* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 29: Additional Health Conditions
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
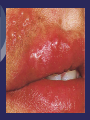
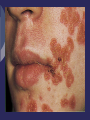
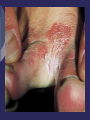
Chapter 23: Additional Health Concerns and General Medical Conditions Skin Infections Viral Infections Virus Small organism that can live only in a cell Upon entering cell it may immediately trigger a disease (influenza) or remain dormant (herpes) Can damage host cell by blocking normal function and using metabolism for own reproduction Virus ultimately destroys cell Herpes Cause of Condition Herpes simplex – viral infection that tends to occur in the same location (mucous membranes) Type I (cold sore) Type II (genitals) Herpes zoster Appears in specific pattern on body (innervated by specific nerve root) Re-appearance of chicken pox virus Signs of Condition Early indication = tingling or hypersensitivity in an infected area 24 hours prior to appearance of lesions Local swelling followed by outbreak of vesicles Heal in generally 10-14 days Care If an athlete has an outbreak they should be disqualified from competition due to contagious nature of condition Utilize universal precautions when dealing with herpes virus Use of antiviral drugs can reduce recurrence and shorten course of outbreak Verruca Virus and Warts Variety of forms exist Different types of human papilloma virus have been identified verruca plana (flat wart), verruca plantaris (plantar wart), and condyloma acuminatum (venereal wart) Uses epidermal layer of skin to reproduce and grow Wart enters through lesion in skin Signs of Condition Small, round, elevated lesion with rough, dry surfaces Painful if pressure is applied May be subject to secondary bacterial infection Care If vulnerable, they should be protected until treated by a physician Use of electrocautery, topical salicylic acid or liquid nitrogen are common means of managing this condition Bacterial Infections Bacteria are single celled microorganisms Disease development Bacterial pathogen enters host, growth of bacteria and production of toxic substances occurs and host attempts to fight infection Two types Staphylococcus Streptococcus Furuncle (Boils) Infection of hair follicle that results in pustule formation Generally the result of a staph infection Become large and painful Folliculitis Inflammation of hair follicle around face/neck or in the groin Impetigo Contagiosa Caused by streptococci Spread through close contact Symptoms of Condition Mild itching and soreness followed by eruption of small vesicles and pustules that rupture and crust Exhibits signs of inflammation Tenderness, warmth, redness and swelling Care Cleansing and topical antibacterial agents Systemic antibiotics Pus filled lesions should be drained Minimize the chances of the infection to spread to others Fungal Infections Cause of Condition Ringworm fungi (tinea) Cause of most skin, nail and hair fungal infections Tinea of the Groin (tinea cruris) Signs and Symptoms Mild to moderate itching and found bilaterally Brownish or reddish lesion resembling outline of butterfly in groin Care Treat until cured Will respond to many of the non-prescription medications Medications that mask symptoms should be avoided Failure to respond to normal management may suggest a non-fungal problem (such as bacteria) and should be referred to a physician May require additional topical medications and oral prescriptions Athlete’s Foot (tinea pedis) Cause of Condition Most common form of superficial fungal infection Webs of toes may become infected by a combination of yeast and dermatophytes Signs of Condition Extreme itching on soles of feet, between and on top of toes Appears as dry scaling patch or inflammatory scaling red papules forming larger plaques May develop secondary infection from itching and bacteria Care Topical antifungal agents and good foot hygiene Respiratory Conditions The Common Cold Cause of Condition Attributed to filterable virus that produces infection in upper respiratory tract in susceptible individual Susceptible individual Physical debilitation from overwork or lack of sleep Chronic inflammation from local infection Inflammation of nasal mucosa from allergy or from breathing in foreign substance Sensitivity to stress Sign of Condition Begins w/ scratchy, sore throat, stuffy nose, watery discharge and sneezing Some may experience a fever Various aches and pains Nasal discharge becomes thick and discolored from inflammation Care Symptomatic treatment (may last 5-10 days) Non-prescription cold medications Eat a balanced diet, consume 64 oz. of water Avoid emotional stress and extreme fatigue Influenza (Flu) Cause of condition Occurs in various forms as an annual