* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Adult Echocardiography Protocol Patient Position For parasternal
Survey
Document related concepts
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Pericardial heart valves wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
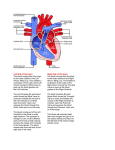
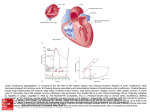
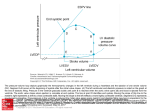
Adult Echocardiography Protocol Patient Position o For parasternal and apical views have the patient lie in the left lateral decubitus (LLD) position with left arm raised above the head. Obtain an adequate ECG which includes visualization of the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. o For subcostal view have the patient lay on their back and bend their knees to soften the abdominal muscles. o For suprasternal notch view have the patient lay on their back with a pillow under their shoulders to allow for the probe to be rotated correctly Cardiac Heart Beats o Capture 2 cardiac heart beats per cine loop unless an abnormal rhythm is present o Change the number of cardiac heart beats captured from 2 to 4-5 for patients with the following abnormalities: atrial fibrillation, significant arrhythmias, rapid heart rate (with a R wave to R wave greater than 500 m/sec on the ECG) Gray Scale Imaging o Adjust overall gain and TGC so that the ventricular and atrial cavities are anechoic Color Doppler o Adjust color gain until Doppler noise is seen, then decrease the gain down just enough to eliminate the noise. o Keep your color box narrow for better resolution Correct Spectral Doppler o The angle of incidence should be less than 20° o Obtain 3 consecutive waveforms, measuring the middle waveform Continuous wave Doppler o Perform continuous wave Doppler tracing on all valves with a velocity greater than 2m/sec o Too wide For the mitral valve, include the pressure ½ time Perform continuous wave Doppler tracing on all valve replacements and repairs *Asterisk within the protocol indicates images or measurements may not be utilized at all clinical sites. Students are still responsible for knowing how to correctly obtain the images or measurements. Cw/backup/protocols/adult echo protocol 13 1 Adult Echocardiography Protocol Parasternal Window from the Long Axis Scan Plane Structure Image Stored Left Ventricle (LV) Acquire cine loop 2D image at a depth of 15-20cm Left Ventricle (LV) Acquire cine loop 2D image at a reduced depth so image fills field of view Aortic Valve (AV) M-mode sweep of aortic valve freeze and acquire DO NOT UNFREEZE THIS IMAGE Aortic Valve (AV) *Measure the following on the aortic valve M-mode: Aortic root end-diastolic dimension Measure the vertical distance from the outer edge of the anterior aortic root to the inner edge (leading edge to leading edge) of the posterior aortic wall at end-diastole. Normal range 2.0-3.7 cm LA end-systolic dimension Measure greatest vertical distance between the anterior side of the posterior aortic wall and the anterior side of the posterior left atrial wall (leading edge to leading edge) at end ventricular systole when the aorta is in its maximal anterior position. Normal range 1.9-4.0cm Aortic valve systolic separation Measure the maximal opening of the aortic valve cusps during the initial part of ventricular systole, using the internal borders of the aortic cusps. Normal range 1.5-2.6 cm M-mode sweep of mitral valve freeze and acquire DO NOT UNFREEZE THIS IMAGE Mitral Valve (MV) Mitral Valve (MV) *Measure the following with the mitral valve M-mode: E-F slope Measure the distance of the steepest initial portion of the anterior MV leaflet by placing a caliper on the steepest point of early diastole and then place a caliper at the end of the slope. Normal range is 70-150 mm/s. E Point Septal Separation (EPSS) Measure the vertical distance from the MV E point to the lowest point of the IVS. Normal range is 2-7 mm. Cw/backup/protocols/adult echo protocol 13 2 Adult Echocardiography Protocol Parasternal Window from the Long Axis Scan Plane Structure Image Stored Left Ventricle (LV) M-mode sweep of left ventricle freeze and acquire