* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3-3.1 Indole Alkaloids
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
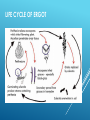
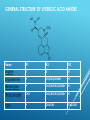
INDOLE ALKALOIDS Vinca, Rauwolfia, Ergot, Nux vomica INDOLE ALKALOIDS ERGOT ALKALOIDS Occurrence: Ergot is the dried sclerotium of a fungus, Claviceps purpurea (Fam. Hypocreacea) that arise on the ovaries of the rye plant (Secale cereale, Fam. Gramineae). Consumption of flour contaminated with Ergot led to many serious intoxications known as (Ergotism- Ignis Fire) in Europe. ERGOT FUNGUS ON WHEAT LIFE CYCLE OF ERGOT : Classification of Ergot Alkaloids A- Clavine Type Alkaloids: Simple water soluble bases with little medicinal value. All end with “clavine: e.g. Agroclavine. B- Lysergic acid Amides: They are all derivatives of (l)-Lysergic acid and subclassified into: 1- Simple lysergic acid amides: Composed of Lysergic acid and simple amines. 2- Polypeptide Alkaloids: Composed of Lysergic acid and at least 3 amino acids. Ergot alkaloids are N-monosubstituted amide derivatives of both lysergic acid and its isomer isolysergic acid that differ only in configuration at C-8. On treatment with ammonia lysergic and isolysergic acids give the corresponding amides ergine and isoergine respectively. COOH COOH 8 N CONH2 N CH3 CH3 N CH3 10 N H N H Lysergic acid Isolysergic acid N H Ergine Members related to lysergic acid (e.g. ergotamine and ergometrine) are levorotatory, more active and designated by suffix “ine”. Members related to isolysergic acid (e.g. ergotaminine and ergometrinine), are dextrorotatory, less active and designated by suffix “inine”. GENERAL STRUCTURE OF LYSERGIC ACID AMIDES Name R1 R2 R3 Ergine H H H Ergometrine H CH(CH3)CH2OH H Methergine H CH(CH2CH3)CH2OH H Methysergide CH3 CH(CH2CH3)CH2OH H LSD H CH2-CH3 CH2-CH3 1SIMPLE LYSERGIC ACID AMIDES Characters: 1- Composed of Lysergic acid and simple amines. 2- Low molecular weight. 3- Water Soluble. Lysergic acid must be in the (l) form. The (d) isomers are inactive. Ergonovine (Ergometrine) OH H 2C CH3 HC HN CO 8 Composed of (l)-lysergic acid and 2-aminopropanol. Its (d) isomer is called Ergometrinine. Uses: It causes vigorous contraction of the uterus. It is mainly used as an oxytocic in order to aid delivery or to prevent postpartum hemorrhage. N CH3 10 N H = = Ergonovine (l) (Ergometrine) Ergonovinine (d) (Ergometrinine) LYSERGIC ACID DIETHYLAMIDE (LSD) LSD has potent CNS stimulant effect. LSD is one of the abused drugs. C2H5 CON C2H5 8 N 10 N H CH3 2- POLYPEPTIDE ALKALOIDS Characters: They are derivatives of Lysergic acid with a complex polypeptides of at least 3 amino acids. They have high molecular weight. They are insoluble in water. This class include medicinally important members. ERGOTAMINE Characters: Its (d) isomer is called Ergotaminine. The peptide moiety is composed of 3 amino acids: a-Hydroxyalanine Proline Phenylalanine OH O CH3 N O Uses: Treatment of migraine as it constricts CO N CH2 O 8 N 9 10 the peripheral blood vessels. Has some oxytocic (ecobolic) activity. N H CH3 Saturation of the 9- 10 double bond of Ergotamine gives Dihydroergotamine, a compound with antimigraine effect but no oxytocic effect. OH O CH3 N O CO N CH2 O 8 N 9 10 N H CH3 Tests for identification: Van-Urk's Reagent (p-dimethyl aminobenzaldehyde (PDAB) in 15% H2SO4, containing traces of FeCl3) + Alkaloid → Deep blue color. Keller’s test: Solution of the alkaloids in acetic acid with traces of FeCl3 + concentrated H2SO4 on the wall of the test tube → blue layer is formed between the two phases. 2- VINCA (CATHARANTHUS) ALKALOIDS Occurrence: Catharanthus or Vinca is the dried whole plant of Catharanthus roseus G. Don (or Vinca rosea L), Fam. Apocynaceae. It contains about 150 alkaloids, the most important are vinblastine and vincristine. 