epidemic Caused by a virus Symptoms of Condition Fever (102-103oF), chills, cough, headache, malaise, and inflamed respiratory mucous membrane w/ non-productive cough, watery eyes General aches and pains, headache becomes worse Weakness, sweating, fatigue may persist for many days Care Bed rest and supportive care Steam inhalation, cough medicines, and gargles Flu prevention – avoid contact with someone that has it Acute Bronchitis Cause of Condition Infectious winter disease that follows common cold or viral infection Fatigue, malnutrition or becoming chilled could be predisposing factors Sign of Condition Upper respiratory infection, nasal inflammation and profuse discharge, slight fever, sore throat and back muscle pains Fever lasts 3-5 days while cough can last 2-3 weeks Yellow mucus indicates infection Pneumonia can complicate condition Care Avoid sleeping in cold environment, avoid exercise in extreme cold w/out protection Rest until fever subsides, drink 3-4 quarts of water daily, ingest antipyretic analgesic, cough suppressant, and antibiotic Bronchial Asthma Cause of Condition Caused by viral respiratory tract infection, emotional upset, changes in barometric pressure or temperature, exercise, inhalation of noxious odor or exposure to specific allergen Sign of Condition Spasm of smooth bronchial musculature, edema, inflammation of mucus membrane Difficulty breathing, may cause hyperventilation resulting in dizziness, coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath and fatigue Care Prevention – determine causative factors Use of prescribed inhalers are effective in acute cases Exercise-Induced Bronchial Obstruction (Asthma) Cause of Condition Brought on by exercise w/ exact cause unknown Loss of heat and water (airway reaction), eating certain foods, sinusitis may also trigger Sign of Condition Airway narrowing due to spasm and excess mucus production Tight chest, breathlessness, coughing, wheezing, nausea, hypertension, fatigue, headache, and redness of skin EIA (continued) Care Regular exercise, appropriate warm-up and cool down, w/ intensity graduated Inhaled bronchodilators may be useful Exercise in warm, humid environment Coaches should be sure to remind athletes to have inhaler with them at all times Other Conditions That Can Affect the Athlete Infectious Mononucleosis Cause of Condition Virus that has incubation period of 4-6 weeks Transmitted through saliva Signs and Symptoms First 3-5 days -severe fatigue, headache, loss of appetite and myalgia Days 5-15 - fever, swollen lymph nodes and sore throat (50% will experience enlarged spleen) Possible jaundice, skin rash, puffy eyelids Care Supportive symptomatic treatment Acetaminophen for headache, fever and malaise Resume training after 3 weeks after onset if spleen not markedly enlarged/painful, athlete is afebrile, liver function is normal, and pharyngitis is resolved Iron Deficiency Anemia Cause of Condition Prevalent in menstruating women and males age 7-14 Three things occur during anemia Small erythrocytes Decreased hemoglobin Low ferritin concentration (compound that contains 23% iron) GI loss of iron in runners is common Aspirin and NSAID’s may cause GI bleeding and iron loss Menstruation accounts for most iron lost in women Vegetarian athletes may also be deficient in intake relative to iron loss Sign of Condition First stage of deficiency, performance declines Athlete may feel burning thighs and nausea from becoming anaerobic May display some mild impairments in maximum performance Care Eat a proper diet including more red meat or dark poultry; avoid coffee and tea (hamper iron absorption) Consume vitamin C (enhance absorption) Take supplements (dependent on degree of anemia) Sickle-Cell Anemia Cause of Condition Hereditary hemolytic anemia - RBC’s are sickle or crescent shaped (irregular hemoglobin) Less ability to carry oxygen, limited ability to pass through vessels, causing clustering and clogging of vessels (thrombi) Signs of Condition Fever, pallor, muscle weakness, pain in limbs Pain in upper right quadrant indicating possible splenic infarction Headaches and convulsions are also possible Care Provide anticoagulants and analgesics for pain Diabetes Mellitus Most common forms are Type I (insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus) and Type II (non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus) Cause of Condition Result of interaction between physical and environmental factors Involves a complete or partial decrease in insulin secretion Insulin Shock Cause of Condition Occurs when the body has too much insulin and too little blood sugar Sign and Symptoms Tingling in mouth, hands, or other parts of the body, physical weakness, headaches, abdominal pain Normal or shallow respiration, rapid heart rate, tremors