DO NOT UNFREEZE THIS IMAGE Left Ventricle (LV) *Measure the following with the left ventricle M-mode: Interventricular Septum in diastole (IVSd) Measure the diastolic thickness of the IVS as the vertical distance from the RV side of the IVS to the LV side of the IVS in end-diastole at a point corresponding to the onset of the QRS complex. Normal range 0.6-1.1 cm Left Ventricle Inner diameter in diastole (LVIDd) Measure the vertical distance from the endocardium of the IVS to the endocardium of the PWLV in end-diastole at a point corresponding to the onset of the QRS complex. Normal range 3.7 – 5.6 cm Left Ventricle Posterior Wall in diastole (LVPWd) Measure the vertical distance from the endocardium of the LVPW to the epicardium in end-diastole at a point corresponding to the onset of the QRS complex. Normal range 0.6 – 1.1 cm Interventricular Septum in systole (IVSs) Measure the systolic thickness of the IVS as the maximal vertical distance that occurs between the RV and LV sides of the IVS at ventricular systole Left Ventricle Inner Diameter in systole (LVIDs) Measure the vertical distance from the endocardium of the IVS at the lowest point of the septal motion to the endocardium of the LVPW in end-systole. Normal range 2.0 – 3.8 cm Left Ventricle Posterior Wall in systole (LVPWs) Measure the systolic thickness of the LVPW at the maximal vertical distance that occurs between the endocardium and epicardium at end-ventricular systole Left Ventricle (LV) Freeze 2D image of left ventricle: Scroll back to end diastole and measure the following: *Right Ventricular Minor Axis in diastole (RVIDd) Measure the inner edge to inner edge dimension is measured at the same level as the LV minor axis dimensions parallel to this measurement. Normal range is 1.9-3.8 cm Interventricular Septum in diastole (IVSd) Measure the vertical distance from the RV side of the IVS to the LV side of the IVS at end-diastole. Normal range is 0.6 – 1.2cm LV minor axis end-diastole (LVIDd) Measure the vertical distance from the endocardium of the IVS to the endocardium Cw/backup/protocols/adult echo protocol 13 3 Adult Echocardiography Protocol Aortic Valve Zoomed Aortic Valve Zoomed Mitral Valve Zoomed Aortic and Mitral Valve of the LVPW at end-diastole. Normal range is 3.5 – 5.6 cm. LV Posterior Wall Diastolic Thickness (LVPWd) = Measure the vertical distance from the endocardium of the LVPW to the epicardium at end-diastole. Normal range is 0.6 – 1.2cm Acquire still frame DO NOT UNFREEZE THE IMAGE! From the previous frozen image, scroll forward to end systole and measure the following: LV minor axis end-systole (LVIDs) Measure the vertical distance from the endocardium of the IVS to the endocardium of the PWLV at end-systole. Normal range is 2.0-4.0 cm. LA end-systole (LAs) Measure the LA at the aortic valve plane, also perpendicular to the aortic root. This is an inner edge to inner edge measurement. Normal range is 2.3 – 3.8 cm. Acquire still frame Freeze 2D image of aortic valve Scroll back to end diastole Measure aortic root at end-diastole with the valve plane perpendicular to the wall of the aortic root at the sinus of Valsalva. Measure inner edge to inner edge. Normal range 2.1 – 3.5 cm Acquire still frame w/measurement DO NOT UNFREEZE THE IMAGE! From the previous frozen image, scroll forward to mid systole: Measure left ventricular outflow track diameter (LVOT) from the base of the aortic valve RCC leaflet to the base of the anterior MV leaflet. Normal measurement 2.cm Acquire still frame w/measurement Acquire cine loop of 2D image of mitral valve Acquire cine loop of Color Doppler across both mitral valve & aortic valve Cw/backup/protocols/adult echo protocol 13 4 Adult Echocardiography Protocol Parasternal Window from the Long Axis Scan Plane Structure Image Stored RVIT Right ventricular inflow track (RVIT) Acquire cine loop of 2D image of right ventricular inflow track (RVIT) Acquire cine loop of color Doppler across the tricuspid valve(TV) RVIT Acquire continuous wave Doppler across the tricuspid valve IF tricuspid regurgitation present *RVOT *RVOT Right ventricular outflow track (RVOT) Acquire cine