1- MONOMERIC ALKALOIDS: H N H3COOC OH N N N N H H3COOC C2H5 Vincamine C2H5 N CH3 H3COOC Catharanthine COOCH3 OH Vindoline Vincamine Enhances the cerebral blood flow, facilitate cerebral circulation metabolism and increase general activity. Vincamine is used in cerebral vascular deficiency and atherosclerosis in elderly patients. 2- DIMERIC ALKALOIDS: MIXED DIMMERS These are dimeric alkaloids having indole and indoline (dihydro-indole) nuclei e.g. Vinblastine and Vincristine Vinblastine and Vincristine They occur in very minute amounts in Vinca (0.003- 0.005); 500 Kg of the plant yield only 1 gm of vincristine. They are very important for cancer treatment. STRUCTURES: Vinblastine (Vincaleukoblastine) is produced by coupling of Catharanthine and Vindoline. Vincristine (leurocristine) has CHO istead of CH3 in the vindoline part of Vinblastine. N N H H3COOC R=CH3 Vinblastine R=CHO Vincristine HO N N R H3COOC COOCH3 OH Vincristine and vinblastine are used as sulphate salt. Vincristine sulphate is less stable. MOA: arrest cell division at metaphase by binding to tubulin and interfere with microtubule formation. Tests for identification: 1-Vanillin /HCl reagent gives with: Vinblastine a pink color. color. Vincristine an orange-yellow 2-Van-Urk's reagent: → Reddish-brown color. Uses : Vinblastine is used for treatment of Hodgkin's disease (Pseudoleukemia or Lymphatic anaemia) and carcinoma resistant to other therapy. Vincristine has a cytotoxic effect .It is useful in the treatment of leukemia in children, small cell lung cancer, cervical and vaginal cancers. 4- NUX-VOMICA ALKALOIDS Source: Dried seeds of Strychnose nux vomica Fam: Loganiaceae Constituents: 5% Alkaloids mainly Strychnine and Brucine. Properties: Brucine is the dimethoxy derivative of Strychnine. Both alkaloids contains 2 Nitrogen atoms. N R R N O O R= H Strychnine R= OCH3 Brucine Tests for identification: Nitric acid test: Drops of concentrated nitric + few crystals of the alkaloids: Strychnine gives a faint yellow color that on evaporation turns to yellow color Brucine gives an intense red color, that on evaporation and addition of SnCl2 solution turns to violet. Uses: Strychnine is extremely toxic. It is used in veterinary medicine as CNS stimulant and tonic. It is used as antidote in barbiturate poisoning. It is also used as rodenticide. Brucine is less toxic than strychnine. It is sometimes used as CNS stimulant, Commercially it is used as alcohol and oil denaturant ALLIED DRUGS -Strychnos ignatii: ovate seeds , nonlignified trichomes. Adulterants: - Strychnos potatorum:seeds smaller and thicker. no alkaloids - Strychnos nux-blanda: same as official drug, but yellowish in colour. no alkaloids 1- RAUWOLFIA ALKALOIDS Source: Rauwolfia roots (Rauwolfia serpentina, Fam. Apocynaceae) Constituents: The most important are Reserpine and Rescinnamine. Properties: Reserpine and related alkaloids are weakly basic diester, tertiary alkaloids and possess a carboxylic group on ring "E". N H3CO N H E H3COOC R= 3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoic acid R= 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamic acid OR Reserpine Recinnamine Alkaline Hydrolysis: 1- Reserpine → methanol. reserpic acid + trimethoxybenzoic acid + 2- Recinnamine → reserpic acid + trimethoxycinnamic acid + methanol. Tests for reserpine: Vanillin /HCl reagent: → violet color. Uses: Reserpine and the related alkaloid rescinnamine are mainly used as antihypertensives (250-500 mg daily) and as tranquilizers (0.1- 1mg Ajmaline:Antiarrythmic or more daily). ALLIED DRUGS R. vomitoria: African : discontinued bands of sclereids and large vessels. R. tetraphylla: South america, india, australiaabundent Sclereids, uniform cork. THANK YOU -PHARMA STREET