* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Spice Lecture
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Ringing artifacts wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
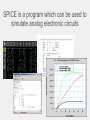
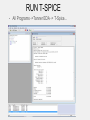
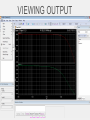
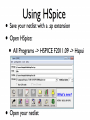
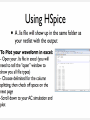
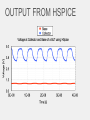
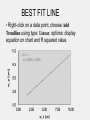
INTRODUCTION Spice Excel SPICE Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis SPICE is a program which can be used to simulate analog electronic circuits Analog filter circuits have a parameter called a ‘Transfer Function’ which maps input to output with relation to frequency v_in circuit v_out Analog filter circuits have a parameter called a ‘Transfer Function’ which maps input to output with relation to frequency Analog filter circuits have a parameter called a ‘Transfer Function’ which maps input to output with relation to frequency Analog filter circuits have a parameter called a ‘Transfer Function’ which maps input to output with relation to frequency Analog filter circuits have a parameter called a ‘Transfer Function’ which maps input to output with relation to frequency Analog filter circuits have a parameter called a ‘Transfer Function’ which maps input to output with relation to frequency A netlist is a text version of the circuit which describes the components and values for the computer to interpret and solve A netlist is a text version of the circuit which describes the components and values for the computer to interpret and solve A netlist is a text version of the circuit which describes the components and values for the computer to interpret and solve A netlist is a text version of the circuit which describes the components and values for the computer to interpret and solve A netlist is a text version of the circuit which describes the components and values for the computer to interpret and solve A netlist is a text version of the circuit which describes the components and values for the computer to interpret and solve A netlist is a text version of the circuit which describes the components and values for the computer to interpret and solve * Basic DC circuit V1 1 0 20 R1 3 1 4k R2 3 2 10k V2 2 0 -10 R3 3 0 8k .OP .END A netlist is a text version of the circuit which describes the components and values for the computer to interpret and solve * Series_RLC Circuit V1 1 0 SIN(0 5 1k) AC 1 R1 2 1 50 L1 2 3 100mH C1 3 0 1uF .AC DEC 100 1 10k .END WHAT IS SPICE? Spice is a software program that simulates electronic circuits and outputs the circuits’ basic characteristics such as: –Voltage –Current –Resistance at any location in the circuit HSpice is a version used in Unix PSpice is a version used in Windows T-Spice simpler tool meant for smaller circuits – this is what you will use in the lab LT spice is free http://www.linear.com/designtools/software/ OptiSPICE is the best because it was written by your professor. WORKFLOW • Create an Spice input file that describes the circuit • Run Spice • Inspect the output THE NETLIST - A netlist describes the circuit to the program - Node 0 is always GROUND name node value R_R1 1 0 100 C_C1 1 2 0.01592u V_V1 2 0 dc 0.0 ac 1.0 sin(0.0 1.0 1.0 0 0) THE INPUT FILE Title “my filter circuit” .options ingold=2 R_R1 1 0 100 C_C1 1 2 0.01592u IC=0 V_V1 2 0 dc 0.0 ac 1.0 sin(0.0 1.0 1.0 0 0) .print ac V(1) .ac LIN 100 0.001 1e+06 .op -The title must be the first line in the netlist .END (in order to recognize the options command) - R1 = 100Ω (Ohms) - C1 = 0.01592uF (micro Farads) with initial condition of 0 - V1 = sine wave with 1Hz frequency, 0 to 1V magnitude - Print ac voltage at node 1 - Want 100 frequency points from 0.001 to 1e+06 LTSpice – demo later Others might be available • Hspice (not likely and difficult to use) • Instructions likely obsolete • PSpice • Not sure we have full licence • Tspice • Might be ok – netlist based I think. • OptiSpice – the best (it’s mine). RUN T-SPICE • All Programs ->Tanner EDA -> T-Spice... VIEWING OUTPUT Using PSpice Using HSPICE TRANSFER FUNCTION • Magnitude Plot - DB vs Hz (log scale) • Phase Plot - Degrees vs Hz Together these plots show the transfer function of the circuit at different frequencies For HSPICE and PSPICE use Excel to generate the plots BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR Input Voltage Output Voltage • 3-terminals: Collector, Base, and Emitter • Common Emitter Amplifier • input = base with respect to the emitter • output = collector with respect to the emitter • Most commonly used configuration for transistor-based amplifiers as it produces the highest voltage, current, and power gain. BJT OUTPUT FROM HSPICE SOME USEFUL NETLIST STATEMENTS • • Analysis Types: • Operating Point (.OC) - Voltage at each node and current from voltage sources • AC Analysis (.AC) - Small signal model output at different frequencies • Transient (.TRAN) - Circuit output as time passes Scale factors: T : E+12 G : E+9 MEG : E+6 K : E+3 M : E-3 U: E-3 N: E-9 P: E-12 F: E-15 SOME USEFUL NETLIST STATEMENTS • Components: Netlist Name Component Type Rname Resistor Cname Capacitor Lname Inductor Vname Voltage Source Voltage source: Vname N+ N- <DC=> DCValue Iname Current Source Current source: Iname N+ N- <DC=> DCValue Qname Bipolar Transistor Mname MOSFET Example Rname N+ N- Value Cname N+ N- Value <IC=Initial Condition> Lname N+ N- Value <IC=Initial Condition> Qname C B E BJT_modelName Mname ND NG NS <NB> ModName <L=VAL> <W=VAL> Sweep Distributions: - DEC : Log distributions of points - LIN: Linear distribution of points LTSpice - demo TIPS IN EXCEL FORMAT CELLS • In the menu, choose Format Cells Scientific Notation: 0 decimals Time [s] Vout [V] 0.E+00 0.000 1.E-10 -0.008 2.E-10 -0.007 3.E-10 0.034 4.E-10 0.140 5.E-10 0.322 6.E-10 0.588 7.E-10 0.934 8.E-10 1.355 9.E-10 1.839 1.E-09 2.373 Number: 3 decimals Excel can split text from one column into multiple columns using the command “Text to Columns” $ • $ is used with cell coordinates, signifies leaving that coordinate constant • Example: rearrange v=d/t to give d=v*t The code PASTE SPECIAL • Example: Make a row of data negative • Copy cell with -1 value, highlight cells that you want to become negative of the current values, Edit Paste Special Multiply Positive “not yet Negative” 0.400 0.400 -0.008 -0.008 -0.007 -0.007 -1 Positive Negative 0.400 -0.400 -0.008 0.008 -0.007 0.007 • Other: transpose, add… BEST FIT LINE • Right-click on a data point, choose Add Trendline using type: Linear, options: display equation on chart and R squared value. STATISTICS • must have the Analysis Toolpak (go to Tools Add-ins, and install). • tools - data analysis - regression - x and y ranges - click residuals SUMMARY OUTPUT Regression Statistics Multiple R 0.999997109 R Square 0.999994218 Adjusted R Square 0.999991328 Standard Error 1182.326494 Observations 4 End NOW TO APPLY YOUR KNOWLEDGE!