* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download chapter-19-1 - High Point University
Grand Unified Theory wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical formulation of the Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Casimir effect wikipedia , lookup
Compact Muon Solenoid wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Standard Model wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear force wikipedia , lookup
Elementary particle wikipedia , lookup
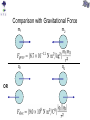
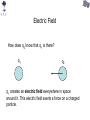
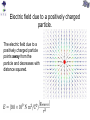
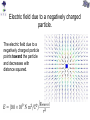
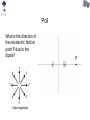
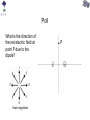
Review You have two neutral pieces of tape stuck together. You rip them apart and notice that each one is charged (because each one is attracted to your neutral hand). Without doing an experiment, we know that they MUST be oppositely charged. Why? Electrostatic Force The observation that “like” charged particles repel and “unlike” charged particles attract comes from experiment. It’s not a memorized fact nor a definition. Experiment shows that for two charged particles if the particles are in a vacuum Coulomb’s Law Fon 2 q2 Fon 1 q1 The electrostatic force is attractive (toward each other) for like charges. Coulomb’s Law Fon 2 q2 Fon 1 q1 The electrostatic force is repulsive (away from each other) for unlike charges. Comparison with Gravitational Force OR m1 m2 q1 q2 At the atomic scale, the electrostatic force dominates interactions of charged particles The mass of a proton is 1.7 x 10-27 kg. The mass of an electron is 9.1 x 10-31 kg. (Note: a proton is roughly 2000 times more massive than an electron.) Compare the gravitational force and electrostatic force of a proton on an electron if they are 0.5 x 10-10 m apart. Poll Two positively charged spheres exert a force of 0.1 N on each other as shown below. What is the direction of the electrostatic force on Sphere A (due to Sphere B)? qA qB Poll Sphere A has a charge 1 C. Sphere B has a charge 10 C. On which sphere is the electrostatic force the largest (in magnitude)? qA 1. Sphere A 2. Sphere B 3. Neither, because the force on each sphere is the same (in magnitude) qB Poll Given a small positive charge and a large negative charge, which figure best represents the forces that the charges place on each other? 1) + − 4) + − 2) + − 5) + − 3) + − 6) + − Poll − + − An assembly is composed of a positive and a negative charge of equal magnitude connected by a rigid rod. The assembly is placed near another negative charge. What is the direction of the net force on the assembly? 1) The net force is directed toward the right. 2) The net force is directed toward the left. 3) The net force is zero. Superposition of Forces in 1-D • If multiple charges are present, the net force on any one charge is equal to the vector sum of the forces due to each of the other charges. • If the charges all lie in a straight line (x-axis), all of the forces will act along the + or – x-axis. – Use + sign for forces acting in positive x-direction. – Use – sign for forces acting in negative x-direction. – Net force will simply be the sum of all forces and will either be in the + or – x-direction. Example Q1 = +7.5C + Q2 = +4.0C − + 0.20 m Q3 = -4.0C 0.20 m What is the net force on Q1 due to Q2 and Q3? x Superposition of Forces in 2-D •If the charges do not lie in a straight line then all of the forces must be resolved into x and y components before addition. –Choose orientation of x and y axes. –Resolve each force into x and y-components. –Use + and – signs to indicate whether each component is in the positive or negative x (or y) direction. –The x-component of the net force will be the sum of the xcomponents of all the forces. –The y-component of the net force will be the sum of the ycomponents of all the forces. –Find magnitude and direction of net force from Pythagorean Theorem and tanq=(Fy/Fx). (Note q is the angle between Fnet and the x-axis.) Example y 0.50 m − What is the net force on Q1 due to Q2 and Q3? − + Q2 Q1 = -4.5C Q1 0.50 m Q3 x Q2 = +5.0C Q3 = -8.2C Electric Field How does q2 know that q1 is there? q1 q2 q1 creates an electric field everywhere in space around it. This electric field exerts a force on a charged particle. Electric field due to a positively charged particle. The electric field due to a positively charged particle points away from the particle and decreases with distance squared. Electric field due to a negatively charged particle. The electric field due to a negatively charged particle points toward the particle and decreases with distance squared. Force on a charged particle by an electric field The force by an electric field on a charged particle is If q is positive, then the force on the particle is parallel to the electric field. If q is negative, then the force on the particle is opposite (i.e. antiparallel) to the electric field. q Poll The electric field at some location and instant of time is in the +y direction. In what direction is the force on a proton at this same location? Poll The electric field at some location and instant of time is in the +y direction. In what direction is the force on an electron at this same location? Poll The electric field at some location and instant of time is in the +y direction. Which is larger, the force on a proton or the force on an alpha particle (i.e. helium nucleus with two protons) at this same location? Poll The electric field at some location and instant of time is in the +y direction. 1 If this electric field is CREATED by a positive charge, +q, where might that charge be located? 4 2 3 Poll The electric field at some location and instant of time is in the +y direction. 1 If this electric field is CREATED by a negative charge, -q, where might that charge be located? 4 2 3 Poll A proton placed at location A experiences an electric force in the direction shown below. What is the direction of the electric field at location A? Poll At location C there is an electric field in the direction indicated, due to charges not shown. A chloride ion (Cl−) is placed at location C. What is the direction of the electric force on the chloride ion? Poll At location D there is an electric field in the direction indicated, due to charges not shown. An electron is placed at location D. What is the direction of the electric force on the electron? Poll An electron is placed at location A. What is the direction of the electric field at location B, due to the electron? Poll A proton is placed at location B. You have calculated the electric field at location A, due to the proton. To draw an arrow representing the electric field you calculated, what should you do? 1. 2. 3. 4. Put the tail at point A. Put the tail at point B. Put the tip at point A. Put the tip at point B. Superposition If there are many charged particles, then the electric field at a point in space is the sum of the electric fields created by all of the charged particles independently. + P + M Poll What is the direction of the net electric field at point P due to the dipole? P Poll What is the direction of the net electric field at point P due to the dipole? P