* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CONOTRUNCAL ANOMALIES A Case Based Review
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Turner syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiothoracic surgery wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
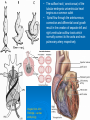
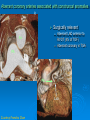
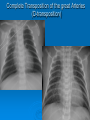
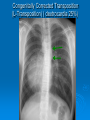
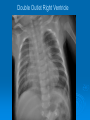
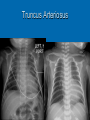
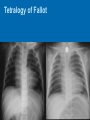
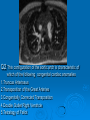
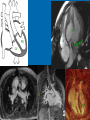
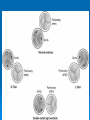
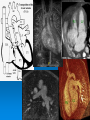
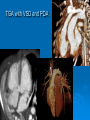
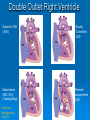
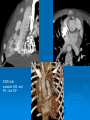
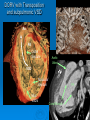
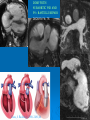
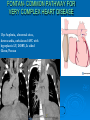
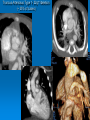
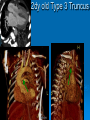
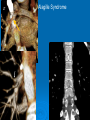
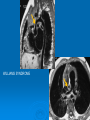
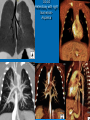
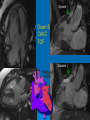
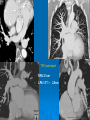
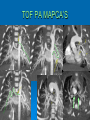
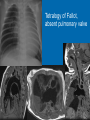
CONOTRUNCAL ANOMALIES A Case Based Review Beverley Newman M.D. Professor of Radiology Lucile Packard Children’s Hospital at Stanford University Thanks to Frandics Chan for supplying • The outflow tract ( conotruncus) of the tubular embryonic univentricular heart begins as a common outlet • Spiral flow through the arteriovenous connection and differential conal growth result in the creation of separate left and right ventricular outflow tracts which normally connect to the aorta and main pulmonary artery respectively Images from John Partridge – cardiac embryology Conotruncal Anomalies Transposition of the Great Arteries Double Outlet Right Ventricle Truncus Arteriosus Tetralogy of Fallot Aberrant coronary arteries associated with conotruncal anomalies R L Surgically relevant Ao Aberrant LAD anterior to RVOT (4% of TOF) Aberrant coronary in TGA PA PA LAD Courtesy Frandics Chan Q1. The most common plain film radiographic appearance of complete transposition of the great arteries in the newborn is: 1. Normal 2. Cardiomegaly and shunt vascularity 3. Egg on a string 4. Bulge of left superior heart border 5. Coeur en Sabot Complete Transposition of the great Arteries (D-transposition) Congenitally Corrected Transposition (L-Transposition) ( dextrocardia 25%) Double Outlet Right Ventricle Truncus Arteriosus Tetralogy of Fallot Q2 This configuration of the aortic arch is characteristic of which of the following congenital cardiac anomalies 1.Truncus Arteriosus 2.Transposition of the Great Arteries 3.Congenitally Corrected Transposition 4.Double Outlet Right Ventricle 5.Tetralogy of Fallot RV RV LV LV LV RV Transposition of the Great Arteries Discordant connections of the ventricles and great arteries CCTGA- also atrioventricular discordance: associated with VSD, ASD, tricuspid abnormality (Ebstein’s),pulmonic stenosis, conduction abnormalities TGA – associated with VSD, ASD, PDA, pulmonary stenosis/atresia, Ao coarctation/interruption, AV valve abnormalities and RV hypoplasia or single ventricle RV RV LV LV TGA with VSD and PDA Q3 Which of the following surgical procedures are used to repair Double Outlet Right Ventricle 1. Arterial switch 2. Rastelli 3. VSD closure and PA outflow tract patch 4. RV to PA conduit 5. Fontan 6. All of the above Double Outlet Right Ventricle Subaortic VSD ( 50%) Doubly Committed VSD Subpulmonic VSD (30%) ( Taussig-Bing) Remote/ uncommitted VSD Frank et al Radiographics : 30;2010 Double Outlet Right Ventricle Both great arteries arise predominantly from the right ventricle. Both great arteries have subvalvular conal muscle Associated with VSD, pulmonary stenosis or atresia,TGA, mitral stenosis or atresia, hypoplastic LV, straddling AV valves, subaortic/aortic valve obstruction/coarctation May physiologically resemble TOF ( subaortic VSD and PS); Transposition ( Subpulmonic VSD); VSD( subaortic VSD); Hypoplastic or univentricular heart Double Outlet Right Ventricle Surgery: Subaortic VSD – Rastelli tunnel through VSD connecting LV with Ao RVOT obstruction may necessitate patch similar to TOF repair or RV – PA conduit Subpulmonary VSD – Switch and VSD patch Doubly committed VSD- Rastelli or switch depending on LV /Ao relationship Remote VSD – may need single ventricle palliation and eventual Fontan DORV with subaortic VSD and PS – like TOF DORV with Transposition and subpulmonic VSD Ao PA Outlet Septum Aortic Valve VSD Muscular Septum Mus. VSDs PA Conal Muscle DORV WITH SUBAORTIC VSD AND PS – RASTELLI REPAIR DECR RV FX, TR Gaca, A Radiology 2008. 