ____________- ________ holds waste (vestigal in humans) Day 9 chick embryo Fig. 15.33