* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 03 EvolutionEvidence
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Molecular paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
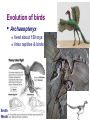
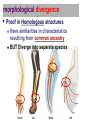
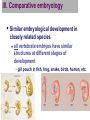
Evidence of Evolution by Natural Selection AP Biology 2007-2008 Dodo bird Evidence supporting evolution Fossil record transition species Anatomical record homologous & vestigial structures embryology & development Molecular record protein & DNA sequence Artificial selection human-caused evolution Fossil record Layers of sedimentary rock contain fossils new layers cover older ones, creating a record over time fossils within layers show that a succession of organisms have populated Earth throughout a long period of time Fossil Record Fossil record A record showing us that today’s organisms descended from ancestral species Evolutionary change in horses 550 500 Body size (kg) 450 Equus 400 350 300 250 Merychippus 200 150 Mesohippus Hyracotherium 100 50 Nannippus 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10 5 0 Millions of years ago Evolution of birds Archaeopteryx lived about 150 mya links reptiles & birds Smithsonian Museum, Washington, DC Land Mammal ? ? ? ? 2006 Fossil Discovery of Early Tetrapod Tiktaalik “missing link” from sea to land animals Study of Paleontology ( Three scientists) Older sediments are below younger sediments. Georges Cuvier (1769-1832) 2005- Gradualism James Hutton (1726-1797) Earth’s geologic features — profound change formed as product of slow but continuous & cumulative processes 2005- Uniformitarianism Charles Lyell (1797-1875) geologic processes have not changed throughout Earth’s history Conclusion: Earth must be much older than 6,000 years 2005- II. Anatomical record Looking at morphological divergence and morphological convergence morphological divergence Proof in Homologous structures Have similarities in characteristics resulting from common ancestry BUT Diverge into separate species Homologous structures Similar structure Similar development Different functions Evidence of close evolutionary relationship recent common ancestor Homologous structures spines leaves succulent leaves needles colored leaves tendrils Example of Morphological divergence (text) All modern vertebrates share a ‘stem reptile’ who crouched low to the ground (common ancestor) Descendents of this stem reptile diversified in new habitats and became bird, reptiles, mammals Its 5-toed limbs became many things Stem reptile: walked crouching on the land Morphological convergence: Proof: Analogous structures Separate evolution of structures Look alike in different lineages But… different internal structure & development different origin no evolutionary relationship Don’t be fooled by their looks! Solving a similar problem with a similar solution Example of…Convergent evolution Flight evolved in 3 separate animal groups evolved similar “solution” to similar “problems” Have analogous structures Does this mean they have a recent common ancestor? Example of Convergent evolution Fish: aquatic vertebrates Dolphins: aquatic mammals similar adaptations to life in the sea not closely related Those fins & tails & sleek bodies are analogous structures! Parallel Evolution Convergent evolution in common niches filling similar ecological roles in similar environments, so similar adaptations were selected but are not closely related marsupial mammals placental mammals Parallel types across continents Niche Burrower Placental Mammals Australian Marsupials Mole Marsupial mole Anteater Numbat Anteater Nocturnal insectivore Mouse Climber Marsupial mouse Spotted cuscus Lemur Glider Stalking predator Chasing predator Sugar glider Flying squirrel Ocelot Tasmanian cat Wolf Tasmanian “wolf” Vestigial organs Modern animals may have structures that serve little or no function remnants of structures that were functional in ancestral species deleterious mutations accumulate in genes for non-critical structures without reducing fitness snakes & whales — remains of pelvis & leg bones of walking ancestors eyes on blind cave fish human tail bone This is not LaMarck’s loss from “disuse”! Vestigial organs Hind leg bones on whale fossils Why would whales have pelvis & leg bones if they were always sea creatures? III. Comparative embryology Similar embryological development in closely related species all vertebrate embryos have similar structures at different stages of development gill