248:1;44 FONTAN- COMMON PATHWAY FOR VERY COMPLEX HEART DISEASE 13yo Asplenia, abnormal situs, dextrocardia, unbalanced AVC with hypoplastic LV, DORV, Lt sided Glenn/Fontan Q5 Which of the following syndromes are most often associated with Truncus Arteriosus 1. Di George Syndrome 2. Heterotaxy with Asplenia 3. Alagille Syndrome 4. Williams Syndrome 5. Down syndrome TRUNCUS ARTERIOSUS Collett Classification Van Praagh Classification TRUNCUS ARTERIOSUS Single arterial vessel arises from the heart which gives rise to aortic, pulmonary and coronary arteries Association with VSD, truncal valve abnormality, RAA, interrupted aortic arch (11-14%), abnormalities of the mitral valve and anomalous pulmonary venous connections Truncus Arteriosus Type 1- 22q11deletion (~ 35% of cases) 2dy old Type 3 Truncus LT Alagille Syndrome WILLIAMS SYNDROME 3d old Heterotaxy with right IsomerismAsplenia Q4 Which of the four features of Tetralogy of Fallot is the most consistently present but also the most variable in severity 1.Overriding Aorta 2. Ventricular Septal Defect 3. Right Ventricular Hypertrophy 4. Pulmonary Outflow Obstruction Tetralogy of Fallot Most common cyanotic congenital heart defect Anterior malposition of the conal septum results in :overriding aorta; pulmonary outflow obstruction; ventricular septal defect and right ventricular hypertrophy Associated with VSD, Right aortic arch ( 25%), pulmonary atresia, PDA, major aorticopulmonary collaterals, ASD, CAVC Systole Down S CAVC TOF Diastole RVOT RV LV TOF post repair RPA 2.1cm LPA 1.3*1 – 2.5cm TOF PA MAPCA’S Tetralogy of Fallot, absent pulmonary valve Conotruncal Anomalies Summary Transposition of the Great Arteries The aorta moves upward and to the right instead of pulmonary artery Truncus Arteriosus Truncal Septum fails to develop Double Outlet Right Ventricle Arterial trunk divides but stays over on the right side Tetralogy of Fallot Truncal septum deviates anteriorly References 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Van Praagh R, Van Praagh S. The anatomy of common aorticopulmonary trunk (truncus arteriosus communis) and its embryologic implications: a study of 57 necropsy cases. Am J Cardiol 1965;16 (3):406–425. Frank L, Dillman JR, Parish V et al .Cardiovascular MR Imaging of Conotruncal Anomalies. RadioGraphics 2010; 30:1069–1094 Donnelly L.F, Higgins C.B. MR Imaging of Conotruncal Abnormalities. AJR 1996;166:925-92 Dorfman AL, Geva T: Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of congenital heart disease: conotruncal anomalies. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 8:645-659, 2006. Partridge J. Cardiac Embryology for Imagers. Restivo A, Piacentini G, Placidi S, Saffirio C, Ma¬rino B. Cardiac outflow tract: a review of some embryogenetic aspects of the conotruncal region of the heart. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 2006; 288(9):936–943. 7. Yoo S, Macdonald C, Babyn P. Chest Radiographic Interpretation in Pediatric Cardiac Patients. Thieme NY 2010. 8. Chan FP . Transposition of the Great Arteries Ch45;Truncus Arteriosus Ch46. In Ho H , Reddy GP Cardiovascular Imaging - Expert radiology series. Elsevier, Mosby, Saunders 2011 9. Gaca AM, Jaggers JJ, Dudley LT, Bisset GS, 3rd. Repair of congenital heart disease: a primerpart 1. Radiology 2008; 247:617-631. 10. Gaca AM, Jaggers JJ, Dudley LT, Bisset GS, 3rd. Repair of congenital heart disease: a primer-Part 2. Radiology 2008; 248:44-60. References 11. Gatzoulis MA, Webb GD, Daubeney PEF, eds. Diagnosis and Management of Adult Congenital Heart Disease. London, UK: Churchill Livingstone, 2003. 12 Jonas RA, DiNardo JA. Comprehensive surgical management of congenital heart disease. London, England.: Arnold/Oxford University Press, 2004 13. Towbin A , Newman B. Syndromes and chromosomal disorders and the heart. In: Slovis T, editor. Caffey’s Pediatric Diagnostic Imaging, 11th edition. Elsevier Inc. (Philadelphia) 2007. Chap 95 16051632 14. McElhinney DB, Driscoll DA, Emanuel BS, Goldmuntz E: Chromosome 22q11 deletion in patients with truncus arteriosus. Pediatr Cardiol 24:569-573, 2003. 15. Feigenbaum H, Armstrong WF, Ryan T. Feigenbaum’s Echocardiography 6th edition 2005