along with irritability and drowsiness Care Adhere to a carefully planned diet including snacks before exercise Must determine food and insulin intake during questioning Diabetic Coma Cause of Condition Sign and Symptoms Loss of sodium, potassium and ketone bodies through excessive urination (ketoacidosis) Labored breathing, fruity smelling breath (due to acetone), nausea, vomiting, thirst, dry mucous membranes, flushed skin, mental confusion or unconsciousness followed by coma Care Early detection is critical as this is a lifethreatening condition Insulin injections may help to prevent coma Epilepsy Disordered cerebral function characterized by periods of altered consciousness, motor activity, sensory phenomena or inappropriate behavior caused by abnormal cerebral neuron discharge Not a disease Symptom manifested by a large number of underlying disorders Cause of Condition For some forms of epilepsy there is genetic predisposition Brain injury or altered brain metabolism Sign of Condition Periods of altered consciousness, motor activity, sensory phenomena or inappropriate behavior May last 5-15 seconds (petit mal seizure) or longer (grand mal seizure) Include unconsciousness and uncontrolled tonic-clonic muscle contractions Care Individuals that experience daily or weekly seizures should be prohibited from participating in collision sports (blow resulting in unconsciousness could result in serious injury) Must be careful with activities involving changes in pressure Can be managed with medication Care (continued) Athlete may experience undesirable side effects – care giver must be aware Be sure to have individual sit or lie down Remain composed Try to cushion athlete’s fall Keep athlete away from surrounding objects that could cause injury Loosen restrictive clothing Do not force anything between the athlete’s teeth Meningitis Cause of Condition Inflammation of meninges surrounding spinal cord and brain Caused by infection brought on by meningococcus bacteria Sign and Symptoms High fever, stiff neck, intense headache, sensitivity to light and sound Progress to vomiting, convulsions and coma Meningitis (continued) Care Cerebrospinal fluid must be analyzed for bacteria and WBC’s If bacteria is found isolation is necessary for 24 hours (very contagious), antibiotics must be administered immediately Monitored closely in intensive care unit Substance Abuse Among Athletes Substance abuse has no place in athletics Use and abuse of substances can have a profound effect on performance Both positive and negative Use of performance enhancing and street drug use occurs throughout athletics, on various levels Performance Enhancing Drugs Drug use designed to improve performance is known as doping Doping “Administration or use of substances in any form alien to the body, or of physiological substances in abnormal amounts and with abnormal methods by healthy persons with the exclusive aim of attaining an artificial and unfair increase in performance in sports.” Stimulants Used to increase alertness, reduce fatigue, increase competitiveness and hostility Some respond with loss of judgment that may lead to personal injury or injury to others Amphetamines Extremely potent and dangerous Injected, inhaled, taken as tablets Most widely used for performance enhancement Can produce euphoria w/ heightened mental status until fatigue sets in, accompanied by nervousness, insomnia, and anorexia In high doses, will reduce mental activity and decrease performance Athlete may become irrational chronic use causing individual to become “hung up” in state of repetitious behavioral sequences Can lead to amphetamine psychosis, manifesting in auditory and visual hallucinations and delusions Physiologically, high doses can cause abnormal pupil dilation, increased blood pressure, hyperreflexia and hyperthermia Anabolic Steroids Synthetic chemical (structure resembles sex hormone, testosterone) Androgenic effects Growth, development and maintenance of reproductive tissues, masculinization Anabolic effects Protein synthesis - causing increased muscle mass and weight, general growth and bone maturation Goal is to maximize this effect Can have deleterious and irreversible effects causing major threats to health Use most commonly seen in sports that involve strength and power In prepubescent boys Ingestion by females Decrease in ultimate height, cessation of long bone growth, acne, deepening of the voice (hirsutism), and swelling of the breasts (gynecomastia) Hirsutism Increases in duration and dose increases the likelihood of androgen effects Abuse may lead to liver and prostate cancer and heart disease Human Growth Hormone (HGH) Produced by anterior pituitary and released into circulatory system Amount released varies with age Can be produced synthetically