pouch in fish, frog, snake, birds, human, etc. Similarity due to: Master Genes (Homeotic genes) A set of genes that determine development in the embryo Failure of one of these genes most often leads to devastating results in body plan These genes are highly ‘conserved’ meaning that they have not changed over evolutionary time. Embryos of many vertebrate species develop in similar ways Example: All vertebrates go through a stage with four limb buds and a tail Ex. Master Genes and Appendages DLx gene expression leads to appendages So, what controls where appendages grow on the body? HOX master gene When present, it suppresses the activity of Dlx Example: embryonic pythons – Hox is expressed along the length of snake’s body – no appendages. Read about this on page 306 Molecular record Comparing DNA & protein structure universal genetic code! Why compare these genes? DNA & RNA compare common genes cytochrome C and b (respiration) hemoglobin (gas exchange) Human/kangaroo Closely related species have sequences that are more similar than distantly related species DNA & proteins are a molecular record of evolutionary relationships Nucleotide substitutions 100 Dog/ cow 75 Human/ cow Rabbit/ rodent 50 Horse/ donkey Llama/ cow Horse/cow Sheep/ goat 25 Human/rodent Pig/ cow Goat/cow 0 0 25 50 75 100 Millions of years ago 125 Comparative hemoglobin structure Human Macaque Dog Bird Frog Lamprey 32 45 67 125 Why does comparing amino acid sequence measure evolutionary relationships? 8 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 Number of amino acid differences between hemoglobin (146 aa) of vertebrate species and that of humans DNA and amino acid sequence differences... ...are greatest among lineages that diverged long ago, ...and less among recently diverged lineages Comparing Cytochrome b Sequences 10 different species compared to the Honeycreeper (bird) Differences shown in red They tend to be neutral mutations and do not affect the overall sequence for the cytochrome b protein (found in cellular respiration) Building “family” trees Closely related species (branches) share same line of descent until their divergence from a common ancestor What data from whole genome sequencing can tell us about evolution of humans Example: the Evolutionary Hypothesis of Common Ancestry Chromosome Numbers in the great apes: human (Homo) chimpanzee (Pan) gorilla (Gorilla) orangutan (Pogo) 46 48 48 48 Testable prediction: If these organisms share a common ancestor, that ancestor had either 48 chromosomes (24 pairs) or 46 (23 pairs). Testable prediction: Common ancestor had 48 chromosomes (24 pairs) and humans carry a fused chromosome; or ancestor had 23 pairs, and apes carry a split chromosome. Chromosome Numbers in the great apes (Hominidae): human (Homo) chimpanzee (Pan) gorilla (Gorilla) orangutan (Pogo) 46 48 48 48 Ancestral Chromosomes Fusion Homo sapiens Inactivated centromere Telomere sequences Centromere Telomere Human Chromosome #2 shows the exact point at which this fusion took place Homo sapiens Inactivated centromere Telomere sequences Chr 2 “Chromosome 2 is unique to the human lineage of evolution, having emerged as a result of head-to-head fusion of two acrocentric chromosomes that remained separate in other primates. The precise fusion site has been located in 2q13–2q14.1 (ref. 2; hg 16:114455823 – 114455838), where our analysis confirmed the presence of multiple subtelomeric duplications to chromosomes 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 12, 19, 21 and 22 (Fig. 3; Supplementary Fig. 3a, region A). During the formation of human chromosome 2, one of the two centromeres became inactivated (2q21, which corresponds to the centromere from chimp chromosome 13) and the centromeric structure quickly deterioriated (42).” Hillier et al (2005) “Generation and Annotation of the DNA sequences of human chromosomes 2 and 4,” Nature 434: 724 – 731. IV. Artificial selection Artificial breeding can use variations in populations to create vastly different “breeds” & “varieties” “descendants” of wild mustard “descendants” of the wolf Natural selection in action Insecticide & drug resistance insecticide didn’t kill all individuals resistant survivors reproduce resistance is inherited insecticide becomes less & less effective Evolution is "so overwhelmingly established that it has become irrational to call it a theory." -- Ernst Mayr What Evolution Is 2001 Professor Emeritus, Evolutionary Biology Harvard University (1904-2005) 2007-2008 Don’t be a Dodo… Ask Questions!! 2007-2008