* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
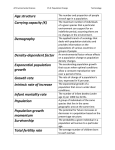
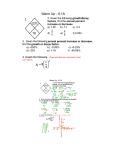
Exponential and Logarithmic Functions ● ● ● The line is the most important function in mathematics The exponential function is a very close second. Everything else is a distant third. ● Quadratics, polynomials, power functions, absolute value, rational functions, etc. Why is the exponential function so important? ● ● The exponential function measures “steady growth” The exponential function measures reproduction. ● Any time that things are making copies of themselves, and exponential function describes what happens. ● Populations → Animals making more animals. ● Investment → Money making more money ● Kinematics → Motion making more motion ● Radiology → Radioactive decay is negative reproduction (negative growth). ● Etc. Why is the exponential function so hard to understand? It grows too fast. ●People oversimplify. ● People oversimplify ● ● The exponential function is NOT about repeated multiplication The exponential function is CLOSELY RELATED to repeated multiplication. Imagine a population of bacteria ● ● ● Start with one bacterium Every five minutes, each bacterium splits, creating two bacteria. What does a graph of this population look like? O mins 5 mins 10 mins 15 mins Bacteria Graph “repeated multiplication” or “geometric growth” Bacteria Graph “repeated multiplication” or “geometric growth” exponential growth Exponential Growth Occurs NOT JUST when every individual is reproducing, But when EVERY FRACTION of every individual is reproducing “repeated multiplication” or “geometric growth” exponential growth Exponential Growth Exponential growth is used to APPROXIMATE situations like bacteria “repeated multiplication” or “geometric growth” exponential growth Every Fraction ● ● ● Populations → Animals making more animals. ● Investment → Money making more money ● Kinematics → Motion making more motion Reasoning about every fraction is very complicated. Repeated multiplication a lie, but it's a very useful lie, one that's not far from the truth. f(x)=2x f(x)=2x +1 *2 f(x)=2x *2 +1 *2 +1 f(x)=2x +1 *2 Going the other way *1/2 -1 +1, *2 -1, *(1/2) -1, *(1/2) y=1, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16, 1/32,... -1, *(1/2) Because I'm shrinking by halves, I will get very close to y=0, but I will never reach it. -1, *(1/2) Because I'm shrinking by halves, I will get very close to y=0, but I will never reach it. This is called an “asymptote” at y=0 Asymptote ● ● A line that your function gets infinitely close to, but never reaches. ● Horizontal ● Vertical ● Oblique (slanted) Every function of the form f(x)=abx has a horizontal asymptote at y=0. Consider the function below: Which of the following statements matches with this function? A) As x approaches infinity, f(x) approaches 0. B) As x approaches negative infinity, f(x) approaches 0. C) As x approaches infinity, f(x) approaches -4. D) As x approaches negative infinity, f(x) approaches -4. E) None of the above Solution D) As x approaches negative infinity, f(x) approaches -4. Alternate Solution ● 3x is sort of like “+1 to x, *3 to y” as I'm going right. ● ● 3x is sort of like “-1 to x, *1/3 to y” as I'm going left. ● ● As x gets bigger, 3x gets bigger and bigger. As x gets smaller, 3x gets closer and closer to 0. As x gets smaller, 3x-4 gets closer and closer to -4. D) As x approaches negative infinity, f(x) approaches -4. Negative b ● If 3^x is like repeatedly multiplying by 3, ● What is 3^(-x) like? ● 3^(-1)^(x)=(1/3)^x. ● 3^(-x) is like repeatedly multiplying by (1/3) Exponential Decay Logarithms ● A logarithm is an inverse of an exponential ● ● (see inverse functions) If I have the function f(x)=6x, then log67 means “what number does x have to be so that 7=6x?” Logarithm ● Logab ● Pronounced “Log base a of b” ● ● Means “the number (power) I have to raise a to to get b.” x=Logab means ax=b Special logarithms ● Log(b) means Log10b ● ln(b) means Logeb, where e≈2.7182818284 ● You only ever need one log function Loga(b)=Log(b)/Log(a)=ln(b)/ln(a) Why e? ● ● ● ● ● You'll find out more about e in studio. When every individual is doubling every time unit, the population fits f(x)=2x, When the same process is updated not just every time unit, but every fraction of every moment (and for every fraction of every individual), the population fits f(x)=ex. Because time is continuous, ex happens a lot more in real life problems than 2x. e is the most important number in mathematics (except for 0 and 1). Much more important than π. Domain of a Logarithmic function ● ● Exponential functions and logarithms are inverses. Because you can never get a negative number OUT OF an exponential, you can never put a negative number INTO a logarithm. Find the domain: a) b) c) d) e) A) x > 5/4 B) x < 5/4 C) x > -5/4 D) x < -5/4 E) None of the above Solution ● The number you put into a logarithm must be positive. ● 5-4x must be positive. ● 5-4x>0 ● 5>4x ● 5/4>x B) x < 5/4