Results in increases muscle mass, skin thickness, connective tissue in muscle, organ weight Can produce lax muscles and ligaments during periods of growth and alterations in bone growth Can cause premature closing of growth plates, acromegaly which may also result in diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, goiter, menstrual disorders, decreased sexual desire and impotence No proof that increased HGH and weight training contributes to strength and muscle hypertrophy Androstenedione Weak androgen produced primarily in testes and in lesser amounts by adrenal cortex and ovaries Increases testosterone in men and particularly women Effects last a few hours No scientific evidence to support or rebuke efficacy or safety of using this ergogenic aid Creatine Supplementation Naturally occurring in the body synthesized by kidneys, liver and pancreas Can also be obtained from ingestion of fish and meat Positive physiological effects Increase workout intensity, prolong ability to perform maximal effort, improves exercise recovery, stimulates protein synthesis, decreases total cholesterol and triglycerides and increases fat free mass Side effects Weight gain No apparent long term side effects May enhance muscular performance during high intensity resistance training Blood Reinjection (Blood Doping, Packing or Boosting) Endurance, acclimatization and altitude make increased metabolic demands for the body, requiring increased blood volume and RBC’s Can replicate physiological responses by removing 900 ml of blood and reinfusing is after 6 weeks (allows time to replenish supply) Can significantly improve performance While unethical, it can also prove to be dangerous Risks involve allergic reactions, kidney damage, fever, jaundice, infectious disease, blood overload (circulatory or metabolic shock) Recreational Substance Abuse Among Athletes It occurs among athletes Desire to experiment, temporarily escape, be part of the group Can be abused and habit forming Drug used for non-medical reasons with the intent of getting high, or altering mood or behavior Psychological vs. Physical Dependence Psychological dependence is the drive to repeat the ingestion to produce pleasure or avoid discomfort Physical dependence is the state of drug adaptation that manifests self in form of tolerance When cease consumption abruptly unpleasant withdrawal occurs Tobacco Use Cigarettes, cigars & pipes are increasingly rare in athletics Smokeless tobacco and passive exposure to others continues to be an ongoing problem Smokeless Tobacco Loose leaf, moist, dry powder, and compressed Posses serious health risk Major substance ingested is nitrosonornicotine Bad breath Stained teeth Tooth sensitivity to heat and cold Cavities and gum recession Tooth bone loss Leukoplakia Oral and throat cancer Absorbed through mucous membranes More addictive habit w/out exposure to tar and carbon monoxide Will increase heart rate but does not impact reaction time Coaches, athletic trainers and professional athletes should avoid use in order to present a positive role model Alcohol Most widely used and abused substance with athletes Depresses CNS Absorbed from digestive tract into bloodstream Does not improve mental or physical abilities and should be avoided by athletes Consumption on a large scale can result in development of a moderate degree of tolerance No place in sports participation Marijuana Formerly most abused drug in Western society Similar components and cellular changes as tobacco Can lead to respiratory disease, asthma, bronchitis, lowered sperm count and testosterone levels, limited immune functioning and cell metabolism Causes increased pulse rate and can cause decrease in strength Psychologically causes diminution of selfawareness and judgment, slower thinking and short attention span Has also been found to alter the anatomical structures suggesting irreversible brain damage Contains cannabinoids (can store like fat cells) May remain in the body and brain for weeks and months resulting in cumulative deleterious effects Drug Testing in Athletics NCAA and USOC have established banned substances lists and testing programs Banned substances list have not been set at the high school level Choice is left up to the individual schools Testing at the high school level is on the rise Program screens for some and leaves out several commonly used substances (alcohol, tobacco and steroids) The Female Athlete Triad Cause of Condition Relationship between disordered eating, amenorrhea and osteoporosis Driven to meet standards of sport or to meet a specific athletic image to attain goals Sign and Symptoms Disordered eating - bulimia and anorexia Osteoporosis - premature bone loss in young women, inadequate bone development Care Prevention is key; identify and educate