* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download SCM Geography Overview
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
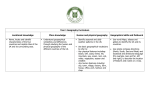
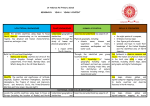
Rivers – Year 3 Skills Map skills – children to use contents and index of atlases to locate key rivers, towns and physical features of United Kingdom, Europe and the World Compare and contrast – study key rivers and regions and compare to our local knowledge Vocabulary – use the correct terminology for all the features and processes related to rivers Fieldwork – opportunities to study our local river and record data ICT – to carry out research about topical issues (floods) and record data about UK and world rivers. Enquiry – set up hypotheses to test when studying rivers in the field Unit Content Locational Knowledge – Locate the key rivers in United Kingdom and Europe as well as other main world rivers. There is also an opportunity here to mark key cities, countries, mountains, coasts and seas. When studying key rivers of the world, the position and significance of the equator, northern and southern hemispheres, the tropics, the Arctic and Antarctic. Place Knowledge – A specific area of UK is studied to compare and contrast with our local area, eg. Somerset Levels and the cause and effect of flooding. Why is it more at risk of flooding than Hemel Hempstead? Physical Geography – Children will learn about the physical features of rivers and watercourses and the processes behind their formation. Children should understand technical vocabulary such as: delta, source, valley, tributary, mouth and floodplain. The water cycle and climate zones will also be studied. Human Geography – Examples of human effects on rivers should be studied, including pollution, conservation, flooding, reservoirs, dams and hydro-electric power. Ecuador and the Americas – Year 4 Skills Map skills - children to use contents and index of atlases to locate key rivers, cities and physical features of Ecuador, South America and North America. Compare and Contrast – make comparisons between Ecuador, USA and UK on social and economic levels. Vocabulary – use the correct terminology for features and processes related to rainforests, volcanoes and earthquakes. ICT – use search engines for research about specific regions. Databases to be built up regarding key countries. Enquiry – test hypotheses about clearing rainforest areas or building in areas prone to earthquakes. Unit Content Locational Knowledge – Locate the rainforest regions of the world. Also note position of equator, tropics and oceans. Know the main cities of Ecuador as well as the countries and capitals of South America. Know key cities, states and countries of North America. Place Knowledge – Make comparisons of life in the main cities. Compare Quito, New York and London. Use databases to research and collate information about social and economic activity. Physical Geography – Children will learn about the different climate zones and land relief across America and within Ecuador. The layers within rainforests will also be studied and technical vocabulary such as canopy, emergent layer, and understory should be learnt. Areas of earthquake and volcanic activity are to be plotted and explored. Terminology such as plates, seismic, epicentre, aftershocks, plugs, vents and fissures to be learnt. Human Geography – This covers the impact on humans of deforestation. The arguments in favour and against to be explored. Also the impact on humans of living in an area prone to earthquakes. Settlements – Year 4 Skills Map skills - Use contents and index of atlases to locate the main settlements of UK. Be familiar with Ordnance Survey maps and know how to use four and six figure grid references. Compare and contrast – Be able to compare with historical settlements and be aware of how priorities have changed for location. Vocabulary – Be familiar with the terminology used with various types of settlements and land use. ICT – Databases to be used for key settlements. Satellite tracking and images used for the aerial viewpoint. Enquiry – Fieldwork provides opportunities to enquire about local land use and jobs through questionnaires. Unit Content Locational Knowledge – Know the main settlements of the UK and Europe. Place Knowledge – Recognise the main features of different sized settlements. Make comparisons between them. Compare hamlet, village, town and city. Physical Geography – Study different climatic regions and land relief and natural resources. See how it affects location of settlements and overall population density. Be familiar with the physical features found on ordnance survey maps and recognise their symbols. Human Geography – Know how human activity affects the environment. Consider issues surrounding green belt land. Enter into debates about school fields being sold off for housing. Be familiar with human features on ordnance survey maps and recognise their symbols. France – Year 5 Skills Map Skills – Use contents and indexes of atlases to locate key countries and cities in Europe. Develop Ordnance Survey Skills when looking at a specific location in France. Compare and contrast – Compare human and physical aspects of specific regions within France. Compare with England, especially relating to London and our local area. Terminology – Use the correct terminology in relation to climate, physical features tourism ICT – Research about physical and human features of cities and regions of France. Compile data bases to compare with cities of England Enquiry – Develop an enquiring approach. Children to be encouraged to ask questions to aid their research. Unit Content Locational Knowledge – Know the member countries of the European Union and their location in Europe. Know the key cities, rivers, mountains and seas in and around France. Place Knowledge – Study a specific city (Paris) and make comparisons with London. Look at major landmarks and history of the city. Discuss the importance of tourism. Physical Geography – Compare the climatic zones with the UK. Know all the key physical features (rivers, mountains, seas). Human Geography – Study the transport links, exports and imports, energy and food. Also research current issues, such as immigration and the problems concerned with Sangatte, near Calais. Local Area Study – Year 6 Skills Map Skills – Children should know how to use grid references to locate specific points on Ordnance Survey maps. They should recognise symbols and be able to make effective use of the key and the scale. Compare and Contrast – An understanding of how the local area has changed through time should be shown. Specific locations will be studied to see how they have developed over the years. Geographical vocabulary – Children should use vocabulary specific to the land uses and processes of change being studied. Enquiry – The enquiry approach should be used to investigate changes in land use and settlement size. Children can generate hypotheses and can search for evidence to prove theories. Questionnaires should be used with local residents and relatives. Fieldwork – Mapping of local area to identify land use ICT – Children can use the internet for maps and research. Information to be collated in a database. Word processing to be used for presentation of some tasks Unit Content Locational Knowledge – An awareness of where Hemel Hempstead is located in comparison to other local settlements is vital. Also, in the wider context of the whole country, children must know where we live. Place knowledge – The specific land use within Hemel Hempstead will be mapped out. This can be compared with other settlements. Physical Geography – The topic will focus on the physical characteristics of the study area, such as weather, rock type, and altitude. Human Geography – This will study how human influence has led to great changes in the study area over time. Current environmental issues will be debated regarding the loss or protection of green belt land and the siting of new retail parks, industry and housing estates. Coastal Studies – Year 6 Skills Map Skills – Children will use contents and index of atlases to familiarise themselves with the key coastal settlements and features of the UK. Ordnance Survey maps will help to analyse specific coastal features. Compare and Contrast – Compare Isle of Wight features with that of our local area. Compare features within the Isle of Wight. Geographical Vocabulary – Children should be familiar with the terminology specific to coasts, such as: erosion, long shore drift, stack, arch, headland etc. Fieldwork – On residential trip to Isle of Wight, visit the Needles and study coastal erosion sites. ICT – Children to use for research purposes in planning trip to Isle of Wight. Travel route sites and tourist attractions to be studied. Enquiry – Ask geographical questions about human influence on coastal erosion. Gather information and opinions to inform own views. Unit Content Locational Knowledge – Know the main coastal towns, cities and regions of the UK and key ports around the world. Know the location of the Isle of Wight and its main settlements. Place Knowledge – Know the layout of the Isle of Wight and compare with local area and other coastal regions. Research details about specific locations on the island. Physical Geography – Children will study the physical processes behind coastal erosion and the formation of coastal features, such as headlands, bays, arches, stacks, spits and bars. Human Geography – This will focus on the causes and effects of human activity in relation to coastal erosion. How can we prevent erosion? The effects of tourism on the environment will also be analysed.