loop of 2D image of right ventricular outflow track (RVOT) Acquire cine loop of color Doppler across the pulmonary valve (PV) *RVOT Acquire pulsed wave Doppler across the pulmonary valve and measure peak velocity *RVOT Acquire continuous wave Doppler across the pulmonary valve IF pulmonary regurgitation present RVIT Parasternal Window from the Short Axis Scan Plane Structure Image Stored AV, TV, PV Acquire cine loop of 2D image of aortic valve, tricuspid valve, and pulmonary valve Pulmonary Valve Acquire cine loop of color Doppler across the Pulmonary artery/valve Pulmonary Valve Acquire pulse wave at pulmonary leaflet tips & measure maximum velocity. Normal range 0.6-1.0 m/s Acquire continuous wave through pulmonary valve for pulmonary valve flow and pulmonary insufficiency with measurements Acquire cine loop of 2D image of the aortic valve & atrial septal wall Pulmonary Valve Aortic Valve Zoomed Aortic Valve not Zoomed Acquire cine loop of color Doppler across the aortic valve Tricuspid Valve Acquire cine loop of color Doppler across the tricuspid valve for tricuspid regurgitation Left Ventricle & Mitral Valve Acquire cine loop of 2D image of left ventricle at level of the mitral valve Left Ventricle & Mitral Valve Acquire cine loop of color Doppler of left ventricle at level of the mitral valve across the septal wall & mitral valve Left Ventricle & Acquire cine loop of 2D image of left ventricle at level of the papillary muscles Papillary muscles Apex of LV Acquire cine loop of 2D image of left ventricle apex Cw/backup/protocols/adult echo protocol 13 5 Adult Echocardiography Protocol Apical Window 4 Chamber Scan Plane Structure Image Stored 4 Chamber Acquire cine loop of 2D image showing all 4 chambers 4 Chamber Acquire cine loop of color Doppler of flow across mitral valve & left atrium for mitral regurgitation 4 Chamber Acquire pulse wave Doppler at the tips of the mitral valve leaflets and freeze image: Measure E to A & descending slope Acquire image with measurement Acquire continuous wave Doppler across mitral valve and freeze image: Measure peak velocity of mitral regurgitation if present Acquire image with measurement Acquire pulse wave Doppler at the opening of the pulmonary vein and freeze image: Documenting the systolic and diastolic forward flow Acquire 2D image with a decreased depth demonstrating the left ventricle and 1/3 of the left atrium 4 Chamber 4 Chamber Left Ventricle & Left Atrium Left Ventricle & Left Atrium Acquire cine tissue Doppler imaging (TDI) of left ventricle and 1/3 of the left atrium: Left Ventricle & Left Atrium Using TDI acquire pulse Doppler from the lateral aspect of the mitral valve annulus: Measure E prime Acquire image with measurement Apical Window 5 Chamber Scan Plane Structure Image Stored 5 Chamber Acquire cine loop 2D image of left atrium, left ventricle, aorta, right atrium, & right ventricle 5 Chamber Acquire cine loop color Doppler across the aortic valve 5 Chamber Acquire continuous wave Doppler across the aortic valve: Measure peak velocity (If continuous wave Doppler gradient is over 2 m/sec trace the spectral envelope) Normal range is 1.0 – 1.7 m/s Acquire image with measurement Acquire pulse wave Doppler of left ventricle outflow track: Measure peak velocity of the left ventricle outflow track. Normal range is 0.7 - 1.1 m/s Acquire image with measurement 5 Chamber Cw/backup/protocols/adult echo protocol 13 6 Adult Echocardiography Protocol Apical Window 4, 3, & 2 Chamber Scan Plane Structure Image Stored RV, TV, RA Acquire cine loop of color Doppler across the tricuspid valve RV, TV, RA Acquire continuous wave Doppler across the tricuspid valve IF tricuspid regurgitation: Measure tricuspid regurgitation Acquire image with measurement *Biplane Simpson’s Method: Acquire an apical 4 chamber image and freeze Scroll to end-diastole and trace the LV cavity and store image Measure the length of the LVED from the mid mitral annulus to the cardiac apex and store image This will give you the LV ED volume DO NOT UNFREEZE THE IMAGE Scroll to end-systole and trace the LV cavity and store image Measure the length of the LVED from the mid