* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide Deck
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Dextropropoxyphene wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
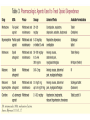
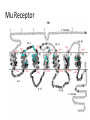
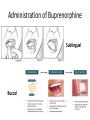
Medication Assisted Treatment Michael Palladini, RPh MBA CAC [email protected] “BUNAVAIL is the first and only FDA-approved buccal film formulation of buprenorphine and naloxone and will compete in the $1.7 billion and growing U.S. opioid dependence market.” -NASDAQ, 9/3/14 Objectives List the medications by generic and brand name, as well as appropriate starting and maintenance dosages for each, utilized for medication assisted treatment. Identify the pharmacological properties of the medications used for opioid dependence treatment, how these properties benefit patients, and the proper use in a clinical setting. Describe the withdrawal symptoms of opioid dependence and the significance of these symptoms in initiating and maintaining treatment with specific medications. Vermont Governor Shumlin's 2014 State of the State Address Opiates/Opioids • • • • • • • • • • Morphine Codeine Heroin Oxycodone Hydrocodone Oxymorphone Hydromorphone Fentanyl Buprenorphine Methadone “Traditional Pain Relievers” Opioids Therapeutic Effects • Analgesia • Sedation/Relaxation • Euphoria • Cough Suppression Side Effects • Nausea/Vomiting • Dizziness • Headache • Constipation • Sweating • Pruritus • Dry mouth • Miosis • Respiratory Depression Tolerance 1. Pharmacokinetic 2. Pharmacodynamic 3. Learned Early Withdrawal • • • • • • • • Muscle aches restlessness anxiety lacrimation (eyes tearing up) runny nose excessive sweating inability to sleep yawning very often Fully Developed Withdrawal • diarrhea • abdominal cramping • goose bumps on the skin • nausea and vomiting • dilated pupils and possibly blurry vision • rapid heartbeat • high blood pressure Current Medications: History of MAT Late 19th Early 20th Century Public perceptions/use Addiction ≠ Disease Increased use in 1950’s and 1960’s Addiction = Disease Methadone use Methadone • • • • • Synthetic opioid “Full agonist action” Use in opioid dependence circa 1965 Narcotic Addict Treatment Act of 1974 Considerable federal and state regulations Buprenorphine • • • • DATA 2000 Semi synthetic opioid “Partial agonist action” The “DEA physician waiver” Naltrexone • Synthetic molecule • “Antagonist action” • FDA original approval for opioid dependence 1984 • FDA approved for alcohol dependence 1994 • Vivitrol® FDA approved in 2006 (alcohol), 2010 (opioid) Opiate Receptors Receptor Location Function Mu1 Brain, Spinal Cord, Intestinal Tract Analgesia, Physical Dependence Mu2 Brain, Spinal Cord, Intestinal Tract Respiratory Depression, Euphoria, Miosis, GI Motility, Physical Dependence Delta Brain, Peripheral Sensory Neurons Analgesia, Physical Dependence, Antidepressant Effects Kappa Brain, Spinal Cord, Peripheral Sensory Neurons Dissociative, Dysphoria, Miosis, Sedation Mu Receptor Treatment • Methadone (Highly Regulated) • Buprenorphine (Moderately Regulated) • Naltrexone (Slightly Regulated) Methadone • DEA Schedule 2 • Clinic Setting Only • 28 PA. CODE CH 715 -Clinic policy/procedures -Physician/Staffing criteria Methadone • • • • • Generic drug (Roxane, Mallinckrodt Pharma) Available in 5mg, 10mg Tablets “Methadose” 40mg wafer 10mg/ml liquid syrup Oral dosage formulations Methadone • Starting Dose = 30mg • Institute upward titration • Maintenance Dosage ranges from: 1 or 2 mg to >200mg/daily • Once daily dosing • “Privilege” dosing schedules Step 0 through Step 6 Methadone • • • • • Inactive metabolites Half-life avg. of 30hrs; range of 4 to 91 hrs 2 to 4 hrs peak Metabolized extensively by CYP450 system Cost = $100/week Methadone Issues • Abuse/Diversion/Overdose Use of other drugs -Opiates/Cocaine/Benzodiazepines • Drug Interactions -Significant • Dosing Issues -Complex/Extensive Metabolism -Prolonged Withdrawal Buprenorphine • DEA Schedule 3 • Only FDA approved medication for OP (Physician-Office Based) treatment of opiate dependence • DATA 2000 • Sublingual Formulation Buprenorphine • • • • Suboxone® (Reckitt-Benckiser) Buprenorphine (Formerly Subutex®, Generic) Zubsolv® (Orexo Pharma) Bunavail® (BioDelivery Sciences) Suboxone Zubsolv Bunavail Administration of Buprenorphine Sublingual Buccal Buprenorphine • Starting dose = 16mg bid or 32mg tid • Variable maintenance dosing -2mg to 24mg daily -single or divided dosing Buprenorphine • • • • • • • • 1 to 4 hours peak Half life of 20 to 73 hours 8 -12 hrs duration (<4mg) 24 -72 hrs duration (>16mg) Partial mu agonist/Kappa antagonist Active metabolites Cost = Office visit ($100 to $400/month) Cost = Medication ( $5 to $8/dose) Buprenorphine Issues • Abuse/Diversion/Overdose • Treatment/Counseling issues -DATA 2000 requirements -Payer requirements • Drug Interactions Naltrexone • • • • • Non-scheduled medication Vivitrol® (Alkermes) 380mg IM q28 days 7-10 days opiate free period Cost= $800+ per monthly injection Naltrexone Naltrexone •Initial peak at 2 hours •Second peak at 23 days •Plasma concentrations begin to decline at 14 days •Half life 5-10 days Naltrexone Issues • • • • Vulnerability to opioid overdose Precipitation of opioid withdrawal Switching from agonist therapy Cost “You can check out any time you like, but you can never leave” MAT Issues/Questions/Concerns • • • • • • Harm Reduction vs. Drug Free Models Diversion Tapering/Detox Profit Motives Long Term Effects Lack of Data