mitral annulus to the cardiac apex and store image This will give you the LV ES volume 4 Chamber 2 Chamber LV, MV, LA *Biplane Simpson’s Method: Acquire an apical 4 chamber image and freeze Scroll to end-diastole and trace the LV cavity and store image Measure the length of the LVED from the mid mitral annulus to the cardiac apex and store image This will give you the LV ED volume DO NOT UNFREEZE THE IMAGE Scroll to end-systole and trace the LV cavity and store image Measure the length of the LVED from the mid mitral annulus to the cardiac apex and store image This will give you the LV ES volume 2 Chamber Acquire cine loop of 2D image of the left atrium & left ventricle 2 Chamber Acquire cine loop of color Doppler across the mitral valve 2 Chamber 3 Chamber Acquire cine loop of 2D image decreasing depth to demonstrate the left ventricle & 1/3 of the left atrium Acquire cine loop of 2D image of the left atrium, left ventricle, & aortic valve 3 Chamber Acquire cine loop of color Doppler across the mitral valve & aortic valve 3 Chamber Acquire cine loop of 2D image decreasing depth to demonstrate the left ventricle & 1/3 of the left atrium Acquire cine loop of 2D image of 4 chamber demonstrating the left ventricle on the LEFT side of the SCREEN & the right ventricle on the RIGHT side of the SCREEN (Mayo Clinic) 4 Chamber Cw/backup/protocols/adult echo protocol 13 7 Adult Echocardiography Protocol Subcostal Window Long Axis Scan Plane Structure Image Stored 4 Chamber Acquire cine loop 2D image of 4 chambers 4 Chamber Acquire cine loop color Doppler across the Interatrial septum (IAS) 4 Chamber Acquire cine loop color Doppler across the interventicular septum 4 Chamber Acquire cine loop color Doppler across the mitral valve & tricuspid valve IVC Acquire cine loop 2D image of inferior vena cava for collapse (change EKG to 5 beats) Aorta Acquire cine loop 2D image of the aorta Aorta Acquire cine loop color Doppler of the aorta Subcostal Window Short Axis Scan Plane Structure Image Stored Acquire cine loop color Doppler across inferior vena cava & hepatic vein (change EKG to 2 beats) IVC Suprasternal Notch Window Long Axis Scan Plane Structure Image Stored Aortic arch and Descending aorta Acquire cine loop 2D image of the aortic arch and descending aorta Aortic arch and Descending aorta Acquire cine loop color Doppler flow of the descending aorta Aortic arch and Descending aorta Acquire continuous wave Doppler through the descending aorta Cw/backup/protocols/adult echo protocol 13 8 Adult Echocardiography Protocol Tips Pharmaceutical Contrast o May be utilized upon receiving a written order from the physician. o Pharmaceutical contrast is indicated for use in patients with 2 or more suboptimal wall segments of the left ventricular endocardial borders. o Pharmaceutical contrast is contraindicated for patients with known or suspected: Right-to-left and bi-directional cardiac shunts Cardiovascular or pulmonary compromise Hypersensitivity to perflutren (lipid micro gas), blood products or albumin (egg white allergy) Aortic Stenosis Additional Views o Interrogate the aortic outflow with non-imaging pedoff probe from the suprasternal notch window. o Reposition the patient to right lateral decubitus (RLD) position and interrogate the aortic outflow with non-imaging pedoff probe from the right Parasternal window. o Acquire multiple spectral Doppler waveforms from both windows and measure to determine the highest velocity documented. Technically difficult exams o Document normal cardiac windows with limited views o Utilize modified views to acquire diagnostic images for physician interpretation Biplane Simpson’s Method of Discs: Uses the summation of the areas from the diameters of 20 cylinders or discs of equal height is used to calculate the end- diastolic volume, end-systolic volume, stroke volume, cardiac output, cardiac index, and ejection fraction. Labs: Troponin: an elevated troponin may indicate a myocardial infarction BNP (Brain natriuretic peptide: an elevated BNP is an indication of the myocardial tissue being stretched as in the case of CHF Cw/backup/protocols/adult echo protocol 13 9